MAINTENANCE MANUAL - Meritor
MAINTENANCE MANUAL - Meritor
MAINTENANCE MANUAL - Meritor
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Important informationAxel Changes UpdatingIn order to keep the maintenance manual up todate, at every modification in the axis, a TechnicalInstruction will be issued with the data andthe implications resulting from these changes.At the bottom of each page of this manual thereis a designated area to record the number ofeach Technical Instruction which involves anypossible changes on that page as the examplebelow.SafetyIt is extremely important wearing safety equipmentsduring shaft maintenance.• When using a hammer or performing anyoperation which involves impact, always usesafety eyes protection.• When handling hot parts or sharp corners,always use protection gloves.<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>3
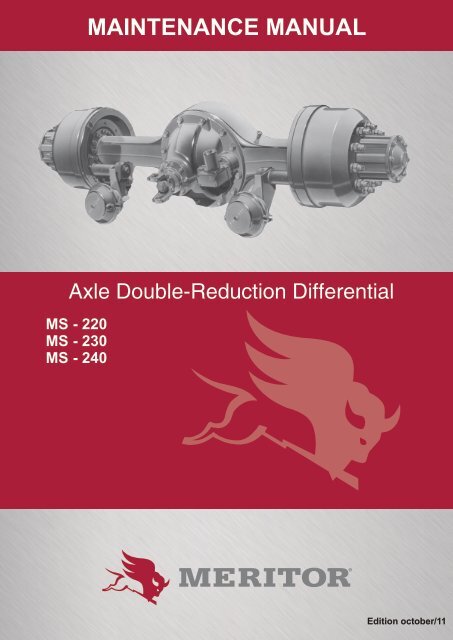
IntroductionThe differential planetary are two-speed driveunits with planetary reduction, which have thefollowing features:A. Generoid System Ring Gear and Pinion;B. Pinion with rod over two tapered roller bearings,which absorb the axial and radial loads,and a cylindrical roller bearing at the topof the head, which absorbs the radial loads;C. Ring Gear and Bearing Cage set, mountedon tapered roller bearings;D. Planetary and Satellites with straight conicalteeth;E. Secondary reduction provided by a SpurGear Planetary system, located under theHipoidal Ring Gear.First Reduction – High SpeedAt high speed, the sun gear is engaged with thebearing cage, which blocks the functioning ofthe planetary system gears.With the planetary gear locked, the motion effortof the Ring Gear and Pinion pair is transmitteddirectly to the gears of the differential system(satellites and planetary).Thus, the drive unit will function as a simplereduction drive system, allowing the vehicle todevelop higher velocities.4 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
IntroductionSecond Reduction – Low SpeedAt low speed, the Sun gear is engaged to theblocking plate.Thus, the drive unit will function as a double--reduction drive system, allowing increasingthe traction capacity of the vehicle.The speed change is effected by a mechanism(electrical, air or vacuum type) mounted on theirdifferential control unit installed in the cabin ofthe vehicle. Turning the mechanism on, the sungear is displaced from its previous position andengages with the locking plate, thereby releasingthe operation of the gears of the planetarysystem.First Reduction – High Speed<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>5
Exploded view6 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
Exploded viewSERIES 220 / 230 / 240ITEM DESCRIPTION ITEM DESCRIPTION1 Differential Case2 Capscrew (Differential BearingCap)3 Washer4 Roll Pin5 Satellite Box (Half planetary)6 Satellite Box (Simple Half)7 Satellite8 Satellite Thrust Washer9 Differential Spider10 Planetary (Short Hub)11 Planetary (Long Hub)12 Planetary Thrust Washer13 Fastener (Satellite Case Assembly)14 Planetary Gear Shaft15 Thrust Washer16 Planetary Gear17 Pin18 Satellite Case Thrust Washer19 Case Half - Flange20 Case Half - Simple21 Fasteners – Bearing Cage22 Bearing Cone (Case Half Flange)23 Bearing Cone (Case Half Simple)24 Bearing Cup (Case Half Flange)25 Bearing Cup (Case Half Simple)26 LH Adjustment Ring27 RH Adjustment Ring28 Cotter Pin29 Lock Screw30 Sun Gear31 Clutch Plate32 Studs (Clutch Plate)33 Tapered Washer34 Nut35 Shift Fork36 Shift Shaft37 Lock Plate Capscrews38 Plug39 Ring Gear and Pinion40 Spigot Bearing41 Snap Ring42 Adjusting Shims (Bearing Cage)43 Bearing Cage (Drive Pinion)44 Bearing Cup (Pinion Inner)45 Bearing Cup (Outer)46 Bearing Cone (Outer)47 Adjusting Shim (Pinion Bearing)48 Bearing Cone (Inner)49 Universal Joint Fork50 Dust Deflector51 Pinion, Oil Seal52 Washer53 Pinion, Nut54 Screws (Bearing Cage)55 Washer56 Ring Gear Thrust Screw57 Nut58 Diaphragm59 Stud (Mechanism Holder)60 Washer61 Nut62 Speed Changing Mechanism63 Roller Pins Spacer64 Roller Pins<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>7
IdentificationThe unit presents identification plates, whichare marked with the basic specifications of product.Before starting the service operations, identifythe unit to be repaired, referring to the nameplateaffixed to the housing and differential housing.This information will allow a correct identificationof the replacement parts desired, thusallowing the execution of a service operationmore quickly and accurately.ModelCust.No.Part.No.RatioSerie No.Date(Model)(Customer number)(Product number)(Differential Reductions)(Serial number)(Manufacturing Date)IDENTIFICATION PLATEIDENTIFICATION PLATEAXEL ASSEMBLY IDENTICATION PLATE8 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
DisassemblyBefore starting the service operations, identifythe unit to be repaired, referring to the nameplateaffixed to the housing and differential housing.• Remove the drain plug, located in the innerface of the case bowl and drain the entire oilin. (Figure 2).• Loose the nuts, locking washers and taperedwashers from the semi-axes fastening studs.Important: To remove tapered washer, supporta brass bar (diam. 38 mm) in the existingdepression in the center of the semi--axle flange and hit it with a brass hammeror use an auxiliary nut, hammering the hexagonalpart of the nut (Figure 4).Figure 2Figure 3PlugCAUTION:1. DO NOT HIT DIRECTLY ON THE SEMI--AXLE.2. DO NOT INSERT WEDGE OR CHISELBETWEEN THE SEMI-AXLE AND THEWHEEL HUB, TO AVOID UNRECOVERA-BLE DAMAGE IN THESE PARTS.Figure 4• Remove semi-axles.• Disconnect the Driveshaft.<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>9
DisassemblyGear Shift Mechanism DisassemblingA. Uncouple the mechanism’s actuation line;B. Remove the nuts and washers from thegear shift mechanism fasteners;C. Remove the mechanism (Figure 5);WARNING:There may be a little tension in the spring of themechanism a bit difficult to remove, but this isnormal.D. If there is a diaphragm installed, removeit manually. If replacement is necessary,discard the diaphragm and the retentionspring (Figure 6).Differential RemovingA. Manually displace the gear shift mechanism(in the opposite direction to the differential)until it is in the low speed position (LS). Thisoperation tends to eliminate the interferencebetween the sun gear and the mouth ofthe housing, helping to make easier disassemblethe differential;B. Remove the nuts and washers from the differentialfastening studs and screws;C. Disassemble the differential from the housingusing appropriate supports and ahydraulic jack. (Figure 7);Important:1. When necessary to use extracting screws,the differential housing flange has threadedholes (2 for the model 220 and 3 for models230/240) for this purpose. You can use thesame screws that fix the differential in thisoperation.2. Hit firmly, when necessary, using a plastichammer to loosen the differential form theeffect of the chemical gasket.D. Install the unit in a suitable support(Figure 8).Figure 5Figure 7Figure 610 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
DisassemblyFigure 8Figure 10Speed Shift RemovingA. Hit the caps and the hinge pin of the fork,using a brass pointer and a plastic hammerstrokes (Figure 9);WARNING:The pin should be removed by the upper side ofthe differential, because its housing is scaled.B. Simultaneously remove the fork and theSun gear (Figure 10);NotE:C. To remove the locking plate, loosen its fasteners.CAUTION:DO NOT HAMMER THE PLATE DIRECTLYOR INSERT CHISEL AND WEDGES BETWE-EN THE PLATE AND THE DIFFERENTIALCASE TO AVOID IRREVERSIBLE DAMAGEIN THESE PARTS. (Figure 11).• Loosen the nut and the Ring Gear screw (Figure112).If necessary, turn the sun gear to make it easierto remove.Figure 11Figure 9<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>11
DisassemblyFigure 14Figure 12Measure and record the clearance value of theteeth of the hipoidal gear pair. Refer to Settingthe backlash gear section (Figure 13).WARNING:Before measuring, remove the entire oil in thering gear and pinion with one of the recommendedsolvents in the Cleaning section and then,dry according to Drying section instructions.Figure 15C. Manually remove the bearing caps and theadjusting rings. (Figure 16)Important: If necessary, stroke slightly thecaps with a plastic hammer in obliquely, toloosen them• Remove the Bearing Cage (Figure 17).Figure 13Bearing Caps RemovingA. Remove and discard the cotter pin of rightside adjusting ring (Figure 14);B. Loosen the bearing cap screws (Figure 15);Figure 1612 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
