The Heart and Circulation - ECC-BOOK - Extracorporeal Circulation ...
The Heart and Circulation - ECC-BOOK - Extracorporeal Circulation ...
The Heart and Circulation - ECC-BOOK - Extracorporeal Circulation ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>The</strong> <strong>Heart</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Circulation</strong><br />
Cardiovascular System = <strong>Heart</strong>, Blood <strong>and</strong> Vessels<br />
Lymphatic System = Lymph nodes, Organs <strong>and</strong> Vessels
<strong>The</strong> <strong>Heart</strong><br />
• External Innervation<br />
– Vagus (parasympathetic)<br />
– C + T sympathetic chain ganglion<br />
• Pericardium (3 layers)<br />
• 1) Outer-fibrous pericardium<br />
– Serous pericardium<br />
• 2) parietal<br />
• 3) visceral (epicardium)<br />
• Pericardial Cavity<br />
– between layers of serous pericardium<br />
– serous fluid<br />
– lubricate heart while beating<br />
pg 524
• Oblique Position<br />
Location of <strong>Heart</strong> in Chest<br />
• Apex = Left of Midline (5th ICS), Anterior to rest of heart<br />
• Base (posterior surface) sits on vertebral column<br />
• Superior Right = 3rd Costal Cartilage, 1” right midsternum<br />
• Superior Left = 2nd Costal Cartilage, 1” left midsternum<br />
• Inferior Right = 6th Costal Cartilage, 1” right midsternum<br />
• Inferior Left = 5th Intercostal Space at Midclavicular line
Location of <strong>Heart</strong> in Thorax<br />
pg 523
pg 555<br />
External Features of <strong>Heart</strong><br />
• Interventricular sulcus<br />
• Coronal/Coronary sulcus<br />
• Auricles of atria<br />
• Apex<br />
• Base<br />
• Coronary vessels<br />
• Ligamentum Arteriosum
Pg 555, 554<br />
<strong>The</strong> Great Vessels <strong>and</strong> major<br />
branches<br />
Aorta (from Left Ventricle)<br />
• Ascending<br />
– Coronary arteries<br />
• Aortic Arch<br />
– Brachiocephalic trunk<br />
– Left Common Carotid<br />
– Left Subclavian<br />
• Descending (Thoracic/Abdominal)<br />
– Many small branches to organs<br />
Pulmonary Trunk (from Rt Ventricle)<br />
- -2 Pulmonary Arteries into lungs<br />
Inferior/Superior Vena Cava<br />
- Coronary sinus
• Epicardium (most superficial)<br />
– Visceral pleura<br />
• Myocardium (middle layer)<br />
– Cardiac muscle<br />
– Contracts<br />
• Endocardium (inner)<br />
– Endothelium on CT<br />
– Lines the heart<br />
– Creates the valves<br />
Layers of<br />
<strong>Heart</strong><br />
pg 524
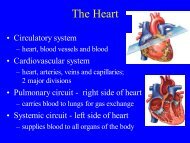
Right <strong>Heart</strong> Chambers: Pulmonary Circuit<br />
• Right Atrium (forms most of base of heart)<br />
– Receives O 2 -poor blood from body via IVC, SVC, Coronary sinus<br />
– Ventral wall = rough Pectinate muscle<br />
– Fossa Ovalis- on interatrial septum, remnant of Foramen Ovale<br />
• Right Ventricle<br />
– Receives O 2 -poor blood from right atrium through tricuspid valve<br />
– Pumps blood to lungs via Pulmonary Semilunar Valve in<br />
pulmonary trunk<br />
– Trabeculae Carnae muscle ridges along ventral surface<br />
– Papillary Muscle-cone-shaped muscle to which chordae tendinae<br />
are anchored<br />
– Moderator B<strong>and</strong>-muscular b<strong>and</strong> connecting anterior papillary<br />
muscle to interventricular septum
Left <strong>Heart</strong> Chambers: Systemic Circuit<br />
• Left Atrium<br />
– Receives O 2 -rich blood from 4 Pulmonary Veins<br />
– Pectinate Muscles line only auricle<br />
• Left Ventricle (forms apex of heart)<br />
– Receives blood from Left Atrium via bicuspid valve<br />
– Pumps blood into aorta via Aortic Semilunar Valve to<br />
body<br />
– Same structures as Rt Ventricle: Trabeculae carnae,<br />
Papillary muscles, Chordae tendinae<br />
– No Moderator B<strong>and</strong>
Chambers of <strong>Heart</strong>
<strong>Heart</strong> Valves: Lub*-Dub**<br />
• *Tricuspid Valve: Right AV valve<br />
– 3 Cusps (flaps) made of endocardium <strong>and</strong> CT<br />
– Cusps anchored in Rt. Ventricle by Chordae Tendinae<br />
– Chordae Tendinae prevent inversion of cusps into atrium<br />
– Flow of blood pushes cusps open<br />
