Algebra II Curriculum Map - Muskogee Public Schools
Algebra II Curriculum Map - Muskogee Public Schools
Algebra II Curriculum Map - Muskogee Public Schools
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
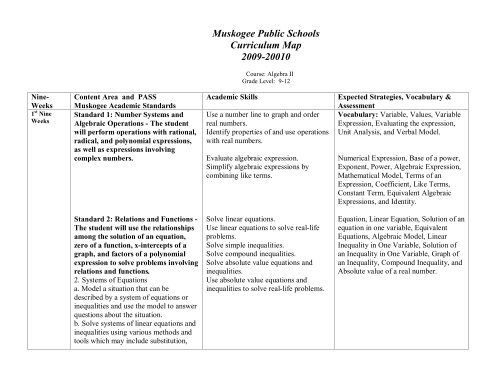
<strong>Muskogee</strong> <strong>Public</strong> <strong>Schools</strong><br />
<strong>Curriculum</strong> <strong>Map</strong><br />
2009-20010<br />
Course: <strong>Algebra</strong> <strong>II</strong><br />
Grade Level: 9-12<br />
Nine-<br />
Weeks<br />
1 st Nine<br />
Weeks<br />
Content Area and PASS<br />
<strong>Muskogee</strong> Academic Standards<br />
Standard 1: Number Systems and<br />
<strong>Algebra</strong>ic Operations - The student<br />
will perform operations with rational,<br />
radical, and polynomial expressions,<br />
as well as expressions involving<br />
complex numbers.<br />
Academic Skills<br />
Use a number line to graph and order<br />
real numbers.<br />
Identify properties of and use operations<br />
with real numbers.<br />
Evaluate algebraic expression.<br />
Simplify algebraic expressions by<br />
combining like terms.<br />
Expected Strategies, Vocabulary &<br />
Assessment<br />
Vocabulary: Variable, Values, Variable<br />
Expression, Evaluating the expression,<br />
Unit Analysis, and Verbal Model.<br />
Numerical Expression, Base of a power,<br />
Exponent, Power, <strong>Algebra</strong>ic Expression,<br />
Mathematical Model, Terms of an<br />
Expression, Coefficient, Like Terms,<br />
Constant Term, Equivalent <strong>Algebra</strong>ic<br />
Expressions, and Identity.<br />
Standard 2: Relations and Functions -<br />
The student will use the relationships<br />
among the solution of an equation,<br />
zero of a function, x-intercepts of a<br />
graph, and factors of a polynomial<br />
expression to solve problems involving<br />
relations and functions.<br />
2. Systems of Equations<br />
a. Model a situation that can be<br />
described by a system of equations or<br />
inequalities and use the model to answer<br />
questions about the situation.<br />
b. Solve systems of linear equations and<br />
inequalities using various methods and<br />
tools which may include substitution,<br />
Solve linear equations.<br />
Use linear equations to solve real-life<br />
problems.<br />
Solve simple inequalities.<br />
Solve compound inequalities.<br />
Solve absolute value equations and<br />
inequalities.<br />
Use absolute value equations and<br />
inequalities to solve real-life problems.<br />
Equation, Linear Equation, Solution of an<br />
equation in one variable, Equivalent<br />
Equations, <strong>Algebra</strong>ic Model, Linear<br />
Inequality in One Variable, Solution of<br />
an Inequality in One Variable, Graph of<br />
an Inequality, Compound Inequality, and<br />
Absolute value of a real number.