DisassemblyC. Remove the satellite case and the thrustwasher, using a suitable support (Figure20);Figure 17Bearing Cage DisassemblyA. Loosen the screws that hold the ring gearand the two halves of the bearing cage. (Figure18);B. Separate bearing cage half flange of thegear, using a suitable puller (Figure 19);Figure 20D. Separate the ring gear from the bearingcage – Simple Half, if it is necessary to replaceone of these parts;NOTE:To remove the case, use preferably a pressor tap with a hammer in a brass pin, supportedin the inner face of the case.E. If necessary, remove the bearing conesfrom the case halves, using an appropriatepuller or a press (Figures 21 and 22)Figure 18Figure 21Figure 19<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>13
DisassemblyC. Separate the two halves of the satellite caseand remove its internal components in thesequence specified by the Figures 25, 26,27 and 28;Figure 22Figure 25Satellite Case DisassemblingA. Mark the two halves of the case and thespider with a not washable ink, in order tomake sure the reassembly in its original positions.(Figure 23).Figure 26Figure 23B. Immobilize the satellite case in a suitabledevice and release the fixing screws of thetwo halves (Figure 24).D. Remove the satellite case – planetary halffrom the device;E. Mark the axes of the planetary gears andthe case before disassembling, so that theoriginal position of these parts can be keptduring the reassembly;Figure 27Figure 2414 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
DisassemblyFigure 28F. Bata os pinos de travamento para dentrodos eixos das engrenagens planetárias (Figure29).NOTE:We caution that the locking pin is installedin a BLIND HOLE. Therefore, the operationof hitting the pin into the shaft must be madewith light hammer strokes, just enough toallow the free passage of the shaft (Figure30);Figure 30The length of the locking pin is smaller than thediameter of the shaft gears, so that the removalof the shaft can be easily done after the pin iswithin the axis.CAUTION:DO NOT APPLY STRONG HAMMER TAPIN-GS BECAUSE, AS THE HOLE IS BLIND, THEEND OF THE PIN MAY MARK THE EYE OFTHE SATELLITE CASE – PLANETARY HALF.G. Remove the axes, planetary gears and innerand outer washers (Figure 31).CAUTION:DURING PLANETARY GEAR REMOVAL,BE CAREFUL TO NOT LOSE OR MIX THEROLLERS AND SPACERS OF A GEAR WITHTHE OTHER. PUT THE GEAR ROLLERS INPLASTIC BAGS.Figure 29• Immobilize the fork/flange of the universaljoint with a suitable tool and release the pinionnut (Figure 32).<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>15
DisassemblyPLANETARYGEAROUTERWASHERROLLERImportant:Do not remove this component with hammerstrokes. It may cause warping and make deepmarks on the bearings, preventing a possiblereuse of them (Figure 34).AXLESPACERINNERWASHERFigure 31Important:To remove the seal easily and safely, insert ascrew driver between the flange and the sealcase, making lever movements at various pointsso that the seal is expelled gradually, with no damagesto the pinion case.Figure 32• Remove the fork/flange from the universaljoint using a suitable puller. (Figure 33).Figure 34• To remove the case, release its fixing screwsand washers (Figure 35).Figure 33Figure 3516 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
DisassemblyCAUTION:DO NOT INSERT WEDGE OR CHISEL BE-TWEEN PINION CASE AND DIFFERENTIALCASE TO AVOID IRREVERSIBLE DAMAGEIN THESE PARTS, AS WELL AS THE AD-JUSTMENT SHIMS.Remove and tie the adjustment shims of pinioncase, so that its original position can be keptduring the assembly in case of reuse of them(Figure 36).Important:Do not hammer the pinion to remove it. Damageto the bearings and impossibility of reusemay result.B. Remove manually the front bearing cone;C. Remove, if necessary, the front and rear bearingcups by using a suitable puller or a press(Figure 38);D. Remove the adjusting shims manually fromthe pinion shaft;E. If necessary, remove the rear bearing coneby using a suitable puller or a press (Figure39);F. Remove and discard the snap ring usingappropriate pliers;Figure 36Pinion Case DisassemblyA. Pull the pinion using a suitable puller or apress (Figure 37);Figure 38Figure 37Figure 39<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>17
Cleaning – Drying – Inspection – StorageG. If it is necessary, remove the spigot bearingusing a suitable puller or a press (Figure40);Carefully remove all gasket particles.Refer to CHEMICAL GASKET.Clean inside the case to remove any impuritiesloosened during the removal of the differential,using the previously mentioned solvents.Carefully clean the breather plug (air jet can beused). If the breather is blocked or damaged,replace it.CAUTION:Figure 40CleaningThe unit may be externally washed, in order tomake easier its removal and disassembly.In this case, all the gaps must be plugged toavoid water or humidity inside the unit.Important:We do not recommend washing the unit afterit is removed from the case. When this cleaningsystem is used, water is retained in thecomponents. This can lead to oxidation (rust)on critical parts and enable the movement ofthese particles of soot in the oil. The prematurewear of bearings, gears and other parts can becaused by this practice.Thus, the unit should be completely disassembled,because it is not possible to clean it upproperly otherwise.Wash all components with machined or rectifiedsurfaces (gears, bearings, shims, cross)using appropriate petroleum-based solventssuch as diesel or kerosene.BLOCKED BREATHER PLUGS CAUSE THEINCREASING OF THE INTERNAL PRESSU-RE OF THE UNIT. OIL LEAKAGE THROUGHTHE SEALS MAY RESULT.DryingParts must be dried immediately after cleaning.Dry the parts using soft and clean cotton rags.NOTE:Except for bearings, parts can be dried withcompressed air.InspectionIt is very important to inspect all componentsof the unit totally and carefully before reassembling.This inspection will show parts withexcessive wear or cracks, which should be replaced.The correct replacement will prevent future failureswith high costs. MERITOR prefers not toreuse parts, because the cost may be much higherin the future, making it not worth the savingsachieved at the time of the repair.DO NOT USE GASOLINEWash cast parts (satellite case, bearing cups,differential case inside) using the previouslymentioned solvents.18 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
Cleaning – Drying – Inspection – StorageBearings InspectionInspect all cylindrical rollers / tapered rollers bearings(cups and cones), including those thatwere not removed from its mounting seats andreplace them in case if you find any of the followingmentioned defects:Remove the bearings to be replaced with suitabledevices (puller or press).C. Wear (with visible depression) on the cuptrack or cone and / or deep indentations,cracks or breaks in the cup seat and / orcone, or on the surfaces of tapered rollers(Figure 43);D. Corrosion (caused by chemical action) orcavity on the operating surfaces (Figure44);Avoid the use of punches and hammers thatcan damage also the seats where the bearingsare mounted.A. Severe wear on the wide face of taperedrollers, with almost total elimination of thecentral undercut, and / or radius worn withsharp edge in the wide face of rollers (Figure41);Figure 43E. Flaking or peeling of the cup surface and /or cone (Figure 45).Figure 41B. Friction signs in the cage of the tapered rollers(Figure 42);Figure 44Figure 42<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>19
