NX Nastran Dynamic Analysis-4 Days.pub - inno-venture.com
NX Nastran Dynamic Analysis-4 Days.pub - inno-venture.com
NX Nastran Dynamic Analysis-4 Days.pub - inno-venture.com
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
SIEMENS UGS <strong>NX</strong> NASTARN Training<br />
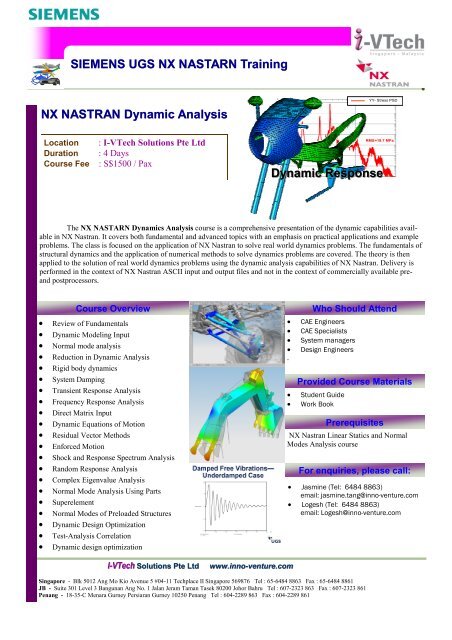
<strong>NX</strong> NASTRAN <strong>Dynamic</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
YY- Stress PSD<br />
Location<br />
Duration<br />
Course Fee<br />
: I-VTech Solutions Pte Ltd<br />
: 4 <strong>Days</strong><br />
: S$1500 / Pax<br />
RMS=19.7 MPa<br />
<strong>Dynamic</strong> Response<br />
The <strong>NX</strong> NASTARN <strong>Dynamic</strong>s <strong>Analysis</strong> course is a <strong>com</strong>prehensive presentation of the dynamic capabilities available<br />
in <strong>NX</strong> <strong>Nastran</strong>. It covers both fundamental and advanced topics with an emphasis on practical applications and example<br />
problems. The class is focused on the application of <strong>NX</strong> <strong>Nastran</strong> to solve real world dynamics problems. The fundamentals of<br />
structural dynamics and the application of numerical methods to solve dynamics problems are covered. The theory is then<br />
applied to the solution of real world dynamics problems using the dynamic analysis capabilities of <strong>NX</strong> <strong>Nastran</strong>. Delivery is<br />
performed in the context of <strong>NX</strong> <strong>Nastran</strong> ASCII input and output files and not in the context of <strong>com</strong>mercially available preand<br />
postprocessors.<br />
Course Overview<br />
• Review of Fundamentals<br />
• <strong>Dynamic</strong> Modeling Input<br />
• Normal mode analysis<br />
• Reduction in <strong>Dynamic</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
• Rigid body dynamics<br />
• System Damping<br />
• Transient Response <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
• Frequency Response <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
• Direct Matrix Input<br />
• <strong>Dynamic</strong> Equations of Motion<br />
• Residual Vector Methods<br />
• Enforced Motion<br />
• Shock and Response Spectrum <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
• Random Response <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
• Complex Eigenvalue <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
• Normal Mode <strong>Analysis</strong> Using Parts<br />
• Superelement<br />
• Normal Modes of Preloaded Structures<br />
• <strong>Dynamic</strong> Design Optimization<br />
• Test-<strong>Analysis</strong> Correlation<br />
• <strong>Dynamic</strong> design optimization<br />
I-VTech<br />
Solutions Pte Ltd<br />
www.<strong>inno</strong>-<strong>venture</strong>.<strong>com</strong><br />
Who Should Attend<br />
• CAE Engineers<br />
• CAE Specialists<br />
• System managers<br />
• Design Engineers<br />
.<br />
Provided Course Materials<br />
• Student Guide<br />
• Work Book<br />
Prerequisites<br />
<strong>NX</strong> <strong>Nastran</strong> Linear Statics and Normal<br />
Modes <strong>Analysis</strong> course<br />
For enquiries, please call:<br />
• Jasmine (Tel: 6484 8863)<br />
email: jasmine.tang@<strong>inno</strong>-<strong>venture</strong>.<strong>com</strong><br />
• Logesh (Tel: 6484 8863)<br />
email: Logesh@<strong>inno</strong>-<strong>venture</strong>.<strong>com</strong><br />
Singapore - Blk 5012 Ang Mo Kio Avenue 5 #04-11 Techplace II Singapore 569876 Tel : 65-6484 8863 Fax : 65-6484 8861<br />
JB - Suite 301 Level 3 Bangunan Ang No. 1 Jalan Jeram Taman Tasek 80200 Johor Bahru Tel : 607-2323 863 Fax : 607-2323 861<br />
Penang - 18-35-C Menara Gurney Persiaran Gurney 10250 Penang Tel : 604-2289 863 Fax : 604-2289 861
SIEMENS UGS <strong>NX</strong> NASTARN Training<br />
<strong>NX</strong> NASTRAN <strong>Dynamic</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
Day 1<br />
Review of Fundamentals<br />
• Review of Fundamentals<br />
• Overview of dynamic analysis process<br />
• Single dof system<br />
• Units<br />
• Single dof system - undamped free vibrations<br />
• Single dof system - damped free vibrations<br />
• Damped free vibrations—underdamped case<br />
• Single dof system - undamped sinusoidal vibrations<br />