– When ventricle is in diastole (relaxed), cusps hang limp in ventricle<br />
– Ventricular contraction increases pressure <strong>and</strong> forces cusps closed<br />
• *Bicuspid (Mitral) Valve: Left AV valve<br />
– 2 cusps anchored in Left Ventricle by chordae tendinae<br />
– Functions same as Rt. AV valve<br />
• **Semilunar valves: prevents backflow in large arteries<br />
– Pulmonary Semilunar Valve: Right Ventricle <strong>and</strong> Pulmonary Trunk<br />
– Aortic Semilunar Valve: Left Ventricle <strong>and</strong> Aorta<br />
– 3 cusps: blood rushes past they’re flattened, as it settles they’re pushed down<br />
(valve closed)
<strong>Heart</strong> Valves<br />
pg 527
Flow of Blood<br />
Pulmonary Circuit<br />
• O 2-poor blood (S+I VC, Coronary Sinus) enters Rt Atrium<br />
• Travels through Tricuspid Valve into Rt Ventricle<br />
• Pumped out through Pulmonary Semilunar Valve into Pulmonary trunk<br />
(branches into Pulmonary Arteries) <strong>and</strong> to lungs<br />
• After circulating through lungs, O 2 -rich blood returns to the heart<br />
through 4 Pulmonary veins<br />
Systemic Circuit<br />
• <strong>The</strong> O 2 -rich blood enters the Left Atrium<br />
• Travels through Bicuspid/Mitral Valve into Left Ventricle<br />
• Pumped out through Aortic Semilunar Valve into Aorta to be<br />
distributed to rest of body by descending aorta <strong>and</strong> branches of aortic<br />
arch
Cardiovascular Circuits<br />
pg 522
Blood Flow to Supply the <strong>Heart</strong> Muscle<br />
• <strong>Heart</strong> wall too thick for diffusion<br />
of nutrients<br />
• Rt <strong>and</strong> Lft Coronary Arteries<br />
– Branch from Ascending Aorta<br />
– Have multiple branches along heart<br />
– Sit in Coronary Sulcus<br />
– Coronary <strong>Heart</strong> Disease<br />
• Cardiac Veins<br />
– Coronary Sinus (largest)<br />
– Many branches feed into sinus<br />
– Sits in Coronary Sulcus
Anatomy of Arteries <strong>and</strong> Veins<br />
• Tunica externa<br />
– Outermost layer<br />
– CT w/elastin <strong>and</strong> collagen<br />
– Protects, Strengthens,<br />
Anchors<br />
• Tunica media<br />
– Middle layer<br />
– Circular Smooth Muscle<br />
– Collagen & Elastic Fibers<br />
– Vaso-constriction/dilation<br />
• Tunica intima<br />
– Innermost layer<br />
– Endothelium<br />
– Minimize friction<br />
• Lumen<br />
pg 546
Vessels of Cardiovascular System:<br />
Arteries<br />
• Carry blood AWAY from heart<br />
• Systemic Circuit: carry O 2 blood<br />
• Pulmonary Circuit: carry de-O 2 blood<br />
• Walls thicker than Veins<br />
– Tunica media > Tunica externa<br />
• 3 Types<br />
– Conducting (elastic)<br />
• large, elastin, high pressure<br />
– Distributing (muscular)<br />
• medium size, to organs<br />
– Arterioles<br />
• smallest
Vessels of Cardiovascular System:<br />
• Smallest blood vessels<br />
Capillaries<br />
• Single layer of endothelium surrounded by basal lamina<br />
• Deliver O 2 <strong>and</strong> nutrients to cells <strong>and</strong> remove waste<br />
• Capillary Beds: networks of caps. Regulating amount of<br />
blood going to cells throughout tissues<br />
• Tendons, Ligaments poorly vascularized<br />
• Epithelium, cartilage has no capillaries
Vessels of Cardiovascular System:<br />
Veins<br />
• Carry blood from capillaries INTO the heart<br />
• Systemic Circuit: O 2 poor blood<br />
• Pulmonary Circuit: O 2 –rich blood<br />
• Thinner walls than arteries<br />
– Tunica externa > tunica media, Less elastin<br />
• Larger lumen than arteries<br />
• Contain valves (made of T. intima)<br />
• Normal movement, Muscular contraction push blood through<br />
• Venules- smallest veins
Movement through Veins<br />
pg 551
Cardiovascular Blood Flow<br />
• <strong>Heart</strong>Arteries(conducting-distributing)<br />
ArteriolesCapillaries of tissues<br />
• At Capillaries O 2 is delivered <strong>and</strong> CO 2 picked up<br />
• CapillariesVenulesVeins<strong>Heart</strong><br />
• Portal System: Special vascular circulation where blood goes<br />
through 2 capillary beds before returning to the heart to<br />
