- Page 2 and 3: Fragile Lands of Latin America PN-
- Page 4 and 5: Fragile Lands of Latin America Stra
- Page 6 and 7: Contents Foreword, Thomas E. Lovejo
- Page 8 and 9: Contents PART FIVE RESEARCH IN PROG
- Page 10 and 11: x Thomas E. Lovejoy as the genesis
- Page 12 and 13: Acknowledgments This book is a coll
- Page 14 and 15: xvi About the Editor and Contributo
- Page 16 and 17: pJ '-,, Mexico ' '-7 Research Sites
- Page 18 and 19: 2 John 0. Browder opment, and all t
- Page 20 and 21: 4 John 0. Browder Gow fbrther devel
- Page 22 and 23: John 0. Browder Common Themes Three
- Page 24 and 25: 8 John 0. Browder Hecht, Susanna, B
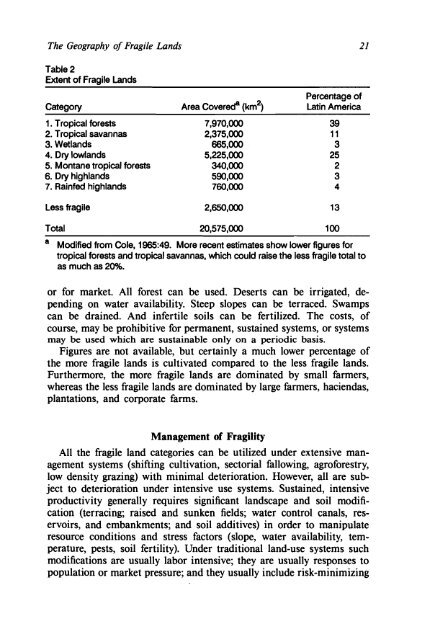
- Page 26 and 27: The Geography of Fragde Lands in La
- Page 28 and 29: Table 1 Categories of Fragile Lands
- Page 30 and 31: Plate 4 Coastal desert, northern Pe
- Page 32 and 33: Figure 1 Map of mountains 1,000-plu
- Page 34 and 35: Figure 3 Map of tropical forests (m
- Page 38 and 39: The Geography of Fragile Lands 23 s
- Page 40 and 41: Development of Fragile Lands: An In
- Page 42 and 43: Development of Fragile Lands 27 pro
- Page 44 and 45: Development of Fragile Lands 29 a b
- Page 46 and 47: Development of Fragile Lands 3 1 Th
- Page 48 and 49: Development of Fragile Lands 33 Ind
- Page 50 and 51: Development of Fragile Lands 35 fra
- Page 52 and 53: Development of Fragile Lands 37 was
- Page 54 and 55: Development of Fragile Lands 39 Tra
- Page 56 and 57: Development of Fragile Lands 41 wer
- Page 58 and 59: Development of Fragile Lands 43 Pie
- Page 60 and 61: nansferring Traditional Technology
- Page 62 and 63: Transferring Traditional Technology
- Page 64 and 65: Transferring Traditional Technology
- Page 66 and 67: Transferring naditional Technology
- Page 68 and 69: Transferring Traditional Technology
- Page 70 and 71: Transfirring Traditional Technology
- Page 72 and 73: Transferring Traditional Technology
- Page 74 and 75: Economic Prospects from Tropical Ra
- Page 76 and 77: Economic Prospects from Tropical Ra
- Page 78 and 79: Economic Prospects from Tropical Ra
- Page 80 and 81: Economic Prospects from Tropical Ra
- Page 82 and 83: Economic Prospects from Tropical Ra
- Page 84 and 85: Economic Prospects from Tropical Ra
- Page 86 and 87:
Economic Prospects from Tropical Ra
- Page 88 and 89:
Agricultural Systems on the Floodpl
- Page 90 and 91:
Agricultural Systems on the Peruvia
- Page 92 and 93:
Agricultural Systems on the Peruvia
- Page 94 and 95:
Agricultural Systems on the Peruvia
- Page 96 and 97:
Table 1 Number of Riberefio Plots b
- Page 98 and 99:
Agricultural Systems on the Peruvia
- Page 100 and 101:
Agricultural Systems on the Peruvia
- Page 102 and 103:
Agricultural Systems on the Peruvia
- Page 104 and 105:
Agricultural Systems on the Peruvia
- Page 106 and 107:
Agricultural Systems on the Peruvia
