KIT-negative gastrointestinal stromal tumors: proo... - ResearchGate
KIT-negative gastrointestinal stromal tumors: proo... - ResearchGate
KIT-negative gastrointestinal stromal tumors: proo... - ResearchGate
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Medeiros et al Am J Surg Pathol • Volume 28, Number 7, July 2004<br />
FIGURE 1. Epithelioid GIST (A) with <strong>negative</strong> <strong>KIT</strong> immunohistochemistry<br />
(B). Note the positive mast cells.<br />
myosarcoma, melanoma, schwannoma, and carcinoma. Notably,<br />
the cytogenetic profiles obtained in four <strong>tumors</strong> were classic<br />
for GIST. Each of the karyotypes was noncomplex and<br />
featured loss of material from the long arm of chromosome 14,<br />
which is the most frequent cytogenetic aberration in GIST. 10<br />
TABLE 2. Cytogenetic Profiles of Four <strong>KIT</strong>-Negative GISTs<br />
Case<br />
No.<br />
Cytogenetic Profile<br />
1 47,XY,add(1)(p11),add(1)(p13),+8,del(14)(q22),−19,r(19)<br />
(p13q13),add(21)(p11),+mar1<br />
2 43–44,X,−X,i(8)(q10),add(11)(p15),−14,−15,−21,+1–2rings<br />
3 45,XX,add(1)(p32),del(14)(q22p32),−22<br />
5 46,XY,der(1)t(1;13)(p11;q11),der(3)t(1;3)(p32,q11),<br />
+i(8)(q10),−14<br />
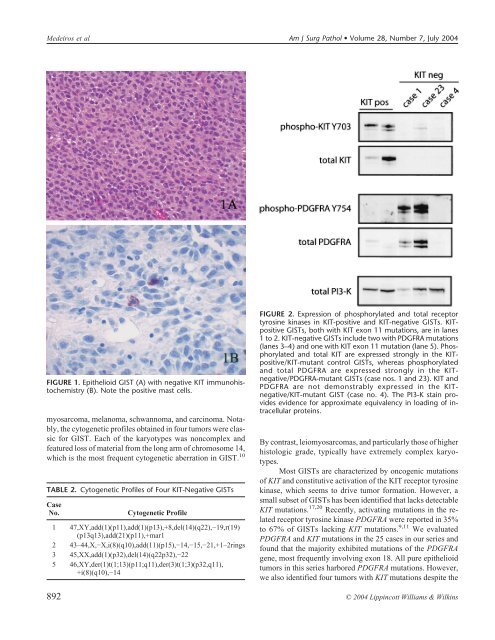
FIGURE 2. Expression of phosphorylated and total receptor<br />
tyrosine kinases in <strong>KIT</strong>-positive and <strong>KIT</strong>-<strong>negative</strong> GISTs. <strong>KIT</strong>positive<br />
GISTs, both with <strong>KIT</strong> exon 11 mutations, are in lanes<br />
1 to 2. <strong>KIT</strong>-<strong>negative</strong> GISTs include two with PDGFRA mutations<br />
(lanes 3–4) and one with <strong>KIT</strong> exon 11 mutation (lane 5). Phosphorylated<br />
and total <strong>KIT</strong> are expressed strongly in the <strong>KIT</strong>positive/<strong>KIT</strong>-mutant<br />
control GISTs, whereas phosphorylated<br />
and total PDGFRA are expressed strongly in the <strong>KIT</strong><strong>negative</strong>/PDGFRA-mutant<br />
GISTs (case nos. 1 and 23). <strong>KIT</strong> and<br />
PDGFRA are not demonstrably expressed in the <strong>KIT</strong><strong>negative</strong>/<strong>KIT</strong>-mutant<br />
GIST (case no. 4). The PI3-K stain provides<br />
evidence for approximate equivalency in loading of intracellular<br />
proteins.<br />
By contrast, leiomyosarcomas, and particularly those of higher<br />
histologic grade, typically have extremely complex karyotypes.<br />
Most GISTs are characterized by oncogenic mutations<br />
of <strong>KIT</strong> and constitutive activation of the <strong>KIT</strong> receptor tyrosine<br />
kinase, which seems to drive tumor formation. However, a<br />
small subset of GISTs has been identified that lacks detectable<br />
<strong>KIT</strong> mutations. 17,20 Recently, activating mutations in the related<br />
receptor tyrosine kinase PDGFRA were reported in 35%<br />
to 67% of GISTs lacking <strong>KIT</strong> mutations. 9,11 We evaluated<br />
PDGFRA and <strong>KIT</strong> mutations in the 25 cases in our series and<br />
found that the majority exhibited mutations of the PDGFRA<br />
gene, most frequently involving exon 18. All pure epithelioid<br />
<strong>tumors</strong> in this series harbored PDGFRA mutations. However,<br />
we also identified four <strong>tumors</strong> with <strong>KIT</strong> mutations despite the<br />
892 © 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins