Renormalization Group: Applications in Statistical Physics I-II
Renormalization Group: Applications in Statistical Physics I-II
Renormalization Group: Applications in Statistical Physics I-II
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
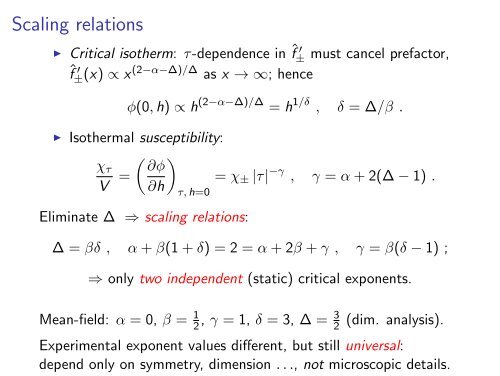
Scal<strong>in</strong>g relations<br />
◮ Critical isotherm: τ-dependence <strong>in</strong> ˆf ′ ± must cancel prefactor,<br />
ˆf ′ ±(x) ∝ x (2−α−∆)/∆ as x → ∞; hence<br />
φ(0, h) ∝ h (2−α−∆)/∆ = h 1/δ , δ = ∆/β .<br />
◮ Isothermal susceptibility:<br />
( )<br />
χ τ ∂φ<br />
V = = χ ± |τ| −γ , γ = α + 2(∆ − 1) .<br />
∂h<br />
τ, h=0<br />
Elim<strong>in</strong>ate ∆ ⇒ scal<strong>in</strong>g relations:<br />
∆ = βδ , α + β(1 + δ) = 2 = α + 2β + γ , γ = β(δ − 1) ;<br />
⇒ only two <strong>in</strong>dependent (static) critical exponents.<br />
Mean-field: α = 0, β = 1 2 , γ = 1, δ = 3, ∆ = 3 2<br />
(dim. analysis).<br />
Experimental exponent values different, but still universal:<br />
depend only on symmetry, dimension . . ., not microscopic details.