• Magnification factor<br />
• Single dof system - damped sinusoidal vibrations<br />
• Magnification factor<br />
• Multi-degree of freedom system<br />
• Classification of dynamic environments<br />
• <strong>Dynamic</strong> excitations<br />
• Finite element dynamic modelling considerations<br />
• Nx nastran documentation<br />
• Text references on dynamic analysis<br />
<strong>Dynamic</strong> Modeling Input<br />
• Nx nastran input file setup<br />
• Nx nastran bulk data entry format<br />
• Finite element analysis<br />
• Commonly used elastic elements<br />
• Coupled versus lumped mass<br />
• Rod finite element<br />
• Justification for nx nastran coupled mass convention<br />
• Mass units<br />
• Mass input<br />
• Conm2<br />
• Basic nx nastran set operations<br />
• Nx nastran set definition<br />
• Tips on model verification<br />
Day 1<br />
Normal Modes <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
• Reasons to <strong>com</strong>pute natural frequencies and normal<br />
modes<br />
• Theoretical results<br />
• Important facts and results regarding<br />
• Normal modes and natural frequencies<br />
• Additional modal properties<br />
• Methods of <strong>com</strong>putation<br />
• Sturm sequence theory<br />
• Lanczos method<br />
• User interface for lanczos method<br />
• User interface for all methods<br />
• Solution control for normal modes<br />
• Case control output<br />
• Workshop #1 - modal analysis of a flat plate<br />
Reduction in <strong>Dynamic</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
• Introduction to dynamic reduction<br />
• Reduction methods for dynamics available with nx<br />
nastran<br />
• Static condensation (internal calculation)<br />
• User interface<br />
• Solution control for guyan reduction<br />
• Difficulties with guyan reduction<br />
• Modal reduction<br />
• Solution control for modal reduction<br />
• Workshop #2 - normal modes analysis using guyan reduction<br />
I-VTech<br />
Solutions Pte Ltd<br />
www.<strong>inno</strong>-<strong>venture</strong>.<strong>com</strong><br />
Singapore - Blk 5012 Ang Mo Kio Avenue 5 #04-11 Techplace II Singapore 569876 Tel : 65-6484 8863 Fax : 65-6484 8861<br />
JB - Suite 301 Level 3 Bangunan Ang No. 1 Jalan Jeram Taman Tasek 80200 Johor Bahru Tel : 607-2323 863 Fax : 607-2323 861<br />
Penang - 18-35-C Menara Gurney Persiaran Gurney 10250 Penang Tel : 604-2289 863 Fax : 604-2289 861
SIEMENS UGS <strong>NX</strong> NASTARN Training<br />
<strong>NX</strong> NASTRAN <strong>Dynamic</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
Rigid Body Modes<br />
Day 2<br />
• Rigid body modes and rigid body vectors –<br />
• Theoretical considerations<br />
• Calculation of rigid body modes<br />
• Selection of “suport” degrees of freedom<br />
• Checking of “suport” degrees of freedom<br />
• Rigid body modes and rigid body vectors<br />
Damping<br />
• Damping<br />
• Structural damping versus viscous damping<br />
• Structural damping versus viscous damping<br />
• (constant displacement<br />
• Damping summary<br />
• Structural damping<br />
• Viscous damping<br />
• Modal damping<br />
• Rayleigh damping<br />
Transient Response <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
• Introduction to transient response analysis<br />
• Direct transient response<br />
• Damping in direct transient response<br />
• Modal transient response<br />
• Damping in modal transient response<br />
• Data recovery in modal transient response<br />
• Mode truncation<br />
• Transient excitation<br />
• Tload1 entry<br />
• Tload2 entry<br />
• Load set <strong>com</strong>bination - dload<br />
Day 2<br />
• Static load – indirect method<br />
• Static load – direct method<br />
• Transient excitation considerations<br />
• Initial conditions<br />
• Modal transient versus direct transient<br />
• Solution control for transient analysis<br />
• Case control output<br />
• Workshop #3 - direct transient response<br />
• Workshop #4 - modal transient response<br />
Frequency Response <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
• Introduction to frequency response analysis<br />
• Direct frequency response<br />
• Modal frequency response<br />
• Excitation definition<br />
• Rload<br />
• Rload2<br />
