PHD Thesis - Institute for Computer Graphics and Vision - Graz ...
PHD Thesis - Institute for Computer Graphics and Vision - Graz ...
PHD Thesis - Institute for Computer Graphics and Vision - Graz ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
3.3. Affine invariant detectors 30<br />
(a)<br />
(b)<br />
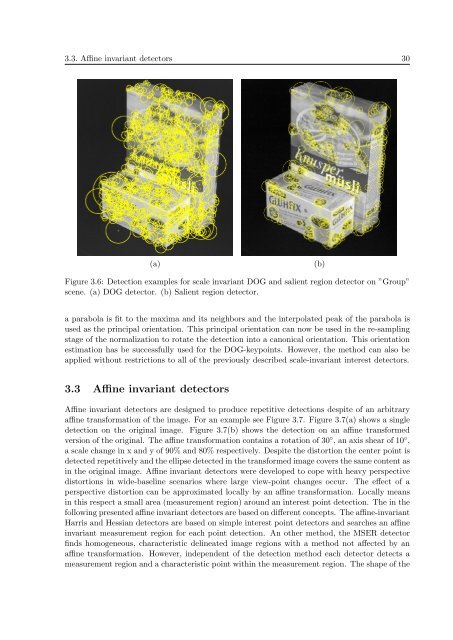
Figure 3.6: Detection examples <strong>for</strong> scale invariant DOG <strong>and</strong> salient region detector on ”Group”<br />
scene. (a) DOG detector. (b) Salient region detector.<br />
a parabola is fit to the maxima <strong>and</strong> its neighbors <strong>and</strong> the interpolated peak of the parabola is<br />
used as the principal orientation. This principal orientation can now be used in the re-sampling<br />
stage of the normalization to rotate the detection into a canonical orientation. This orientation<br />
estimation has be successfully used <strong>for</strong> the DOG-keypoints. However, the method can also be<br />
applied without restrictions to all of the previously described scale-invariant interest detectors.<br />
3.3 Affine invariant detectors<br />
Affine invariant detectors are designed to produce repetitive detections despite of an arbitrary<br />
affine trans<strong>for</strong>mation of the image. For an example see Figure 3.7. Figure 3.7(a) shows a single<br />
detection on the original image. Figure 3.7(b) shows the detection on an affine trans<strong>for</strong>med<br />
version of the original. The affine trans<strong>for</strong>mation contains a rotation of 30 ◦ , an axis shear of 10 ◦ ,<br />
a scale change in x <strong>and</strong> y of 90% <strong>and</strong> 80% respectively. Despite the distortion the center point is<br />
detected repetitively <strong>and</strong> the ellipse detected in the trans<strong>for</strong>med image covers the same content as<br />
in the original image. Affine invariant detectors were developed to cope with heavy perspective<br />
distortions in wide-baseline scenarios where large view-point changes occur. The effect of a<br />
perspective distortion can be approximated locally by an affine trans<strong>for</strong>mation. Locally means<br />
in this respect a small area (measurement region) around an interest point detection. The in the<br />
following presented affine invariant detectors are based on different concepts. The affine-invariant<br />
Harris <strong>and</strong> Hessian detectors are based on simple interest point detectors <strong>and</strong> searches an affine<br />
invariant measurement region <strong>for</strong> each point detection. An other method, the MSER detector<br />
finds homogeneous, characteristic delineated image regions with a method not affected by an<br />
affine trans<strong>for</strong>mation. However, independent of the detection method each detector detects a<br />
measurement region <strong>and</strong> a characteristic point within the measurement region. The shape of the