- Page 108 and 109:
Agricultural Systems on the Peruvia
- Page 110 and 111:
Agricultural Systems on the Peruvia
- Page 112 and 113:
Agricultural Systems on the Peruvia
- Page 114 and 115:
Appendix B Soil Test Data, Selected
- Page 116 and 117:
Production and Profit in Agroforest
- Page 118 and 119:
Prodtccfion and Profit in Agrofwest
- Page 120 and 121:
Production and Profit in Agrofirest
- Page 122 and 123:
Production and ProJit in Agroforest
- Page 124 and 125:
Product ion and Profit in Agrofores
- Page 126 and 127:
Appendix A Santa Rosa Agroforeshy F
- Page 128 and 129:
Costs and Benejts of Floodplain For
- Page 130 and 131:
Costs and Benejts of Floodplain For
- Page 132 and 133:
Costs and Benefits of Floodplain Fo
- Page 134 and 135:
Costs and Benefits of Floodplain Fo
- Page 136 and 137:
Costs and Benejts of Floodplain For
- Page 138 and 139:
Costs and Benefits of Floodplain Fo
- Page 140 and 141:
Appendix A Species with DBH 2 5 crn
- Page 142 and 143:
Appendix B B. 1 Acai Fruit Output (
- Page 144 and 145:
Sustained Yield Management of Natur
- Page 146 and 147:
Sustained Yield Management of Natur
- Page 148 and 149:
Sustained Yield Management of Natur
- Page 150 and 151:
Sustained Yield Management of Natur
- Page 152 and 153:
Cuyabeno Wildlife Production Reserv
- Page 154 and 155:
Cuyabeno WildlifP Production Reserv
- Page 156 and 157:
Cuyabeno Wildlife Production Reserv
- Page 158 and 159:
Cuyabeno Wildlife Production Reserv
- Page 160 and 161:
Cuyabeno Wildlife Production Reserv
- Page 162 and 163:
Cuyabeno Wildlife Production Reserv
- Page 164 and 165:
Extractive Reserves Extractive Rese
- Page 166 and 167:
Extractive Reserves 153 extraction
- Page 168 and 169:
Extractive Reserves Income Generati
- Page 170 and 171:
Extractive Reserves 157 Table 1 Are
- Page 172 and 173:
Extractive Reserves Table 2 Rubber
- Page 174 and 175:
Extractive Reserves 161 embodies th
- Page 176 and 177:
Extractive Reserves 163 Perspective
- Page 178 and 179:
Appendix A (Continued) Tree and Fru
- Page 180 and 181:
Indigenous Soil Management in Amazo
- Page 182 and 183:
Indigenous Soil Management in Amazo
- Page 184 and 185:
Indigenous Soil Management in Amazo
- Page 186 and 187:
Indigenous Soil Management in Amazo
- Page 188 and 189:
Indigenous Soil Management in Amazo
- Page 190 and 191:
Indigenous Soil Management in Amazo
- Page 192 and 193:
Indigenous Soil Management in Amazo
- Page 194 and 195:
Indigenous Soil Management in Amazo
- Page 196 and 197:
An Economic Analysis oj- Huastec Fo
- Page 198 and 199:
An Economic Analysis 01' Huastec Fo
- Page 200 and 201:
Plate 1 A Huastec: farmer, walking
- Page 202 and 203:
An Economic Analysis of Huastec For
- Page 204 and 205:
Table 1 Main Characteristics of Hua
- Page 206 and 207:
An Economic Analysis of Huastec For
- Page 208 and 209:
An Economic Analysis of Huastec For
