Tunisia : Country Studies - What is GIS
Tunisia : Country Studies - What is GIS
Tunisia : Country Studies - What is GIS
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Tun<strong>is</strong>ia</strong> Role of contractual arrangements in improving health system performance<br />
system, the architecture of the public and private health care facilities and their<br />
objectives and the fundamental conditions of orientation of the health system by the<br />
authorities in charge and the adv<strong>is</strong>ory bodies that have been set up.<br />
Health care <strong>is</strong> provided by public, parapublic and private health care facilities.<br />
The public health facilities are usually classified according to three levels: primary,<br />
secondary and tertiary. Primary level compr<strong>is</strong>es basic health centres and d<strong>is</strong>trict<br />
hospitals. Basic health centres provide preventive care and curative health care services<br />
as well as health education for:<br />
Treatment of common d<strong>is</strong>eases<br />
Mother and child care, including family planning<br />
Prevention and control of communicable and infectious d<strong>is</strong>eases, particularly through<br />
immunization<br />
Pre-school, school and university medical services<br />
D<strong>is</strong>semination of hygiene principles and practices and rules relating to environmental<br />
protection through health education<br />
Collection and use of epidemiological and stat<strong>is</strong>tical health data.<br />
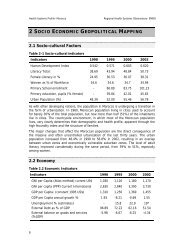
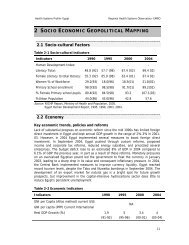
At the end of 2000, there were 1981 basic health care centres throughout the<br />
country with a national average of 1 centre per 4826 population.<br />
D<strong>is</strong>trict hospitals, beside the services similar to those of the basic health centres,<br />
also provide general, maternity and emergency services, and have hospital beds. At the<br />
end of 2002, there were 106 d<strong>is</strong>trict and maternity hospitals with a total capacity of<br />
2711 beds.<br />
The secondary level compr<strong>is</strong>es regional hospitals that provide specialized<br />
medical and surgical care, in addition to those services mentioned for primary, or firstline,<br />
facilities. Every county town has one or two regional hospitals, which makes a<br />
total number of 32 hospitals and 5126 beds for <strong>Tun<strong>is</strong>ia</strong> as a whole.<br />
The tertiary level compr<strong>is</strong>es the university-oriented health facilities which, while<br />
sharing some attributes with first-line and second-line facilities, have as their primary<br />
objective to provide high specialized care, graduate and post-graduate education of<br />
health personnel as well as to develop research in the medical, pharmaceutical and<br />
dental areas.<br />
Almost all of these third-line institutions have the legal status of public health<br />
institutions, as specified in the Health Organization Law and defined in detail in a<br />
specific decree <strong>is</strong>sued on 2 December 1991, granting autonomy to these facilities in<br />
their admin<strong>is</strong>trative and financial management, as with public facilities. They are 20<br />
such institutions. The number of departments in these teaching hospitals <strong>is</strong> 177 with 40<br />
specialties totalling 8305 beds (2002).