M. Sc. BIOCHEMISTRY - Shiats.edu.in
M. Sc. BIOCHEMISTRY - Shiats.edu.in
M. Sc. BIOCHEMISTRY - Shiats.edu.in
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
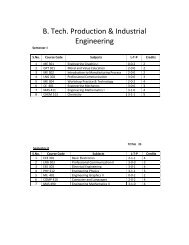
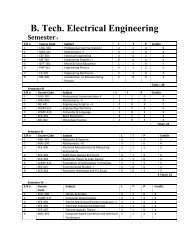
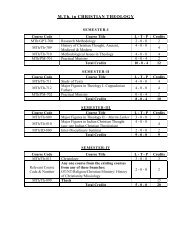
1. Mitosis of Onion Root Tips2. Tissue Types <strong>in</strong> Dicot Stem3. Tissue Types <strong>in</strong> Monocot Stem4. Tissue Types <strong>in</strong> Dicot Root5. Tissue Types <strong>in</strong> Monocot Root6. Gram Sta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g of BacteriaMAS 711 Statistics I 3 (2-0-1)Standard – deviation, Coefficient of variation, standard error of mean.Theory of Probability : equally likely, mutually exclusive events , def<strong>in</strong>itions of probability, addition& multiplication theorems of probability & problems based on them.Normal & B<strong>in</strong>omial Distributions.Simple correlation & regression, Multiple- regression, Multiple & Partial- Correlation.Test<strong>in</strong>g of Hypothesis : Concept of Hypothesis, Degrees of freedom, Level of significance. Type I& Type II errors. X 2 , t, Z & F – tests. (def<strong>in</strong>ition, applications & problems based on these tests).SEMESTER-IIBCBT 705 Intermediary Metabolism- II 3(2-0-1)Unit 1: Am<strong>in</strong>o acid catabolism: <strong>in</strong>troduction to digestion and absorption, am<strong>in</strong>o acid degradationpathways and their mode of degradation- Transam<strong>in</strong>ation, oxidative deam<strong>in</strong>ation, deam<strong>in</strong>ation andimportance. Urea cycle, formation of excretory products, l<strong>in</strong>k<strong>in</strong>g to TCA cycle and regulation.Unit 2: Am<strong>in</strong>o acid biosynthesis: overview, biosynthesis of essential am<strong>in</strong>o acidstryptophan,tyros<strong>in</strong>e, val<strong>in</strong>e, lys<strong>in</strong>e. Biosynthesis of non-essential am<strong>in</strong>o acids: glyc<strong>in</strong>e, ser<strong>in</strong>e, cyst<strong>in</strong>e,threon<strong>in</strong>e, phenylalan<strong>in</strong>e, histid<strong>in</strong>e, pral<strong>in</strong>e, arg<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>e.Unit 3: Pur<strong>in</strong>e & Pyrimid<strong>in</strong>e nucleotide metabolism: <strong>in</strong>troduction, denovo and salvage pathwaysof pur<strong>in</strong>e and pyrimid<strong>in</strong>e nucleotide biosynthesis. Catabolism of pur<strong>in</strong>e and pyrimid<strong>in</strong>e nucleotides.Biosynthesis of nucleotide coenzymes.Unit 4: Membranes- Transport phenomenon: biomembranes, diffusion- passive and facilitatedand active transport proceses. Mechanism of ATP synthase and its regulation, malate aspartateshuttle.Practicals:1. Parametric analysis of section of prote<strong>in</strong>-dye.2. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of prote<strong>in</strong> from milk.3. Fractionation of egg prote<strong>in</strong>s.4. Quantification of serum prote<strong>in</strong>s by honey method.5. Estimation of prote<strong>in</strong> from leaf tissue.6. Isolation of DNA from plant /bacterial sample.7. Quantification of DNA.8. Isolation of RNA from bacterial/ plant tissue.BCBT 706 Techniques <strong>in</strong> Biochemistry and Instrumentation 3(2-0-1)