Nine-<br />
Weeks<br />
1 st Nine<br />
Weeks<br />
Content Area and PASS<br />
<strong>Muskogee</strong> Academic Standards<br />
elimination, matrices, graphing, and<br />
graphing calculators.<br />
Academic Skills<br />
Expected Strategies, Vocabulary &<br />
Assessment<br />
Standard 2: Relations and Functions -<br />
The student will use the relationships<br />
among the solution of an equation,<br />
zero of a function, x-intercepts of a<br />
graph, and factors of a polynomial<br />
expression to solve problems involving<br />
relations and functions.<br />
1. Functions and Function Notation<br />
b. Add, subtract, multiply, and divide<br />
functions using function notation.<br />
d. Use algebraic, interval, and set<br />
notations to specify the domain and<br />
range of functions of various types.<br />
Represent relations and functions.<br />
Graph and evaluate linear functions.<br />
Use the slope-intercept form of a linear<br />
equation to graph linear equations.<br />
Use the standard form of a linear<br />
equation to graph linear equations.<br />
Write Linear Equations.<br />
Write direct variation equations.<br />
Relation, Domain of a Relation, Range of<br />
a Relation, Function, Ordered Pair,<br />
Coordinate Plane, Equation in Two<br />
Variables, Solution of an Equation in<br />
Two Variables, Independent Variable,<br />
Dependant Variable, Graph of an<br />
Equation in Two Variables, Linear<br />
Function, Function Notation, X and Y-<br />
intercept, Slope-intercept Form, Standard<br />
Form of a Linear Equation, Direct<br />
Variation, and Constant of Variation.<br />
Standard 3: Data Analysis and<br />
Statistics - The student will use data<br />
analysis and statistics to formulate<br />
and justify predictions from a set of<br />
data.<br />
1. Analysis of Collected Data Involving<br />
Two Variables<br />
a. Interpret data on a scatter plot using a<br />
linear, exponential, or quadratic<br />
model/equation.<br />
b. Identify whether the model/equation is<br />
a curve of best fit for the data, using<br />
various methods and tools which may<br />
include a graphing calculator.<br />
Use a scatter plot to identify the<br />
correlation shown by a set of data.<br />
Approximate the best-fitting line for a<br />
set of data.<br />
Scatter Plot, Positive, Negative, and<br />
Relatively No Correlation,<br />
Standard 2: 2 a and b (written above)<br />
Graph linear inequalities in two<br />
variables.<br />
Linear Inequality in Two Variables,<br />
Solution of an Inequality in Two
Nine-<br />
Weeks<br />
1 st Nine<br />
Weeks<br />
Content Area and PASS<br />
<strong>Muskogee</strong> Academic Standards<br />
Academic Skills<br />
Use linear inequalities to solve real-life<br />
problems.<br />
Expected Strategies, Vocabulary &<br />
Assessment<br />
Variables, and Half-planes.<br />
Represent piecewise functions.<br />
Use piecewise functions to model reallife<br />
quantities.<br />
Piecewise Function and Step Function.<br />
Represent absolute value functions.<br />
Use absolute value functions to model<br />
real-life situations.<br />
Vertex of an Absolute Value Graph<br />
Standard 2: 2 a and b (written above)<br />
Graph and solve systems of linear<br />
equations in two variables.<br />
Use linear systems to solve real-life<br />
problems.<br />
Use algebraic methods to solve linear<br />
systems.<br />
Use linear systems to model real-life<br />
situations.<br />
Graph a system of linear inequalities to<br />
find the solutions of the system.<br />
Use systems of linear inequalities to<br />
solve real-life problems.<br />
Solve linear programming problems.<br />
Use linear programming to solve reallife<br />
problems<br />
Graph linear equations in three variables<br />
and evaluate linear functions in two<br />
variables.<br />
Use functions of two variables to model<br />
real-life situations.<br />
Solve systems of linear equations in<br />
three variables.<br />
Use linear systems in three variables to<br />
System of Two Linear Equations,<br />
Solution of a System of Linear Equations,<br />
System of linear inequalities in two<br />
variables, Solution of a system of linear<br />
inequalities, Graph of a system of linear<br />
inequalities, Optimization, Linear<br />
Programming, Objective Function,<br />
Constraints, Feasible Region, Threedimensional<br />
coordinate system, Z-axis,<br />
Ordered Triple, Octants, Linear Equation<br />
in Three Variables, Function of Two<br />
Variables, System of Three Linear<br />
Equations, and Solution of a System of<br />
Three Linear Equations.
Nine-<br />
Weeks<br />
Content Area and PASS<br />
<strong>Muskogee</strong> Academic Standards<br />
Academic Skills<br />
model real-life situations.<br />
Expected Strategies, Vocabulary &<br />
Assessment<br />
2 nd Nine<br />
Weeks<br />
Add and subtract matrices, multiply a<br />
matrix by a scalar, and solve matrix<br />
equations.<br />
Use matrices in real-life situations.<br />
Multiply two matrices.<br />
Use matrix multiplication in real-life<br />
situations.<br />
Evaluate determinants of 2 3 2 and 3 3 3<br />
matrices.<br />
Use Cramer’s rule to solve systems of<br />
linear equations.<br />
Matrix, Dimensions of a Matrix, Entries<br />
of a Matrix, Equal Matrices, Scalar,<br />
Scalar Multiplication, Determinant,<br />
Cramer’s Rule, and Coefficient Matrix.<br />
Standard 2: Relations and Functions -<br />
The student will use the relationships<br />
among the solution of an equation,<br />
zero of a function, x-intercepts of a<br />
graph, and factors of a polynomial<br />
expression to solve problems involving<br />
relations and functions.<br />
1. Functions and Function Notation<br />
a. Recognize the parent graphs of<br />
polynomial, exponential, radical,<br />
quadratic, and logarithmic functions and<br />
predict the effects of transformations on<br />
the parent graphs, using various methods<br />
and tools which may include graphing<br />
calculators.<br />
2. Systems of Equations<br />
a. Model a situation that can be<br />
described by a system of equations or<br />
Graph quadratic functions.<br />
Use quadratic functions to solve real-life<br />
problems.<br />
Quadratic Function, Parabola, Vertex of a<br />
Parabola, Axis of Symmetry of a<br />
Parabola, and Standard Form.