Cleaning – Drying – Inspection – StorageFigure 45Hypoid Generoid Pair InspectionInspect these gears for wear or damage like:cracks, depressions, scores and chips. Checkthe seats of the bearing cones and the splinesof the pinion as well.NOTE:The generoid hypoid drive pinions and ringgears are machined in matched sets to ensurethe ideal position of tooth contact.Thus, when it is necessary to replace a damagedring gear or pinion, both drive gearand pinion must be replaced as a set.Satellite Case Set InspectionCheck the components of the differential systemand replace the parts that present depressions,cracks, excessive out-of-roundness ofbores and half rounds or major wear in the worksurfaces. Also inspect the work areas specifiedbelow:A. Thrust washer seats, half rounds for installingthe legs of the spiders on both halvesof the satellite case;B. Contact surfaces for thrust washers of satellitesand planetary;C. Spider legs;D. Teeth and splines of the side gears;E. Teeth and bore of all satellites.Important:If it is necessary to replace a pinion or side gear,the whole set should be replaced, including thethrust washers. A combination of new and usedparts could cause premature failure of the set.Planetary System InspectionA. Inspect the diameters and the teeth of theside and sun gears and the straight teethof hypoid ring gear for wear and damage.Those parts that have cracks, depressions,scoring or chipping must be replaced;B. Inspect all contact surfaces of the planetarygear thrust washers. If any of them showexcessive wear, depressions or warping,replace them all;C. Inspect all bearing rollers and spacersD. Inspect the mounting seats of the planetarygears in the satellite case – planetary half.Check that the bores are free of burrs atboth ends;E. Inspect the diameters of the planetary gearsaxes. If any of the axes shows wear, grooves,or depressions in the diameter, replaceall of them;F. Inspect the speed changing fork and thelow speed engaging teeth (locking plate)and replace parts with wear, warping or depressions.Semi-Axes InspectionCheck for notches and excessive wear of thesplines and for out-of-roundness of the flangebores.Differential Case InspectionCheck for cracks on any surface or burrs onthe machined parts.20 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
Maintenance / RestorationUniversal Joint Fork / Flange InspectionReplace fork / flange of the universal joint incase it presents excessive wear in the Oil SealLips work area.Case InspectionCheck for crack signs; loosen fasteners, burrsor grooves on the machined surfaces.EstocagemAfter the parts have been cleaned, dried andinspected, they must be assembled immediatelyor covered with a thin film of oil as specifiedin Section LUBRICATION for the purpose ofpreventing oxidation.The parts that have to be stored must be coveredwith a reasonable coating of oil or anyantioxidant and kept in closed boxes or wrappedfor protection from dust, humidity or rust(except for components already protected bypaint, galvanization, etc.).MaintenanceReplace all the parts that show wear or are damagedand always use <strong>Meritor</strong> Genuine Parts,to ensure a maintenance service with satisfactoryresults, once the use of non-genuine partswill diminish the life of the unit.E. Remove grooves, marks, burrs or otherimperfections of the machined surfaces;F. Threads must be clean and without damageto get an exact fit and proper tightening torque;G. Whenever possible, use a press to the reassembleof the parts;H. Tighten all fasteners and locking componentswith the values specified on the sectionTIGHTENING TORQUE;I. Remove any burrs or grooves from thecase.RestorationIn the interest of safety and preservation of thelife of the maintenance being performed, MERI-TOR recommends that repairs not be made bywelding operation, which can affect the structuralintegrity of components, and distort thosealready undergoing heat treatment processes.The weld repair can only be approved wherestrict controls are imposed with equipment normallyonly found in manufacturing locations.Important:In deciding whether a part should be repairedor destroyed, have in mind that we, manufacturers,never hesitate to destroy a piece that issomehow doubtful.For a better instruction, we inform some basicinspection criteria, for the purpose of repairsand/or replacement of components:A. Replace nuts and bolts that present roundedcorners in the head and / or damagedthreads;B. Replace lock washers, flat washers, snaprings and cotter pins;C. Whenever the unit is reconditioned, also replacethe pinion seal, and the fork hinge pincaps;D. Remove all gasket particles. Refer to CHE-MICAL GASKET section;MERITOR has adopted liquid adhesive as itsmain locking element, then, this section describesthe needed cautions for a proper use of thisliquid adhesive.Liquid adhesives set in absence of air and,being liquids, fill quickly and evenly throughoutthe space between the threads, making possibleto obtain a more efficient and safer lockingthan the existing conventional systems.<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>21
Liquid AdhesiveFeatures of Liquid AdhesivesPRODUCT TYPE COLOR SETTING TIME271RED2 HOURSLOCTITE241BLUE6 HOURS221VIOLET6 HOURS1334RED6 HOURSTHREE BOND1305GREEN6 HOURS1341BLUE10 HOURSDisassemblingUse approved mechanical disassembling proceduresto take apart the components thatwere originally assembled with liquid adhesive.WARNING:Do not use any impact wrench nor hammer thefasteners in order to avoid damages to its heads.If the removal of a nut, for instance, is difficultdue to the wear of its head or because of therequired torque, reduce the resistance of the liquidadhesive by heating the head of this componentto approximately 150ºC (320°F), whiletrying to loosen it. This procedure must be doneslowly to avoid thermal tensions in the componentsof this set.CleaningCarefully clean the threaded holes and thethreads of screws, nuts and studs to eliminatedirt, oil, grease or humidity. This removal mustbe done with a cleaning agent such as trichloroethyleneor other chlorinated solvent.In this case, apply the minimum torque valuerecommended by MERITOR. If the screw orfastener does not turn, its condition is satisfactory.If the fastener turns, remove it and applythe procedures described in this section.Applying ProceduresA. Apply the liquid adhesive so that it coversall the spaces between the threads. In caseof internal threads (with blind holes), apply4 to 6 drops into the threaded hole. (Figure46).NOTE:When the hole is a CLOSED HOLE, apply theliquid adhesive to its thread, because whenthe liquid adhesive is applied to the threadof the screw and it is introduced, the air insidethe hole is pushing against, expellingthe liquid adhesive.B. Tighten the fixing components to the torquevalues specified in the section TIGHTE-NING TORQUES.ReassemblingBefore starting this operation, check the applyinglocations as specified in the section Reassembly.In the case if there are fastenerswhich had adhesive applied originally but werenot removed during the disassembly, check thetorque condition of each one of them.Figure 4622 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
Liquid AdhesiveDescriptionChemical gasket material is a substance with apasty consistency that sets at ambient temperatureforming a resistant packing. The gasketmaterials adopted by <strong>Meritor</strong> are:174 and 574 (LOCTITE) and NEUTRAL SILI-CON (DOW CORNING 780, or 5699 LOCTITETREE BOND 1216).CAUTION:THE EXCESSIVE APPLICATION CAU-SES THE DISPLACEMENT OF CHEMICALGASKET INTO THE UNIT AND DIFFICUL-TIES IN FUTURE DISASSEMBLIES. FAILU-RES IN THE APPLICATION OF THE GASKETCORD COULD BE THE CAUSE OF FUTURELEAKAGE.CleaningCarefully clean both joining surfaces to eliminateparticles of the previous gasket, oil, greaseor humidity. The removal of these particlesmust be done with a flat-bladed tool or sandpaper, followed by cleaning with an oil-free solvent,like xylol, toluol or methyl ethyl ketone.Avoid making scratches in these surfaces becausethis could cause leakage in the future.DryingBe sure that the surfaces to be joined are perfectlydry before applying the chemical gasket.Applying ProceduresA. Apply a continuous gasket cord of approximately3 mm in diameter when the joint isneutral silicone or apply with a brush when itis 174 and 574 (Loctite), all the way around ofone of the mating surfaces and all the mountingholes to ensure a complete seal that preventsleakage (Figure 47).3mm diameterB. After applying the chemical gasket, joint immediatelyboth mating surfaces in order tospread the gasket cord properly;C. Tighten the fasteners to the required torquevalue specified in the Section TIGHTENINGTORQUES.Pinion Case AssemblingA. Assemble the new bearing cups (rear andfront), using suitable tools or a press. (Figure48);WARNING:1. Check that the cup seats are clean andfree of burrs.2. During the assembling operation, be surethat there is no material pullout in the pinioncase.3. Check that the cups are perfectly seatedon its housings.B. Install the new bearing cone using a suitabletools or a press (Figure 49);WARNING:Check that the cone is perfectly seated on thepinion.Figure 47Figure 48<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>23