achieve 2 nd function<br />
– (eg) Hepatic Portal System: aids digestion by picking up digestive<br />
nutrients from stomach + intestines <strong>and</strong> delivers to liver for<br />
processing/storage<br />
– Pick-up occurs at capillaries of stomach <strong>and</strong> intestine<br />
– Via Hepatic Portal Vein goes to capillaries of liver<br />
– Via Hepatic Vein blood goes back to heart
Hepatic Portal System<br />
pg 570
pg 568<br />
Vascular Anastomoses<br />
• Vessels unite <strong>and</strong> connect<br />
• Arteriole Anastomoses<br />
– Communication between arteries<br />
– Joints, Abdominal Organs, Brain,<br />
<strong>Heart</strong><br />
• Venous Anastomoses<br />
– Communication between veins<br />
– More common<br />
– (eg) back of h<strong>and</strong><br />
• Vaso Vasorum<br />
– Tiny arteries, veins, capillaries in<br />
tunica externa of vessels to<br />
nourish them (outer half)
Fetal <strong>Circulation</strong>: 2 main differences<br />
• All major vessels are in place by 3 rd month<br />
• Blood flows in same direction as in adults<br />
1) Fetus must transport blood<br />
to <strong>and</strong> from the placenta<br />
2) Lungs are not functional,<br />
<strong>and</strong> do not need much<br />
blood
Fetal <strong>Circulation</strong>: Blood to Placenta<br />
• Fetus must supply placenta w/blood<br />
• Umbilical Vessels: carries blood to/from placenta<br />
– 2 Umbilical Arteries = bring blood that contains waste &<br />
little O 2 from fetus to placenta<br />
– 1 Umbilical Vein = brings blood w/O 2 <strong>and</strong> nutrients to<br />
fetus from placenta (some goes to portal vein to process in<br />
liver)<br />
• Ductus Venosus = shunt taking blood returning from<br />
placenta to fetus directly to heart, largely bypassing<br />
liver<br />
– Too much blood for liver to h<strong>and</strong>le<br />
– Results in highly O 2 blood going to heart
Fetal <strong>Circulation</strong>: Bypassing the Lungs<br />
• Fetal Lungs are not functional <strong>and</strong> do not need large<br />
amounts of blood<br />
• Foramen Ovale (becomes Fossa Ovalis)<br />
– Small hole in inter-atrial septum allows blood to flow<br />
directly from Rt. Atrium to Lft. Atrium<br />
– This largely bypasses the Rt. VentriclePulmonary trunk<br />
that would bring blood to lungs<br />
• Ductus Arteriosus (becomes Ligamentum Arteriosum)<br />
– Shunt directs blood from Pulmonary Trunk to Aortic arch,<br />
largely bypassing lungs
Pg 106<br />
Bypassing the Lungs
Remnants of Fetal <strong>Circulation</strong><br />
• Ligamentum teres = Round ligament<br />
– Remnant of the umbilical vein<br />
– Anterior abdominal wall<br />
• Ligamentum venosum<br />
– Remnant of ductus venosum<br />
– On liver’s inferior surface<br />
• Medial Umbilical Ligaments<br />
– Remnant of umbilical arteries<br />
– Anterior abdominal wall below navel<br />
– Also gives branch to urinary bladder
<strong>The</strong> Lymphatic System<br />
• Function: to collect excess tissue fluid collecting at<br />
arteriole end of capillary beds, <strong>and</strong> return leaked blood<br />
proteins to blood (maintain osmotic pressure needed to<br />
take up water into bloodstream)<br />
• Lymph is moved through vessels<br />
– Pulse of nearby arteries<br />
– Contraction of surrounding skeletal muscle<br />
– Regular movement of body (wiggling legs)<br />
– Muscle in Tunica Media<br />
• Lacteals-lymphatic capillaries w/unique function<br />
– In mucosa of small intestine, receive digested fat from intestine<br />
– Fatty lymph becomes milky = Chyle<br />
– Chyle goes to bloodstream
Lymphatic System…<strong>The</strong> Players:<br />
• Lymph- clear fluid from loose CT at capillaries<br />
• Lymphatic capillaries (near blood capillaries) <br />
• Lymph collecting vessels (small, 3 tunicas, # valves)<br />
<br />
• Lymph nodes (sit along collecting vessels)-clean<br />
lymph of pathogens, they are NOT gl<strong>and</strong>s<br />
• Lymphatic trunks (convergence large collecting<br />
vessels)<br />
– Lumbar, intestinal, bronchomediastinal, subclavian, jugular<br />
• Lymphatic ducts empty into veins of neck