• Frequency response considerations<br />
• Freqi entries<br />
• <strong>Dynamic</strong> data recovery<br />
• Modal versus direct frequency response<br />
• Sort1 versus sort2 output<br />
• Solution control for frequency response<br />
• Case control output<br />
• Frequency-dependent springs and dampers<br />
• Cbush<br />
• Pbush<br />
• Pbusht<br />
• Frequency-dependent impedance sample<br />
• Sample using cbush element<br />
• Displacement output for cbush element<br />
• Force output for cbush element<br />
• Workshop #5 - direct frequency response<br />
• Workshop #6 - modal frequency response<br />
I-VTech<br />
Solutions Pte Ltd<br />
www.<strong>inno</strong>-<strong>venture</strong>.<strong>com</strong><br />
Singapore - Blk 5012 Ang Mo Kio Avenue 5 #04-11 Techplace II Singapore 569876 Tel : 65-6484 8863 Fax : 65-6484 8861<br />
JB - Suite 301 Level 3 Bangunan Ang No. 1 Jalan Jeram Taman Tasek 80200 Johor Bahru Tel : 607-2323 863 Fax : 607-2323 861<br />
Penang - 18-35-C Menara Gurney Persiaran Gurney 10250 Penang Tel : 604-2289 863 Fax : 604-2289 861
SIEMENS UGS <strong>NX</strong> NASTARN Training<br />
<strong>NX</strong> NASTRAN <strong>Dynamic</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
Day 3<br />
Residual Vector Methods<br />
• Concept of modal approach<br />
• How do i <strong>com</strong>pensate for the missing modal contents<br />
• Residual vector<br />
• User interface for residual vector<br />
• Example<br />
• Input file for using modal method<br />
• With residual vector<br />
• Results <strong>com</strong>parison<br />
• General re<strong>com</strong>mendation<br />
Enforced Motion<br />
• Enforced motion in dynamic analysis<br />
• <strong>Analysis</strong> methods<br />
• Method 1<br />
• Degree of freedom sets<br />
• Basic equations<br />
• Equations for transient response<br />
• Equations for frequency response<br />
• Modal reduction<br />
• User interface<br />
• The type field<br />
• Example: executive and case control decks<br />
• Example: bulk data deck<br />
• Workshop #7 - direct transient response with<br />
• Enforced acceleration<br />
• Workshop #8 – modal transient response<br />
• With enforced acceleration<br />
• Workshop #9 - direct frequency<br />
• Response with enforced displacement<br />
• Workshop #10 - modal frequency<br />
• Response with enforced displacement<br />
Day 3<br />
Shock and Response Spectrum<br />
<strong>Analysis</strong><br />
• Response spectrum<br />
• Response spectrum generation<br />
• Applying spectra<br />
• Workshop #11 – generation of shock spectrum input<br />
• Workshop #12 – application of the shock spectrum<br />
Random Response <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
• Classification of dynamic environments<br />
• Random response analysis<br />
• Random analysis theory<br />
• Examples of random dynamic environments<br />
• Example of ensemble of ergodic random data<br />
• Autocorrelation and autospectrum<br />
• Calculation of linear system response to<br />
• Ergodic random excitation<br />
• Definition of multiple input-output spectral<br />
• Relationship for a linear system<br />
• Random analysis as implemented in nx nastran<br />
• Randps entry<br />
• Tabrnd1 entry<br />
• Input required for random response analysis<br />
• Random analysis re<strong>com</strong>mendations<br />
• Workshop #13 - random response with single input<br />
• Workshop #14 - random response with<br />
• Multiple inputs<br />
I-VTech<br />
Solutions Pte Ltd<br />
www.<strong>inno</strong>-<strong>venture</strong>.<strong>com</strong><br />
Singapore - Blk 5012 Ang Mo Kio Avenue 5 #04-11 Techplace II Singapore 569876 Tel : 65-6484 8863 Fax : 65-6484 8861<br />
JB - Suite 301 Level 3 Bangunan Ang No. 1 Jalan Jeram Taman Tasek 80200 Johor Bahru Tel : 607-2323 863 Fax : 607-2323 861<br />
Penang - 18-35-C Menara Gurney Persiaran Gurney 10250 Penang Tel : 604-2289 863 Fax : 604-2289 861
SIEMENS UGS <strong>NX</strong> NASTARN Training<br />
<strong>NX</strong> NASTRAN <strong>Dynamic</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
Day 4<br />
Complex Eigenvalue <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
• Complex eigenvalue analysis<br />
• Complex eigensolutions - theory<br />
• Complex eigensolutions in nx nastran<br />