ReassemblyFigure 51Figure 49C. Install the new spigot bearing using a suitabletool or a press (Figure 50);WARNING:Make sure that the bearing is correctly seatedon the pinion. For installation use an adequatedriver that pushes only on the inner race of thebearing.A. Rest an appropriate driver bush on thepress table and position the new spigot bearingon the driver (Figure 52);B. Rest an appropriate driver bush on thepress table and position the new spigot bearingon the driver (Figure 53);The spigot bearing for the Differentials 230 and240 may present an optional building form (Figure51);Check the type to be installed before installingthis component. The optional construction mayrequire a specific assembling process.Figure 52INNER RACERINGDRIVER BUSHFigure 53Figure 5024 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
ReassemblyC. Place the pinion on the spigot bearing;D. Press the pinion until it seats firmly againstthe spigot bearing;E. Release the pressure and lower the drivepinion and spigot bearing assembly;WARNING:After assembling, the thrust ring must be positionedtowards the pinion or the rollers andthe outer race may be loosened. Otherwise, incase of installation of spigot bearing by thrustring process specification, the pinion may bedamaged.J. Press the front bearing cone and check thepreload. Refer to PINION BEARING PRE-LOAD ADJUSTMENT section (Figure 56).K. Install the new pinion seal using a suitabletool (Figure 57);WARNING:For 230 Axes, be sure that the seat is free of oilor grease before installing the seal.F. Install a new snap ring with a suitable snapring plier (Figure 55);G. Lubricate bearing cups and cones with theoil recommended in the section LUBRICA-TION;H. Install the bearing shim in the hypoid pinionshaft;I. Place the hypoid pinion in the cage;Figure 56PRESSFigure 54Figure 57Figure 55<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>25
ReassemblyL. Apply Lithium Soap Based Grease for extremepressure to the Seal Lips (Figure 58);L1. For 230 Axes, apply sealing paste (3M IndustrialAdhesive 847) on the external surfaceof the seal (Figure 58);ReassemblyL. Before installing the new seal, be sure thatthe Pinion case and the seal seating surfacesare free of any dirt.Figure 59Figure 58TRIPLE LIPS FOR ALL AXESM. Place the fork/flange of universal joint in thepinion slot;NOTE:In case if it is necessary to replace the dustdeflector, use a suitable tool.N. Install the pinion nut and tighten it manually.Pinion Case InstallationA. Select and install the adjustment shims forthe pinion case using guiding pins (Refer toPinion Installation section) and apply liquidgasket Loctite 174 or 574 in the differentialcase before installing the shims (Figure 59);B. Install the pinion case (Figure 60);Figure 60C. Install the washer and fixing screws of thepinion case and tighten them with the torquespecified in the Tightening Torquessection (Figure 61);D. Immobilize the universal joint fork/flangewith a suitable tool and tighten the pinionnut with the specified torque of the TighteningTorques section (Figure 62);Figure 6126 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
ReassemblyB. Place the planetary gears (with rollers andspacers) and the washers (inner and outer)in the satellite case (planetary half) aligningthe holes of the washers and case to makeeasier the installation of the axes (Figure64);C. Install the axes of planetary gears;Figure 62E. Install a torque wrench on the pinion nutand check the resistive torque value to rotatethe Generoid hypoid pinion. Increase, asnecessary, the torque applied on the pinionnut (up to the maximum torque allowed), tomeet the values specified on the PINIONBEARINGS section.WARNING:Before reinstalling the planetary gear shaft, inspectthe eye of the case and make sure thatthere are not burrs which could damage thediameter of the axle. Be sure that the originalassembling position of these components waskept. Install the shafts gradually, to avoid damagesin the contact areas of the rollers.D. Install the locking pins (Figure 65);Satellite Case AssemblingLUBRICATE all the satellite case componentsbefore installing them (Figure 63).A. Apply grease (SHELL 71032 ALVANIAEP-2 or TEXACO - 995 MULTIFAK EP-2)in the holes of the planetary gears. Installthe rollers and the spacer in each gear (Figure63).Figure 64Figure 63Figure 65<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>27
ReassemblyE. Immobilize the satellite case planetary-halfusing a suitable device (Figure 66);F. Place the planetary – short hub with itsthrust gear, in the case planetary-half (Figure67);Figure 68Figure 66WARNING:We caution that the inadvertently installation ofthe planetary in the case planetary-half, mayresult in the inversion of its original positions(Figure 69).PLANETARY HALF CASESIMPLE HALFCASETHRUSTWASHERFigure 67G. Place the satellites, its thrust washers andthe spider (Figure 68);H. Then, place the planetary – long hub, andits thrust washer;I. Install the case satellite-half, observing theoriginal alignment;PLANETARY LONG HUBPLANETARY SHORT HUBFigure 6928 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
ReassemblyJ. Install four fasteners in the main differentialcase equidistant to each other. Tightenthem to the torque value specified in TighteningTorques Section;K. Remove the satellite-set case from the device;L. Check the rotation resistance of the planetarysatellite-set. Refer to Satellite system /Planetary section;M. Apply Liquid Adhesive (Loctite 271 orTHREE BOND 1305), to the fixing screwsof the satellite case. Refer to the section LiquidAdhesive;N. After check / correct, install and tighten theremaining fixing screws of the satellite casesto the specification of Tightening Torquessection, install the satellite case thrustwasher with grease, to avoid it falling intothe differential case during the installation.Differential Case AssemblingA. Install the new bearing cones in both halvesof the differential case using a suitable toolor a press (Figure 70 e 71);Figure 71C. Install the satellite case and its thrust washerusing a suitable device (Figure 20);D. Install the case half-flange in the ring gear(Figure 72);E. Apply Liquid Adhesive (Loctite 271 orTHREE BOND 1305), to the threads ofthe ring gear fixing screws. Refer to LiquidAdhesive Section;F. Install and tighten the fixing screws accordingto the Tightening Torques section specification(Figure 73).WARNING:1. Make sure the cone seats are clean andfree of burrs.2. During the assembling operation, be surethat there is no material pulling off fromthe Differential Case.3. Make sure that the cones are perfectly seatedin its housings.B. Install the Differential Case simple half inthe ring gear;Figure 72Figure 70Figure 73<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>29
ReassemblyInstallation of Differential Case SetA. Temporarily install the bearing cups, adjustingrings, bearing caps and its Capscrews.Tighten the Capscrews to the torque valuespecified in Tightening Torques section;B. Seat the cap in the cones and install the seton the differential case (Figure 74);C. Place the adjusting rings on the caps andmanually turn them, up to get them seatedon the bearings (Figure 75);WARNING:During Differential Case installation, there is atendency of the set sliding towards the left bearingcap, making harder the assembling operation.Thus, it is recommendable to assemblefirst the Left Side Bearing Cap adjusting ring(ring gear side).D. Place the bearing caps and tighten them slightly.Try to turn the rings (Figure 76);WARNING:If it is not possible to turn the rings manually(with no forcing), they must be out of position.Remove the bearing caps and reposition theadjusting rings, to avoid irreparable damage tothe differential case and bearing caps.Figure 74Figure 76Figure 75E. Apply Liquid Adhesive (Loctite 271 orTHREE BOND 1305), to the threads of theCapscrews. Refer to the Liquid Adhesivesection;WARNING:The liquid adhesive must be applied only afterbearing preload, gear backlash and ring gearand pinion teeth contact adjustments have beenperformedo.F. Install and tighten washers and Capscrewsto the specified torque values of the sectionTightening Torques.30 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
