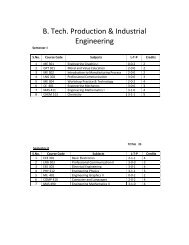
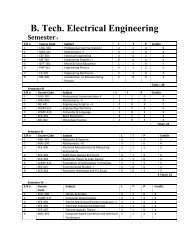
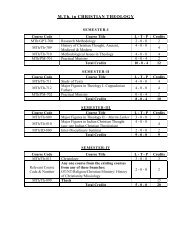
Study of Hygienic practices of street food vendors in ... - Shiats.edu.in
Study of Hygienic practices of street food vendors in ... - Shiats.edu.in
Study of Hygienic practices of street food vendors in ... - Shiats.edu.in
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Chirag Gadi, K. Lakshmi Bala, Avanish KumarIdentification <strong>of</strong> critical control po<strong>in</strong>ts and application <strong>of</strong> control measuresCCPs were identified along the ma<strong>in</strong> steps <strong>of</strong> <strong>street</strong> <strong>food</strong> cha<strong>in</strong> for production <strong>of</strong>safe <strong>street</strong> <strong>food</strong>.RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONIn this study the <strong>food</strong> safety and hygienic <strong>practices</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>street</strong> <strong>food</strong> <strong>vendors</strong> <strong>in</strong>Allahabad City have been studied. In addition to this bacteriological safety <strong>of</strong> water and<strong>food</strong> items sold by <strong>street</strong> <strong>food</strong> <strong>vendors</strong> with regard to Coliform and Salmonella wereevaluated.Personal hygiene, health and <strong>food</strong> handl<strong>in</strong>g <strong>practices</strong> were observed which showedthat out <strong>of</strong> 30 <strong>vendors</strong> chosen for survey, (80%) were <strong>in</strong> healthy condition and (20%) <strong>of</strong>them were suffer<strong>in</strong>g from cold and fever. 73.3% <strong>of</strong> the <strong>vendors</strong> cont<strong>in</strong>ue <strong>food</strong> preparationdur<strong>in</strong>g illness. Regard<strong>in</strong>g reasons for hand wash<strong>in</strong>g maximum percentage <strong>of</strong> <strong>vendors</strong>(33.4%) and (30%) washed hands after us<strong>in</strong>g the toilets and handl<strong>in</strong>g garbage. Otherreasons <strong>of</strong> hand wash<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>clude dur<strong>in</strong>g and after <strong>food</strong> preparation (16.6%), after meals(10%), blow<strong>in</strong>g nose (6.6%) and handl<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> raw <strong>food</strong>s (3.4%). Bhaskar et al. (2004)reported that defective personal hygiene can facilitate the transmission <strong>of</strong> pathogenicbacteria found <strong>in</strong> environment and on people's hands via <strong>food</strong> to humans.Hygiene dur<strong>in</strong>g handl<strong>in</strong>g and cook<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> <strong>street</strong> <strong>food</strong>s was observed. 20% <strong>vendors</strong>cooked <strong>food</strong> <strong>in</strong> advance <strong>of</strong> sale and (16.6%) <strong>of</strong> them cooked <strong>food</strong> on morn<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> sale.After prepar<strong>in</strong>g their <strong>food</strong>s they kept them and served them at ambient temperature.Only (23.3%) <strong>of</strong> the <strong>vendors</strong> reheat the <strong>food</strong>. 50 per cent <strong>vendors</strong> served <strong>food</strong> <strong>in</strong> steelplate and glass followed by dona (26.6%) and some served on leaves (10%) and newspaper (13.4%) with bare hands (36.6%). Handl<strong>in</strong>g with bare hands may result <strong>in</strong> crosscontam<strong>in</strong>ation, hence <strong>in</strong>troduction <strong>of</strong> microbes on safe <strong>food</strong> (FAO, 1997).Personal hygiene <strong>of</strong> the <strong>vendors</strong> was observed and it was found that clothes <strong>of</strong> the(46.6%) <strong>vendors</strong> were moderately clean and clothes <strong>of</strong> (13.4%) <strong>vendors</strong> were dirty, 60per cent had short nails which were not polished. About (40%) <strong>of</strong> the <strong>vendors</strong> werechew<strong>in</strong>g tobacco dur<strong>in</strong>g <strong>food</strong> handl<strong>in</strong>g and (73.3%) <strong>of</strong> the <strong>vendors</strong> did not wiped theirhands after every serv<strong>in</strong>g. Paulson D.S. (1994) reported that outbreaks are generallycaused by <strong>food</strong>s due to poor personal hygiene <strong>of</strong> the <strong>vendors</strong> and that have been mishandledor mistreated dur<strong>in</strong>g preparation or storage. Unhygienic surround<strong>in</strong>gs like sewage, improperwaste disposal system, and <strong>in</strong>adequate water supply attract flies and houseflies whichfurther <strong>in</strong>creases <strong>food</strong> contam<strong>in</strong>ation (Chumber et al., 2007).4