PHD Thesis - Institute for Computer Graphics and Vision - Graz ...
PHD Thesis - Institute for Computer Graphics and Vision - Graz ...
PHD Thesis - Institute for Computer Graphics and Vision - Graz ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
5.3. Computational complexity 74<br />
6.5<br />
6<br />
a<br />
5.5<br />
a e<br />
5<br />
4.5<br />
b e<br />
4<br />
b<br />
3.5<br />
8 8.5 9 9.5 10 10.5 11 11.5 12<br />
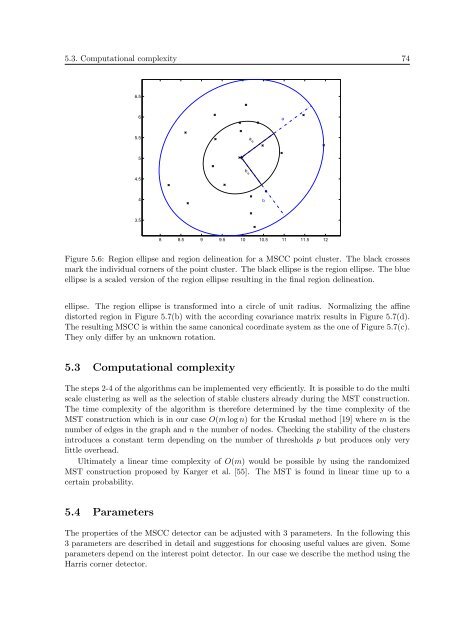
Figure 5.6: Region ellipse <strong>and</strong> region delineation <strong>for</strong> a MSCC point cluster. The black crosses<br />
mark the individual corners of the point cluster. The black ellipse is the region ellipse. The blue<br />
ellipse is a scaled version of the region ellipse resulting in the final region delineation.<br />
ellipse. The region ellipse is trans<strong>for</strong>med into a circle of unit radius. Normalizing the affine<br />
distorted region in Figure 5.7(b) with the according covariance matrix results in Figure 5.7(d).<br />
The resulting MSCC is within the same canonical coordinate system as the one of Figure 5.7(c).<br />
They only differ by an unknown rotation.<br />
5.3 Computational complexity<br />
The steps 2-4 of the algorithms can be implemented very efficiently. It is possible to do the multi<br />
scale clustering as well as the selection of stable clusters already during the MST construction.<br />
The time complexity of the algorithm is there<strong>for</strong>e determined by the time complexity of the<br />
MST construction which is in our case O(m log n) <strong>for</strong> the Kruskal method [19] where m is the<br />
number of edges in the graph <strong>and</strong> n the number of nodes. Checking the stability of the clusters<br />
introduces a constant term depending on the number of thresholds p but produces only very<br />
little overhead.<br />
Ultimately a linear time complexity of O(m) would be possible by using the r<strong>and</strong>omized<br />
MST construction proposed by Karger et al. [55]. The MST is found in linear time up to a<br />
certain probability.<br />
5.4 Parameters<br />
The properties of the MSCC detector can be adjusted with 3 parameters. In the following this<br />
3 parameters are described in detail <strong>and</strong> suggestions <strong>for</strong> choosing useful values are given. Some<br />
parameters depend on the interest point detector. In our case we describe the method using the<br />
Harris corner detector.