Reassembly• Adjust the differential bearings preload. Referto the section Bearing Cage Bearings.• Adjust the Backlash Gear. Refer to the sectionBacklash Gear.• Check the tooth contact of the hypoid pair.Refer to the section Tooth Contact, RingGear and Pinion• Apply Liquid Adhesive (174 and 574 LOCTI-TE) to the Ring Gear Thrust Screw.• Install and adjust the ring gear thrust screw.Refer to the section Adjusting The Ring GearThrust Screw.Assembling the Speed Change SystemA. Install the clutch plate through the followingprocedure:Figure 77Model: 220a) Place the clutch plate;b) Apply Liquid Adhesive (Loctite 241 orTHREE BOND 1334), to the threads of theClutch Plate fixing screws.c) Install and tighten the new fixing screws ofthe plate to the specified torque values ofthe section Tightening Torques.Modelo:230/240a) Screw the four fasteners of the Locking Plateas much as enough to keep a dimensionof 26,6-27,2mm, between the top of thefastener and the contact surface of the plate(on the differential case);b) Place the locking plate upon the fasteners;c) Install new conical washers;d) Apply Liquid Adhesive (Loctite 241 orTHREE BOND 1334), to the threads of thefasteners;e) Install and tighten the fixing nuts to the specifiedtorque values in the section TighteningTorques (Figure 77).Figure 78D Apply sealing paste 3M – Industrial Adhesive847 to the outer surface of the plugs;E Install new plugs and the shift shaft. (Figure79).PLUGSB. Install the new locking screw which holdsthe adjusting ring at the Ring Gear side andthe cotter pin which locks the ring in the oppositeside;C. Place the sun gear and the fork (Figure 78);Figure 79<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>31
ReassemblyF. Apply a silicon adhesive cord to the contactsurface of the mechanism in the case andthen, install the Shift Mechanism (Figures79 A and 79 B) (Figures 79 A and 79 B)Figure 80Figure 79AD. Gradually press the center of the diaphragmup to reach the base of the mechanismCAUTION:1 - THE DIAPHRAGM SHOULD BE ALIG-NED SO THAT THE HOLES MATCH THEFASTENERS.2 - DO NOT FORCE THE DIAPHRAGMBASE. THE METALLIC REINFORCE-MENT SHOULD BE DAMAGED.Figure 79B3 - THE CENTER OF THE DIAPHRAGMSHOULD STAY NEARLY 2.7 MM ABOVETHE FLANGE SURFACE, SO IT IS NOTTENSIONED.Installation of the Mechanism Diaphragm(When Existing)A. Clean and Inspect the Fork Shaft for scratchesand burrs;B. Apply extreme pressure Lithium Soap basedgrease, to the fork shaft;C. Place the diaphragm and the retentionspring on the fork shaft (Figure 80);Important:Before positioning this component, be sure thatthe following points are correct: assemblingside with alignment of the holes with the fixingbase fasteners. This is important because thediaphragm has only one mounting position.E. Make sure the diaphragm is assembled withouttorsion;F. Wipe excess grease from the fork shaft.Installation of DifferentialA. Check the case for differential fasteningstuds looseness (if applicable). Apply LiquidAdhesive (Loctite 271 or THREE BOND1305) to the loosen fasteners;B. Reinstall and tighten these fasteners asmuch as enough to the total engagement ofthe threads;C. Apply NEUTRAL SILICON to the mouthof the case. Refer to the section ChemicalGasket;32 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
ReassemblyD. Before starting the installation, make surethat the mechanism is set to Low Speed(LS), to avoid interference between the sungear and the mouth of the case and allowan easy installation of the differential;E. Place the differential on the case;F. Start the installation of the differential in thecase with four flat washers and four nuts,equidistantly spaced.CAUTION:DO NOT TRY TO INSTALL THE DIFFEREN-TIAL ON THE CASE USING A HAMMER.THIS PRACTICE MAY DAMAGE THE FLAN-GE AND CAUSE OIL LEAKAGE.Important:1. Install the flat and tapered (if any) washerson all of the studs located in places that arenot easily accessible. In some instances, it isimpossible to install them after the differentialis in its final position in the case.2. Tighten the four nuts with flat washers in analternated sequence, to drive the set alignedto the next nuts or screws.3. In case if there are screws fixing the differentialapply Liquid Adhesive (Loctite 241 orTHREE BOND 1334) to them. Refer to theLiquid Adhesive section.• Install the semi-axes.• Install and tighten the drain plug to the specifiedtorque in the section Tightening Torques.WARNING:After tightened, at least one of the threadsshould remain above the mounting surface.• Fill the unit with the oil specified in the sectionLubrication• Install and tighten the oil filling and level inspectionplug to the torque specified in thesection Tightening TorquesWARNING:After tightening, at least one of the threadsshould remain above the mounting surface.Ring Gear Thrust Screw AdjustingA. After the assembly settings, screw the boltwith its nut until its end touch the rear faceof the ring gear and then return 1/3 turnback to ensure a clearance of 0.6 to 0.9 mm(Figure 81). Tighten the nut to the specifiedtorque in the section Tightening Torques.• Install the shift mechanism in the differentialwith application of chemical gasket (NEU-TRAL SILICON).WARNING:Be sure that the shift fork position is compatiblewith the rest position of the shift mechanismdrive shaft.CLEARANCE:• Install and tighten the fixing washers andnuts of the mechanism to the specified torquein the section Tightening Torques.• Connect the shaft drive to the mechanismline.Figure 81<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>33
Pinion BearingsThe preload control avoid the bearings to operatewith excessive pressure (reducing wearlife) or with free play (produces noise and reduceswear life of the differentialThe preload is obtained through the installationof a selection shim between the pinion bearingcones (Figure 82).PINION BEA-RINGS ADJUS-TING SHIMFigure 82Identification of Pinion Bearing Adjusting ShimsIt is available for setting a series of shims that vary in thickness, as indicated in the tables “A” and“B”.IMPORTANT:The thickness value is marked in each pad.New BearingsUSED BearingsN.m lbf.in N.m lbf.in1,7 - 4,0 15 - 35 1,1 - 2,3 10 - 20WARNING:These values must be obtained before installingthe seal in the pinion case.CODETHICKNESS(MM)CODETHICKNESS(MM)CODETHICKNESS(MM)02807002807102807202807302807402807502807602807702807802807902808002808102808211,8911,9111,9411,9611,9912,0112,0412,0712,0912,1212,1412,1712,1902808302808402808502808602808702808802808902809002809102809202809302809402809512,2212,2412,2712,3012,3212,3412,3712,4012,4212,4512,4712,5012,5202809602809702809802809902810002810102810202810302810402810502810602810712,5512,5712,6012,6212,6512,6712,7012,7312,7512,7812,8012,83Table “A” for models 220/23034 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
Pinion BearingsCODETHICKNESS(MM)CODETHICKNESS(MM)CODETHICKNESS(MM)02903402903502903602903702903802903902904002904102904202904302904402904502904618,3018,3318,3518,3818,4018,4318,4518,4818,5118,5318,5618,5918,6102904702904802904902905002905102905202905302905402905502905602905702905818,6418,6618,6918,7218,7418,7718,7918,8218,8518,8718,9018,9202905902906002906102906202906302906402906502906602906702906802906902918018,9518,9819,0019,0319,0519,0819,1119,1319,1619,1819,2119,24Table “B” for model 240We recommend that the initial assembling is done with the shims of the recommended range inthe table “C”, which allow to obtain immediately (in most cases) the desired setting:WARNING:The identification is marked in the outer diameter or in one of faces of the shim.ModelRECOMMENDED RANGEMM INches220/230 12,30 - 12,50 0,484 - 0,492240 18,79 - 18,90 0,740 - 0,744Tabla “C”Drag Torque Determining Procedure(Using a press)A. Lubricate all pinion bearings with the oil recommended in the section Lubrication;B. Press the front bearing cone and turn the pinion cage several times to ensure a suitableseating between caps and cones. Keep the pinion cage under pressure load, according tospecification of table “D”;ModelLOAD (ton)220 11230 11240 14Tabla “D”<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>35
Pinion BearingsC. Wrap a cord around the pilot diameter of the pinion cage with a dynamometer (good qualitybalance), tied at its end;D. Pull the dynamometer horizontally and note the value (pounds or kilograms) recorded in itsscale;NOTE:For convenience, we reported in the table “E” the readings that should be obtained to meetthe preload values.ModelNEW BEARING USED BEARINGkg lb kg lb240 2,1 - 4,8 4,5 - 10,6 1,3 - 2,8 3,0 - 6,0220/230 2,6 - 6,2 5,8 - 13,5 1,7 - 3,6 3,8 - 7,7Table “E”E. Note the value obtained with the rotating set, but not the starting value (Figure 83);PRESSFigure 83F. Measure the pilot diameter of the pinion cage and then divide by two to determine the value ofthe radius;NOTE:For convenience, we inform on table “F”, the radius value to be considered.radiusModelcm in.240 8,4 3,31220/230 6,6 2,60Table “F”36 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
