forced convection heat transfer from a circular cylinder embedded in ...
forced convection heat transfer from a circular cylinder embedded in ...
forced convection heat transfer from a circular cylinder embedded in ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
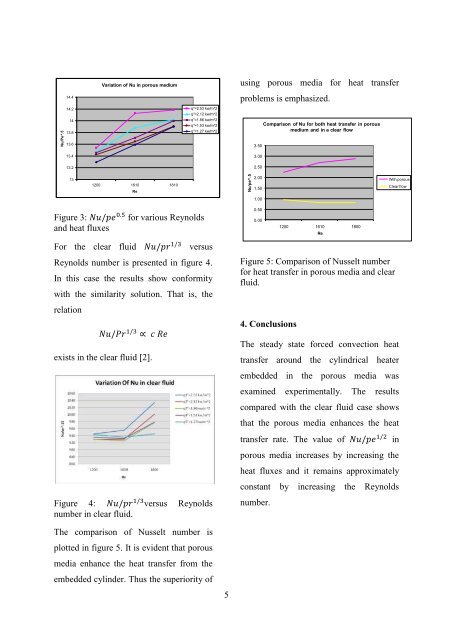
Variation of Nu <strong>in</strong> porous medium<br />
us<strong>in</strong>g porous media for <strong>heat</strong> <strong>transfer</strong><br />
Nu/Pe^.5<br />
14.4<br />
14.2<br />
14<br />
13.8<br />
13.6<br />
q''=2.53 kw/m^2<br />
q''=2.12 kw/m^2<br />
q''=1.86 kw/m^2<br />
q''=1.53 kw/m^2<br />
q''=1.27 kw/m^2<br />
problems is emphasized.<br />
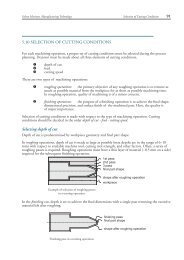
3.50<br />
Comparison of Nu for both <strong>heat</strong> <strong>transfer</strong> <strong>in</strong> porous<br />
medium and <strong>in</strong> a clear flow<br />
13.4<br />
3.00<br />
13.2<br />
2.50<br />
13<br />
1200 1610 1810<br />
Re<br />
Nu/pe^.5<br />
2.00<br />
1.50<br />
1.00<br />
With porous<br />
Clear flow<br />
Figure 3:<br />
and <strong>heat</strong> fluxes<br />
For the clear fluid<br />
for various Reynolds<br />
versus<br />
Reynolds number is presented <strong>in</strong> figure 4.<br />
In this case the results show conformity<br />
with the similarity solution. That is, the<br />
relation<br />
exists <strong>in</strong> the clear fluid [2].<br />
Figure 4: versus Reynolds<br />
number <strong>in</strong> clear fluid.<br />
0.50<br />
0.00<br />
Figure 5: Comparison of Nusselt number<br />
for <strong>heat</strong> <strong>transfer</strong> <strong>in</strong> porous media and clear<br />
fluid.<br />
4. Conclusions<br />
The steady state <strong>forced</strong> <strong>convection</strong> <strong>heat</strong><br />
<strong>transfer</strong> around the cyl<strong>in</strong>drical <strong>heat</strong>er<br />
<strong>embedded</strong> <strong>in</strong> the porous media was<br />
exam<strong>in</strong>ed experimentally. The results<br />
compared with the clear fluid case shows<br />
that the porous media enhances the <strong>heat</strong><br />
<strong>transfer</strong> rate. The value of<br />
porous media <strong>in</strong>creases by <strong>in</strong>creas<strong>in</strong>g the<br />
<strong>heat</strong> fluxes and it rema<strong>in</strong>s approximately<br />
constant by <strong>in</strong>creas<strong>in</strong>g the Reynolds<br />
number.<br />
1200 1610 1800<br />
Re<br />
<strong>in</strong><br />
The comparison of Nusselt number is<br />
plotted <strong>in</strong> figure 5. It is evident that porous<br />
media enhance the <strong>heat</strong> <strong>transfer</strong> <strong>from</strong> the<br />
<strong>embedded</strong> <strong>cyl<strong>in</strong>der</strong>. Thus the superiority of<br />
5