• Input required for <strong>com</strong>plex eigenanalysis<br />
• Workshop #12 - <strong>com</strong>plex eigenanalysis<br />
Normal Mode <strong>Analysis</strong> Using Parts<br />
Superelement<br />
• What is a superelement?<br />
• How are parts superelement defined in nx nastran?<br />
• Sample problem - steel stamping<br />
• Model definition for sample problem<br />
• Sample problem - steel stamping superelement 1<br />
• Partitioned solutions<br />
• Theory of static condensation<br />
• Advantages of superelement analysis<br />
• Disadvantages of superelement analysis<br />
• Conventional analysis<br />
• Superelement analysis<br />
• Superposition of partial solutions<br />
• Superelement reduction methods available in<br />
• <strong>Dynamic</strong> analysis<br />
• Degrees of reduction<br />
• Guyan or static reduction<br />
• Comparison of reduction methods<br />
• Advantages of each reduction method<br />
• Calculation of normal modes using<br />
• Static reduction only<br />
• Calculation of normal modes using<br />
• <strong>Dynamic</strong> reduction for superelements<br />
• Senqset<br />
• Spoint<br />
Day 4<br />
• Qset<br />
• Qset1<br />
• Bset<br />
• Bset1<br />
• Cset<br />
• Cset1<br />
• Default cms method “fixed boundary” cms<br />
• Solution by hand<br />
• Solution using nx nastran sol 103<br />
• Output from spring model cms run<br />
YY- Stress PSD<br />
RMS=19.7 MPa<br />
<strong>Dynamic</strong> Response<br />
I-VTech<br />
Solutions Pte Ltd<br />
www.<strong>inno</strong>-<strong>venture</strong>.<strong>com</strong><br />
Singapore - Blk 5012 Ang Mo Kio Avenue 5 #04-11 Techplace II Singapore 569876 Tel : 65-6484 8863 Fax : 65-6484 8861<br />
JB - Suite 301 Level 3 Bangunan Ang No. 1 Jalan Jeram Taman Tasek 80200 Johor Bahru Tel : 607-2323 863 Fax : 607-2323 861<br />
Penang - 18-35-C Menara Gurney Persiaran Gurney 10250 Penang Tel : 604-2289 863 Fax : 604-2289 861
SIEMENS UGS <strong>NX</strong> NASTARN Training<br />
<strong>NX</strong> NASTRAN <strong>Dynamic</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong><br />
Day 4<br />
Normal Modes of Preloaded<br />
Structures<br />
• Normal modes with differential stiffness<br />
• Workshop #14 - normal modes with preload<br />
<strong>Dynamic</strong> Design Optimization<br />
• What is “design optimization”?<br />
• Basic features implemented in nx nastran<br />
• Strengths of nx nastran structural optimization<br />
• Optimization capabilities supported<br />
• Basic optimization problem statement<br />
• Design optimization in nx nastran<br />
• Commonly used optimization bulk data entries<br />
• Workshop #18 - optimization using normal modes<br />
• Direct specification of <strong>com</strong>monly used functions<br />
• Optimization example using frequency response<br />
• Optimization statement<br />
• <strong>Dynamic</strong> load input<br />
• Tabled4 entry for this sample<br />
• <strong>Dynamic</strong> response sensitivity<br />
• Description of the design model<br />
• Workshop #19 - optimization using<br />
• Frequency response<br />
• Results of optimization<br />
• Wheel response<br />
• Driver’s seat response<br />
• Conclusion<br />
Eigen Frequency Hz<br />
Eigen Frequency Hz<br />
1.0E+05<br />
1.0E+04<br />
1.0E+03<br />
1.0E+02<br />
700<br />
700<br />
600<br />
Mode 1<br />
Mode Mode 2 1<br />
600<br />
Mode Mode 3 2<br />
500<br />
500<br />
Mode Mode 4 3<br />
400 1P Mode 4<br />
400 1P<br />
300<br />
300<br />
200<br />
200<br />
100<br />
100<br />
0<br />
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700<br />
0 100 200 Rotational 300Speed 400Hz<br />
500 600 700<br />
Rotational Speed Hz<br />
Total RMS = 537.26<br />
537.92<br />
537.91<br />
1.0E+01<br />
1.0E+00<br />
1.0E-01<br />
1 10 100<br />
1001<br />
FREQUENCY<br />
I-VTech<br />
Solutions Pte Ltd<br />
www.<strong>inno</strong>-<strong>venture</strong>.<strong>com</strong><br />
Singapore - Blk 5012 Ang Mo Kio Avenue 5 #04-11 Techplace II Singapore 569876 Tel : 65-6484 8863 Fax : 65-6484 8861<br />
JB - Suite 301 Level 3 Bangunan Ang No. 1 Jalan Jeram Taman Tasek 80200 Johor Bahru Tel : 607-2323 863 Fax : 607-2323 861<br />
Penang - 18-35-C Menara Gurney Persiaran Gurney 10250 Penang Tel : 604-2289 863 Fax : 604-2289 861