Pinion BearingsG. Multiply the value of “E” item by the “F” itemand then make the following calculation:kg x cm = result in kgf. Cmlb x inches = result in lbf.polH. Check if the obtained result matches thespecified limits.If the value found is over the maximum specifiedlimit, replace the shims by others of greaterthickness.If the value found is below the maximum specifiedlimit, replace the shims by others of smalerthickness.Example of CalculationDataradius - 8,4 cm (3,31”)reading in the dynamometer 2,3 kg (5,0 lb).Calculation Procedure2,3kg x 8,4 cm = 19,3 kgf.cm5,0lb x 3,31” = 16,55 lbf.polConverting to N.m19,3 x 0,098 = 1,9 N.m16,55 x 0,113 = 1,9 N.mWARNING:To convert lbf.pol in N.m multiply it by the factorof 0,113 and kgf.cm in N.m multiply it by afactor of 0,098.Drag Torque Determining Procedure(Without press)If a press is not available during the serviceoperation, use the following procedure:A. Lubricate all the pinion bearings with the oilspecified on the section Lubrication;B. Install the fork/flange of the universal joint(without the pinion seal);C. Immobilize the pinion (by the fork/flange ofuniversal joint), using a suitable device;D. Tighten the pinion nut to the minimum valuespecified in the section Tightening Torques;E. Turn the pinion cage several times to ensurea suitable seating between caps andcones;F. Do then the same procedure specified onpages 53 e 54 (from “C” to “G”);G. If the value is found below the minimumspecified limit, gradually tighten the pinionnut (if necessary, up to the maximum torquevalue specified in the section (TighteningTorques) to obtain the desired preload;WARNING:Note the value obtained with the rotating set, butnot the starting value.H. If, after tightening to the maximum torquethe desired preload is not obtained, replacethe shims by others of a smaller thicknessand repeat the inspection procedure;I. Remove the fork/flange of the universaljoint and continue the reassembling of thedifferential.<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>37
Pinion assemblyThis adjustment helps to position the drive pinionin relation to the ring gear for the purpose of ensuringthe ideal position of tooth contact betweenring gear and pinion.The desired distance is obtained by the installationof a shim set under the drive pinion bearingcage (Figure 86).ADJUSTINGSHIM SETOF THEDRIVEPINIONBEARINGCAGEFigure 86Identifying the Drive Pinion Bearing Cage Adjusting ShimsIt is available a series of adjusting shims for this adjustment. They are differentiated by its thickness(see table “G”).model code THICKNESS (mm)028455-6 0,25240028454-8 0,13028453-0 0,08027288-4 0,13220027289-2 0,25230027290-6 0,08Table “G”NOTE:Shims are not identified because their differencein thickness is quite noticeable.The proper combination of these parts will formthe shims packet, which should ensure the desiredposition of the pinion.Important:The package should always be made of a minimumof three pieces, and the thicker shimshould be placed at its end so as to ensure maximumsealing.38 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
Pinion assemblyShims Determination Procedure(With caliper)Shims Determination Procedure(Without caliper)A. Write down the nominal mounting dimension(ND) for the drive pinion. This dimensionis the nominal distance taken from thecenter of the ring gear to the rear drive pinionbearing cone seating face (Figure 87);This process consists of a mathematical calculation,and the result is sufficiently satisfactorywhen only the ring gear and drive pinion set isreplaced.Other components that can affect the properposition of the drive pinion are: the differentialcase, the drive pinion bearing cage and theinner pinion bearing. Therefore, if any of thesecomponents need to be replaced; this mathematicalprocess may be used as a first attemptto select the shims for the proper adjustment inthe contact of the drive pair.modelnD240 219,08230 206,38220 200,00Table “H”Figure 87A table “H” mostra o valor da DN a ser consideradopara cada modelo:B. Identify and right down the drive pinion variation(PV);All drive pinions have an individual variationwith respect to their ND. This variation, expressedin hundredths of a millimeter, and a + or– sign is stamped on the pinion’s head (Figure88);A. Take note of the variation value (PV) on thedrive pinion to be replaced;B. Observe the variation value (PV) on thenew drive pinion. If the value is the same asthe original drive pinion, the thickness of theoriginal shim pack must be maintained.If the value is different, perform the followingcalculations:B1. Measure and write down the thickness ofthe original shim pack (pack thickness PT);B2. Check the variation value (PV) stamped onthe head of the original drive pinion. If thisnumber is (+), subtract this value from thethickness dimension of the original shimpack. If it is (–), add it.The resulting value will establish a master thicknessfor shim packs used for the assemblyof a drive pinion whose ND dimension is equalto zero.B3. Take note of the value obtained in Step B2to use it in the calculation of the thicknessfor the shim pack of the new drive pinion.B4. Observe the variation value (PV) of the newdrive pinion. If the value is (+), add it to thevalue obtained in Step B3. If it is (–), subtractit;B5. The final result obtained will establish thethickness of the new shim pack to be usedin the installation of the new hipoidal pair.Figure 88<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>39
Pinion assemblyExample of Calculation “1”Data:EP (original pack)..........................0,90VP (original drive pinion..............+0,05VP (new pinion)............................-0,13CalculationsEP (original pack)..........................0,90VP (original drive pinion)..............-0,05EP (master pack).........................=0,85VP (new drive pinion)...................-0,13EP (new pack).............................=0,72Exemplo De Cálculo “2”Data:EP (original pack)..........................0,90VP (original drive pinion)..............-0,05VP (new drive pinion)...................-0,13Shims Determination Procedure(With caliper)WARNING:In the following operations, ensure the cleaningof the indicated components:1. Mating surfaces between the componentsof special tool;2. Mating surfaces of the components ofspecial tool;3. Mating surfaces between differential caseand drive pinion, which is crucial.- The special tool is made of the followingcomponents: (Figure 90).1. Centering discs2. Centering axle shaft3. Drive pinion simulator4. Adapters for Drive Pinion Bearing - Rear5. Locking Washer – Drive Pinion Bearing -Front6. Knurled Nut7. Dial support8. ShimsFigure 9040 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
Pinion assemblyA. According to the model of the rear axle,install the rear bearing adapter in the drivepinion simulator. (Figure 91).B. Install the rear drive pinion bearing on theadapter. (Figure 92).Figure 94Figure 91E. Install the drive pinion front bearing lock washerand the knurled nut, tightening it manually.(Figure 95).F. Check if the drive pinion and the differentialcase contact surfaces are clean and free ofscratches or scores.G. Install the drive pinion cage in the differentialcase without the adjusting shims. (Figure96).Figure 92C. Install the drive pinion bearing cage on thedrive pinion rear bearing with the face to fitthe differential facing down (Figure 93).D. Install the front bearing in the face of thedrive pinion cage (Figure 94).Figure 95Figure 93<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>41
Pinion assemblyK. According to the differential model, installspecific centering discs with their respectiveshaft in the bearing housing of the differentialcase.L. According to the rear axle model, select theproper shim:Figure 96H. Install four capscrews and initially tightenthem in a cross sequence. (Figure 97).I. Then with a torque wrench in the samecross sequence, apply the final torque to:67 - 91 lbf pé ( 90 -125 N.m). (Figure 98).J. Make sure the differential case assemblybearing housing and the centering discsfrom the special tool are perfectly clean andlubricate them with a thin oil film.model SHIM PACK220 4.72230 11.10240 23,80Then install it over the upper end of the pinionsimulator, after making sure that the contactsurfaces of both parts are absolutely clean (Figure99).M. Install a hundredth dial in the bracket. Placethe support and the touch probe of the dialover the default shim surface and adjustthe instrument at “0” (zero) reading. (Figure100).Figure 97Figure 99Figure 98Figure 10042 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