Nine-<br />
Weeks<br />
2 nd Nine<br />
Weeks<br />
Content Area and PASS<br />
<strong>Muskogee</strong> Academic Standards<br />
inequalities and use the model to answer<br />
questions about the situation.<br />
Academic Skills<br />
Expected Strategies, Vocabulary &<br />
Assessment<br />
3. Quadratic Equations and Functions<br />
a. Solve quadratic equations by<br />
graphing, factoring, completing the<br />
square and quadratic formula.<br />
Factor quadratic expressions and solve<br />
quadratic equations by factoring.<br />
Find zeros of quadratic functions.<br />
Solve quadratic equations by finding<br />
square roots.<br />
Use quadratic equations to solve real-life<br />
problems.<br />
Binomial, Trinomial, Factoring,<br />
Monomial, Quadratic Equation in One<br />
Variable, Zero of a Function, Square<br />
Root, Radical Sign, Radicand, Radical,<br />
Rationalizing the Denominator<br />
Standard 1: Number Systems and<br />
<strong>Algebra</strong>ic Operations - The student<br />
will perform operations with rational,<br />
radical, and polynomial expressions,<br />
as well as expressions involving<br />
complex numbers.<br />
3. Complex Numbers<br />
*a. Recognize that to solve certain<br />
problems and equations, number systems<br />
need to be extended from real numbers<br />
to complex numbers.<br />
Note: Asterisks (*) have been used to<br />
identify standards and objectives that<br />
must be assessed by the local school<br />
district. All other skills may be assessed<br />
by the Oklahoma School Testing<br />
Program (OSTP).<br />
b. Add, subtract, multiply, divide, and<br />
simplify expressions involving complex<br />
numbers.<br />
Solve quadratic equations with complex<br />
solutions and perform operations with<br />
complex numbers.<br />
Apply complex numbers to fractal<br />
geometry.<br />
Imaginary Unit i, Complex Number,<br />
Standard Form of a complex number,<br />
Imaginary Number, Pure Imaginary<br />
Number, Complex Plane, Complex<br />
Conjugates, and Absolute Value of a<br />
Complex Number<br />
Standard 2: 3 a (written above)<br />
b. Graph a quadratic function and<br />
Solve quadratic equations by completing<br />
equations the square.<br />
Completing the Square
Nine-<br />
Weeks<br />
Content Area and PASS<br />
<strong>Muskogee</strong> Academic Standards<br />
identify the x- and y-intercepts and<br />
maximum or minimum value, using<br />
various methods and tools which may<br />
include a graphing calculator.<br />
c. Model a situation that can be<br />
described by a quadratic function and<br />
use the model to answer questions about<br />
the situation.<br />
Academic Skills<br />
Use completing the square to write<br />
quadratic functions in vertex form.<br />
Solve quadratic equations using the<br />
quadratic formula.<br />
Use the quadratic formula in real-life<br />
situations.<br />
Graph quadratic inequalities in two<br />
variables.<br />
Solve quadratic inequalities in one<br />
variable.<br />
Expected Strategies, Vocabulary &<br />
Assessment<br />
Discriminant of a Quadratic Equation,<br />
Quadratic Inequality in Two Variables,<br />
and Quadratic Inequality in One<br />
Variable.<br />
Write quadratic functions given<br />
characteristics of their graphs.<br />
Use technology to find quadratic models<br />
for real-life data.<br />
Best-fitting Quadratic Model<br />
Use properties of exponents to evaluate<br />
and simplify expressions involving<br />
powers.<br />
Use exponents and scientific notation to<br />
solve real-life problems.<br />
Scientific Notation<br />
3 rd Nine<br />
Weeks<br />
Standard 1: Number Systems and<br />
<strong>Algebra</strong>ic Operations - The student<br />
will perform operations with rational,<br />
radical, and polynomial expressions,<br />
as well as expressions involving<br />
complex numbers.<br />
2. Polynomial and Rational Expressions<br />
a. Divide polynomial expressions by<br />
lower degree polynomials.<br />
Standard 2: Relations and Functions -<br />
The student will use the relationships<br />
among the solution of an equation,<br />
Evaluate a polynomial function.<br />
Graph a polynomial function.<br />
Add, subtract, and multiply polynomials.<br />
Use polynomial operations in real-life<br />
problems.<br />
Factor polynomial expressions.<br />
Use factoring to solve polynomial<br />
equations.<br />
Divide polynomials and relate the result<br />
to the remainder theorem and the factor<br />
theorem.<br />
Use polynomial division in real-life<br />
Polynomial Function, Leading<br />
Coefficient, Constant Term, Degree,<br />
Standard Form of a Polynomial Function,<br />
End Behavior, Factor by Grouping,<br />
Quadratic Form, Polynomial Long<br />
Division, and Synthetic Division.