- Page 210 and 211:
An Economic Analysis of Huastec For
- Page 212 and 213:
An Economic Analysis of Huastec For
- Page 214 and 215:
An Economic Analysis of Huastec For
- Page 216 and 217:
An Economic Analysis of Huastec For
- Page 218 and 219:
Appendix B Value of Huastec Product
- Page 220 and 221:
PART THREE Strategies for Sustainab
- Page 222 and 223:
21 0 John M. Treacy would also curb
- Page 224 and 225:
John M. Treacy Land and Agriculture
- Page 226 and 227:
214 John M. Treacy water. In order
- Page 228 and 229:
John M. Treacy Terraces are invaria
- Page 230 and 231:
218 John M. Treacy Table 1 Crops Pl
- Page 232 and 233:
220 John M. Treacy ancient walls, a
- Page 234 and 235:
222 John M. Treacy Table 2 Per Hect
- Page 236 and 237:
224 John M. Treacy der population p
- Page 238 and 239:
226 John M. Treacy Agricultural ter
- Page 240 and 241:
228 John M. Treacy Morlon, P. B. Or
- Page 242 and 243:
Raised Fields and Sustainable Agric
- Page 244 and 245:
232 Clark L. Erickson and Kay L. Ca
- Page 246 and 247:
234 Clark L. Erickson and Kay L. Ca
- Page 248 and 249:
236 Clark L. Erickson and Kay L. Ca
- Page 250 and 251:
Plate 3 Young potato plants on rais
- Page 252 and 253:
240 Clark L. Erickson and Kay L. Ca
- Page 254 and 255:
242 Clark L. Ericlcron and Kay L. C
- Page 256 and 257:
244 Clark L. Erickson and Kay L. Ca
- Page 258 and 259:
246 Clark L. Erichon and Kay L. Can
- Page 260 and 261:
Clark L. Erickson and Kay L. Candle
- Page 262 and 263:
Arroyos and the Development of Agri
- Page 264 and 265:
Arroyos in Northern Mexico 253 Plat
- Page 266 and 267:
Arroyos in Northern Mexico 255 Plat
- Page 268 and 269:
Arroyos in Northern Mexico 25 7 uns
- Page 270 and 271:
Arroyos in Northern Mexico 259 lowe
- Page 272 and 273:
A rrqvos in Northern Mexico 261 rap
- Page 274 and 275:
Arroyos in Northern Mexico 263 The
- Page 276 and 277:
Arroyos in Northern Mexico 265 fami
- Page 278 and 279:
Arroyos in Northern Mexico 26 7 Doz
- Page 280 and 281:
Arroyos in Northern Mexico 269 Turr
- Page 282 and 283:
Developing the Choc6 Region of Colo
- Page 284 and 285:
Developing the Choc6 Region 275 and
- Page 286 and 287:
Developing the Chocb Region 277 sho
- Page 288 and 289:
Developing the Chocb Region 279 the
- Page 290 and 291:
Socioeconomic Analysis of Agrofores
- Page 292 and 293:
Table 3 Preliminary Financial Asses
- Page 294 and 295:
Socioeconomic Analysis of Agrofores
- Page 296 and 297:
Abaetetuba (Brazil), 119, 120(fig.)
- Page 298 and 299:
Index Biomass, 27, 92, 135 Birds, 1
- Page 300 and 301:
Costa Rica, 277 ?in forest, 61, 134
- Page 302 and 303:
Index Green manure, 234, 241 Green
- Page 304 and 305:
Index Massaranduba latex, 66(table)
- Page 306 and 307:
Index Podocnemis spp. See River tur
- Page 308 and 309:
Index Seeds, 80, 82, 85, 94, 134, 1
- Page 310:
Index Ubu~u, 117 Ucayali River, 79,