Pinion assemblyN. Then, with the dial support firmly positionedon the default shim surface, put the touchprobe over the centering shaft.Continuing, move the probe across the centeringshaft up to the pointer of the instrumentindicate a maximum value. This valueindicates that the probe is exactly over thecentering shaft diameter. (Figure 101).NominalDimensionWrite down the maximum value (MV) indicatedby the pointer of the dial indicator.O. See the value known as nominal dimensionof this differential.Nominal dimension is the distance taken fromthe seating face of the drive pinion rear bearingto the center of the ring gear. (Figure 102).Each model has a specific nominal dimension,as shown below:Figure 102P. Check and write down the number stampedon the top of the pinion. This value indicates(according to its preceding signal) howmany hundredths of a millimeter have to beadded or subtracted from the corrected nominaldimension. (Figure 103).Differential Specific NominalModel Dimension220 200.00230 206.38240 219.08Figure 103Q. Subtract the maximum value (MV) of the differentialnominal dimension from its specificcorrected nominal dimension.The result will be the thickness of the shimpack(s) to be added to obtain proper drive pinion/ringgear tooth contact.Exemple:In a 220 differential, we find the following values:Figure 1011. Nominal dimension maximum value (MV) ofthe differential, determined with the help ofa special tool: Vm = 200,702. Stamped number in the top of the drive pinion:-063. Specific Nominal Dimension (SND) of thisdifferential model; Cne = 200,00<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>43
Satellite System/PlanetaryFrom these data we get the following:The number -6 stamped on the top of the drivepinion indicates that its height variation in relationto the differential nominal dimension is 0.06mm lower than the specific nominal dimension(SND), so: :200,00 - 0,06 = 199,94Therefore, 199.94 is the corrected nominal dimension(CND) for the differential.To determine the thickness of the shim pack(s)needed to obtain a proper drive pinion/ring geartooth contact, we subtract CND (corrected nominaldimension) from Mv (maximum value).Figure 105B. Put a torque wrench on the end of this deviceand check the rotation resistance valueof the satellite/planetarium assembly. Theobtained value must be less than. (Figure106);Vm - Cnec = Thickness of the shim pack200,70 - 199,94 = 0,76 mmWe, therefore, have to add 0.76 mm of shimsbetween the differential and the drive pinion assemblyto obtain a proper drive pinion/ring geartooth contact.A. Immobilize the differential case and insertthe device, which must engage with thesplines of one planetary. (Figure 104);NOTE:A suitable Inspecting Tool may be built froma cut shaft axle with a welded nut on its end,for attaching the torque wrench (Figure105);Figure 106The preload is obtained through the correct positioningof the bearing adjusting rings (Figure107).Figure 107Figure 10444 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
Differential Cage BearingsPreload Adjusting MethodA. Gradually tighten the “X” ring until the backlashof the ring gear/drive pinion is eliminated(Zero clearance);WARNING:Tightening must be gradual so that the ringdoes not press on the bearing (cup and cone)after the ring gear is seated in the drive pinion.B. Gradually tighten the “Y” ring until the radialclearance of the bearings is eliminated.C. Loosen the “X” ring 3 or 4 notches (nut).D. To obtain the desired preload, tighten the“Y” ring until the axial clearance is eliminated,and then tighten 2-3 notches more (fornew bearings) or 1-2 notches (for used bearings)or tighten it to a torque value of 25-30lb-ft.E. Check the Backlash Gear as specified inthe section BACKLASH GEAR.Important:To move the rings, always use a “T” bar or ordinarybars which engage in two opposite notches(Figure 108). Never hammer the notcheswith hammers or chisels, as this may cause irreparabledamage in the adjusting rings.Alternative MethodA. Loosen the “Y” ring until axial clearance ofthe bearings is obtained;B. Tighten the “X” ring until the backlash of thehypoid set teeth is eliminated (Zero clearance);WARNING:Tightening must be gradual so that the ringdoes not press on the bearing (cup and cone)after the ring gear touches the drive pinion.C. Meça a distância entre os pedestais dascapas dos mancais (nas diagonais A e B)com um micrômetro adequado (Figure 109)e anote os valores obtidos;D. Loose the “X” ring 3 to 4 notches or holesand gradually tighten the “Y” ring to expandthe bearing caps about 0.006~0.013inch (0.15~0.33 mm) for new bearings or0.003~0.006 inch (0.08~0.16 mm) for usedbearings, which is the bearing preload;E. Do a new measurement and compare theresult with the values obtained in step “C”.(Figure 110);Figure 109Figure 108<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>45
Backlash GearFigure 112Figure 110F. Check if the expansion specified in the step“D” was obtained. If not, do a new alternatedtightening process with measurement/comparison to obtain the specified expansion.• Check, then, the runout of the rear surfaceof the ring gear (Figure 111). If found valueexceeds 0.019 inches (0,20 mm), removethe ring gear, check the causes and correctthem.Immobilize the drive pinion, manually rotate thering gear in both directions and take the reading.The value for the backlash should be between0.010~0.016 inches (0.25~0.40 mm).In case if it is necessary to increase or decreasethe backlash, loosen the “X” ring and tightenthe “Y” ring (or vice versa) in the same proportion,so as not to change the preload of the bearings(Figure 113).Important:When the hypoid pair is reused, it is recommendableto keep the original backlash (measurefound before disassembling the differential assembly).Figure 111Important:The differential case (simple and flange halves)and the locking plate must be inspected andreplaced if any engagement problem is found.INCREASESTHE CLEARANCEDECREASESCLEARANCEFigure 113Check the backlash gear of the hypoid pairusing the following procedure:Rest the pointer of a dial indicator on one of thering gear teeth. (Figure 112);Inspection ProcessA. Apply yellow iron oxide (diluted in thin oil) ina number of teeth of the ring gear (Figure114);B. Block the ring gear with the help of a leveror a slat and manually rotate the drive pinion,until you have the impression of contacton the convex side (forward gear) of thering gear’s teeth (Figure 115);46 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
Teeth Contact, Ring Gear and PinionFigure 114Figure 115C. Make sure the contact obtained by the manualprocess meets the standard (Figure102). If not, use the correction methods listedunder “Incorrect Contacts”;D. Then, remove the yellow iron oxide remainingin the teeth of the hypoid pair.Satisfactory ContactsFor convenience, we indicate the terminologyused in this section in Figure 116.The contact pattern for the manual process indicatesthat the position of the gears is correct,resulting in a contact area from the center tothe toe and the heel/top and the root of the tooth.This area of contact covers approximately70~80% of the ring gear tooth’s length (Figure117).<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>47
Teeth Contact, Ring Gear and PinionCONCAVE SIDEIncorrect ContactsHeight Variations on the ToothIf the drive pinion is not at the proper depth, thecontact can show tooth height variation. If so,correct its position by varying the thickness ofthe shim pack under the drive pinion bearingcase (refer to Table “J”).CONVEX SIDEINCREASEDEPHTFigure 116PATTERN FOR <strong>MANUAL</strong> PROCESSSHALLOW CONTACTFigure 119Figure 117DECREASEDEPTHIf the convex side is satisfactory, consider thecontact of the concave side of the tooth (reversegear) automatically accepted.The pattern with load application shows theresulting contact when the gears approvedby manual process suffer the action of a load(working operation). The contact area extendsitself throughout the length of the ring gear tooth(Figure 118).LOAD APPLICATION PATTERNDEEP CONTACTFigure 120Figure 11848 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
