Saurischian dinosaurs
Saurischian dinosaurs
Saurischian dinosaurs
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
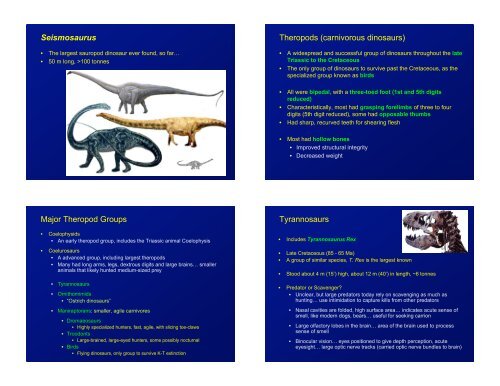
Seismosaurus<br />
• The largest sauropod dinosaur ever found, so far…<br />
• 50 m long, >100 tonnes<br />
Theropods (carnivorous <strong>dinosaurs</strong>)<br />
• A widespread and successful group of <strong>dinosaurs</strong> throughout the late<br />
Triassic to the Cretaceous<br />
• The only group of <strong>dinosaurs</strong> to survive past the Cretaceous, as the<br />
specialized group known as birds<br />
• All were bipedal, with a three-toed foot (1st and 5th digits<br />
reduced)<br />
• Characteristically, most had grasping forelimbs of three to four<br />
digits (5th digit reduced), some had opposable thumbs<br />
• Had sharp, recurved teeth for shearing flesh<br />
• Most had hollow bones<br />
• Improved structural integrity<br />
• Decreased weight<br />
Major Theropod Groups<br />
• Coelophysids<br />
• An early theropod group, includes the Triassic animal Coelophysis<br />
• Coelurosaurs<br />
• A advanced group, including largest theropods<br />
• Many had long arms, legs, dextrous digits and large brains… smaller<br />
animals that likely hunted medium-sized prey<br />
• Tyrannosaurs<br />
• Ornithomimids<br />
• “Ostrich <strong>dinosaurs</strong>”<br />
• Maniraptorans: smaller, agile carnivores<br />
• Dromaeosaurs<br />
• Highly specialized hunters, fast, agile, with slicing toe-claws<br />
• Troodonts<br />
• Large-brained, large-eyed hunters, some possibly nocturnal<br />
• Birds<br />
• Flying <strong>dinosaurs</strong>, only group to survive K-T extinction<br />
Tyrannosaurs<br />
• Includes Tyrannosaurus Rex<br />
• Late Cretaceous (85 - 65 Ma)<br />
• A group of similar species, T. Rex is the largest known<br />
• Stood about 4 m (15’) high, about 12 m (40’) in length, ~6 tonnes<br />
• Predator or Scavenger?<br />
• Unclear, but large predators today rely on scavenging as much as<br />
hunting… use intimidation to capture kills from other predators<br />
• Nasal cavities are folded, high surface area… indicates acute sense of<br />
smell, like modern dogs, bears… useful for seeking carrion<br />
• Large olfactory lobes in the brain… area of the brain used to process<br />
sense of smell<br />
• Binocular vision… eyes positioned to give depth perception, acute<br />
eyesight… large optic nerve tracks (carried optic nerve bundles to brain)