5.1 INTEGRALES DOBLES 5.2 INTEGRALES TRIPLES
5.1 INTEGRALES DOBLES 5.2 INTEGRALES TRIPLES
5.1 INTEGRALES DOBLES 5.2 INTEGRALES TRIPLES
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
MOISES VILLENA Integración Múltiple<br />
178<br />
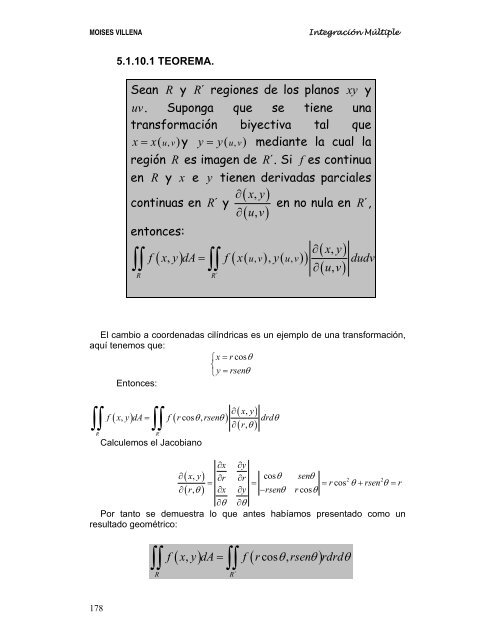
<strong>5.1</strong>.10.1 TEOREMA.<br />
Sean R y R ´ regiones de los planos xy y<br />
uv. Suponga que se tiene una<br />
transformación biyectiva tal que<br />
x= x(<br />
uv , ) y y = y(<br />
uv , ) mediante la cual la<br />
región R es imagen de R ´ . Si f es continua<br />
en R y x e y tienen derivadas parciales<br />
∂(<br />
x, y)<br />
continuas en R ´ y en no nula en R ´ ,<br />
∂(<br />
uv , )<br />
entonces:<br />
∂(<br />
xy , )<br />
f ( x, y) dA = f ( x( uv , ) , y( uv , ) ) dudv<br />
∫∫ ∫∫<br />
∂ uv ,<br />
R R´<br />
( )<br />
El cambio a coordenadas cilíndricas es un ejemplo de una transformación,<br />
aquí tenemos que:<br />
⎧x=<br />
rcosθ<br />
⎨<br />
⎩y<br />
= rsenθ<br />
Entonces:<br />
∫∫ ∫∫<br />
R R´<br />
( xy , )<br />
( r,<br />
θ )<br />
∂<br />
f ( x, y) dA = f ( r cos θ, rsenθ) drdθ<br />
∂<br />
Calculemos el Jacobiano<br />
∂ ( xy , )<br />
=<br />
∂ ( r,<br />
θ )<br />
∂x ∂r ∂x ∂y<br />
∂r<br />
∂y cosθ<br />
=<br />
−rsenθ<br />
senθ<br />
2 2<br />
= rcos θ + rsen θ = r<br />
rcosθ<br />
∂θ ∂θ<br />
Por tanto se demuestra lo que antes habíamos presentado como un<br />
resultado geométrico:<br />
∫∫ ∫∫<br />
( , ) = ( cos , )<br />
f x y dA f r θ rsenθ rdrdθ<br />
R R´