Teeth Contact, Ring Gear and PinionOBTAINED CONTACT MEANING HOW TO CORRECTSHALLOW CONTACTThis indicates that the pinion istoo far from the ring gear, resultingin a contact too close to thetop of the tooth (Figure 119).Get the pinion closer by decreasingthe thickness of the drivepinion cage adjusting shims pack(refer to the section Pinion AssemblingDistance Adjustment).This will make the contact movesto the root of the tooth (Figure117).DEEP CONTACTThis indicates that the pinion istoo close to the ring gear, resultingin a contact too close to theroot of the tooth (Figure 120).Move the pinion away, increasingthe thickness of the drive pinioncage adjusting shims pack (referto the section Pinion MountingDistance Adjustment). This willmake the contact moves to thetop of the tooth. (Figure 117).Table “J”Length Variations on the ToothCheck, then, if the contact has varied in terms of length of the tooth. If so, change the depth of thering gear varying the gear backlash (see Table “K”).OBTAINED CONTACT MEANING HOW TO CORRECTCONTACT IN THE EXTREMEEND OF THE TOOTHIndicates that the ring gear isvery close to the pinion, causingthe contact to be too close to thetop of the tooth (Figure 121).CONTACT IN THE HEEL OFTHE TOOTHIndicates that the crown is toofar from the pinion, resulting in aclose contact of the heel of thetooth (Figure 122).Table “K”<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>49
LubricationCONTACT IN THE EXTREME END OF THE TOOTHCONTACT IN THE HEEL OF THE TOOTHFigure 121 Figure 122The use of incorrect lubricants or inadequate additives generally is the major cause of differentialfailure occurrences.The specified lube oil for differentials must have extreme pressure (EP) features, API-GL-5 serviceclassification of the American Petroleum Institute and meet the requirements of the U.S.military specification MIL-L-2105-C.This type of oil, better known as hypoid oil, have a lubricating film which is able to bear the loadpressure of heavy loads, which makes it adequate for hypoid gears, whose conditions are quitesevere.ViscosityGenerally, the high viscosity degree of monoviscous oil is suitable for high environmental temperatures.In addition to extending wear time of the gears, the option for multiviscous oil will satisfy the foundtemperature conditions.The table below represents the viscosity selection of oils:MILITARYENVIROMENTAL TEMPERATUREOIL DESCRIPTIONSPECIFICATIONSMÍN..MÁX.MIL - L2105 - C/D API GL-5 85W/140 -12 Cº -X-MIL - L2105 - C/D API GL-5 80W/140 -15 Cº -X-MIL - L2105 - C/D API GL-5 80W/90 -26 Cº -X-MIL - L2105 - C/D API GL-5 75W/90 -40 Cº -X-MIL - L2105 - C/D API GL-5 75W/140 -40 Cº -X-MIL - L2105 - B API GL-5 90 0 Cº -X-MIL - L2105 - B API GL-5 140 +4 Cº -X-50 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
LubricationInspection and RecommendationsCheck, every 1.250 miles (2.000 km), if the oillevel is correct.Perform the draining operation while the oil isstill warm. This allows the lubricant to drain freelyand more quickly, reducing the time requiredto completely drain the oil from the differential.Complete the level or refill until the lubricantdrain off slightly by the lower edge of the holefor oil filling and level inspection.The shaft should not be internally washed withany kind of solvent (kerosene, gasoline, diesel,etc.).After every oil change, and before applying thevehicle to normal operation, drive within thespeed limit of 25 mph (40 km/h), for 5 to 10minutes or 1 to 2 miles (2 to 3 km) to ensurethat all lines have been properly filled withoil. If the differential is a replacement unit notscheduled for immediate use, all bearings andgears should be covered with a good coat ofanti-corrosion oil.In this case, the differential should be kept in asealed box to be reused, to avoid the contact ofdust and other impurities with the unit.Perform oil change every 100.000 miles(160.000) km or once a year, whichever occursfirst.Vehicles that operate on the highway or offroad in severe applications, using the maximumpermitted load, should make the oil change inintervals of 25.000 to 31.000 miles (40.000 to50.000 km) or every six months, whichever occursfirst.Magnetic Plug<strong>Meritor</strong> recommends the use of magnetic plugsfor the axle oil draining port.Important:The magnetic plug loses its efficiency quicklywhen it accumulates too many metallic particlesand, therefore, should be cleaned beforethis happens. After removal and cleaning, theplug can be reused. It is recommended that thisprocedure be practiced once or more within theoil change period.Changing PeriodsNew or Reconditioned UnitsDuring the initial period (break-in), perform thedifferential oil change from 1.250 to 3.100 miles(2.000 to 5.000 km). This initial oil change is recommendedto ensure the removal of metallicparticles typically generated in bigger amountsduring this phase.After the break-in periodVehicles that operate primarily on the highway,with workloads below its maximum permittedload.<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>51
Tightening Torques• The indicated torques apply to lightlyanti-oxidant oil coated parts.• For dry parts, torque 10% higher thanspecified.• For parts lubricated with oil from theunit, apply a torque 10% lower.ITEM DESCRIPTION12345678910111213Drive pinion nutCapscrews (pinion bearing case fasteners)Capscrews (differential case fasteners)Plug (oil filling and level inspection)Capscrews (bearing caps fasteners)Capscrews (ring gear and differential case)Nuts (locking plate fasteners)Capscrews (lock plate fasteners)Capscrews (differential fasteners)Nuts (differential fasteners)Drain plugNuts (fasteners for speed changing control mechanism)Shift shaft lock nut14 Vent plugSPECIFIED TORQUE N.m (lbf.PÉ)220 230 2401000- 1250 (740-920)91-120 (67-91)125-150 (92-110)47 mín. (35 mín.)295-360 (220-265)205-250 (150-265)575- 640 (425- 475)270- 330 (200-245)250-305 (185-225)47 mín. (35 mín.)46- 62 (34-46)14 mín. (10 mín.)27 mín. (20 mín.)1000-1250 (740-920)91-150 (67-91)125-150 (92- 110)47 mín. (35 mín.)295-360 (220- 265)205- 250 (150-185)175- 220 (130-160)270- 330 (200-245)250- 305 (185- 225)47 mín. (35 mín)46- 62 (34-46)250- 1530 (920-1130)91- 120 (67-91)125- 150 (92-110)47 mín. (35 mín.)575-705 (425-520)205- 250 (150-185)175-220 (130-160)575- 640 (425- 475) 575- 640 (425- 475)270- 330 (200-245)14 mín. (10 mín.)27 mín. (20 mín.)47 mín. (35 mín.)46-62 (34-46)200- 260 (150-190)14 mín. (10 mín.)27 mín. (20 mín.)Liquid Adhesive174- 574 (LOCTITE)High TorqueHigh TorqueHigh TorqueMedium TorqueMedium TorqueMedium TorqueMedium TorqueMedium Torque174-574 (LOCTITE)* Some assemblies may be optionally equipped with fastening by studs. This will not change the torque value for the nuts.52 <strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
InstructionSpeed Changing Mechanism OperationAll MERITOR two-speed rear axles are extremelyeasy to operate.To obtain a smooth and accurate engagement,use the sequences listed below:1. CHANGE ONLY IN THE SHAFT:A. From low speed (LS) to high speed (HS)(AV)ImportantDo not shift the shaft from high to low speed(HS to LS) when the vehicle is performing speedswhich can drive the engine to revolutionshigher than the maximum (governed).If the shift system is triggered in this condition,the coupling is not complete until the vehiclespeed drops to a speed corresponding to themaximum (governed) engine revolutions.First, keep the throttle and lift the power buttonof the changing mechanism.Then release the throttle or press the clutch pedaland wait a while to complete the engagementand re-accelerate.B. From high speed (HS) to low speed (LS)First, keep the throttle and push the power buttonof the changing mechanism.Then release and press the accelerator as fasteras possible, or press and release the clutchpedal quickly.CAUTIONIF THE ACTIVATION IS DONE IN A DOW-NHILL THE PROBLEM WILL BE MORECRITICAL, BECAUSE THE VEHICLE SPE-ED DOES NOT REDUCE BUT INCREASES,MAKING IMPOSSIBLE THE COUPLING INLS. IT CAN NOT EVEN RETURN TO HS, IFTHE SPEED GETS TOO HIGH.IN THIS CASE, IMMEDIATELY ACTIVATETHE TOP GEAR (THE LONGER ONE) OFTHE TRANSMISSION, FOR NOT STAYING INNEUTRAL.2. SHIFT AND SHAFT COMBINED CHAN-GING:A. Top gear in the transmission = low speed inthe shaft:First, shift the gear normally. Then lower thepower button of the changing mechanism shortlybefore releasing the clutch pedal.B. Lower gear in the transmission + low speedin the shaft:First, keep the throttle and lift the power buttonof the changing mechanism.Then, shift the gear normally.<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>53
Always use Technical Manuals of...<strong>MAINTENANCE</strong> <strong>MANUAL</strong>
Always use original partsFor more details, see the Spare Parts CatalogCustomer service55 11 3684.674155 11 3684.6867Purchase the CD-ROM failure analysis of components of the axistractionCustomer ServiceAv. João Batista, 825 - Osasco - SP - 06097-105Tel. (11) 3684-664 - (11) 3684-6867AfterMarket (Peças de Reposição)R. Ester Rombenso, 403 - Osasco - SP - 06097-120Tel. (11) 0800-555530www.arvinmeritor.com