Nine-<br />
Weeks<br />
3 rd Nine<br />
Weeks<br />
Content Area and PASS<br />
<strong>Muskogee</strong> Academic Standards<br />
zero of a function, x-intercepts of a<br />
graph, and factors of a polynomial<br />
expression to solve problems involving<br />
relations and functions.<br />
6. Polynomial Equations and Functions<br />
a. Solve polynomial equations using<br />
various methods and tools which may<br />
include factoring and synthetic division.<br />
Academic Skills<br />
problems.<br />
Find the rational zeros of a polynomial<br />
function.<br />
Use polynomial equations to solve reallife<br />
problems.<br />
Expected Strategies, Vocabulary &<br />
Assessment<br />
Use the fundamental theorem of algebra<br />
to determine the number of zeros of a<br />
polynomial function.<br />
Use technology to approximate the real<br />
zeros of a polynomial function.<br />
Repeated solution<br />
c. Given the graph of a polynomial<br />
function, identify the x- and y-intercepts,<br />
relative maximums and relative<br />
minimums, using various methods and<br />
tools which may include a graphing<br />
calculator.<br />
Analyze the graph of a polynomial<br />
function.<br />
Use the graph of a polynomial function<br />
to answer questions about real-life<br />
situations.<br />
Local Maximum and Minimum.<br />
Use finite differences to determine the<br />
degree of a polynomial function that will<br />
fit a set of data.<br />
Use technology to find polynomial<br />
models for real-life data.<br />
Finite Differences<br />
Standard 1: Number Systems and<br />
<strong>Algebra</strong>ic Operations - The student<br />
will perform operations with rational,<br />
radical, and polynomial expressions,<br />
as well as expressions involving<br />
complex numbers.<br />
Evaluate nth roots of real numbers using<br />
both radical notation and rational<br />
exponent notation.<br />
Use nth roots to solve real-life problems.<br />
Use properties of rational exponents to<br />
evaluate and simplify expressions.<br />
Nth Root of A, Index of a Radical,<br />
Simplest Form of Radical, and Like<br />
Radicals.
Nine-<br />
Weeks<br />
3 rd Nine<br />
Weeks<br />
Content Area and PASS<br />
<strong>Muskogee</strong> Academic Standards<br />
1. Rational Exponents<br />
a. Convert expressions from radical<br />
notations to rational exponents and vice<br />
versa.<br />
b. Add, subtract, multiply, divide, and<br />
simplify radical expressions and<br />
expressions containing rational<br />
exponents.<br />
Academic Skills<br />
Use properties of rational exponents to<br />
solve real-life problems.<br />
Expected Strategies, Vocabulary &<br />
Assessment<br />
Standard 2: Relations and Functions -<br />
The student will use the relationships<br />
among the solution of an equation,<br />
zero of a function, x-intercepts of a<br />
graph, and factors of a polynomial<br />
expression to solve problems involving<br />
relations and functions.<br />
1. Functions and Function Notation<br />
b. Add, subtract, multiply, and divide<br />
functions using function notation.<br />
c. Combine functions by composition.<br />
e. Find and graph the inverse of a<br />
function, if it exists.<br />
Perform operations with functions<br />
including power functions.<br />
Use power functions and function<br />
operations to solve real-life problems.<br />
Power Function, Composition, Inverse<br />
Relation, and Inverse Functions<br />
Graph square root and cube root<br />
functions.<br />
Use square root and cube root functions<br />
to find real-life quantities.<br />
Radical Function<br />
Standard 1:1 a and b (written above)<br />
Solve equations that contain radicals or<br />
rational exponents.<br />
Use radical equations to solve real-life<br />
problems.<br />
Extraneous Solution<br />
Standard 3: Data Analysis and<br />
Use measures of central tendency and<br />
Statistics, Mean, Median, Mode,
Nine-<br />
Weeks<br />
Content Area and PASS<br />
<strong>Muskogee</strong> Academic Standards<br />
Statistics - The student will use data<br />
analysis and statistics to formulate<br />
and justify predictions from a set of<br />
data.<br />
* 2. Measures of Central Tendency and<br />
Variability<br />
a. Analyze and synthesize data from a<br />
sample using appropriate measures of<br />
central tendency (mean, median, mode,<br />
weighted average).<br />
b. Analyze and synthesize data from a<br />
sample using appropriate measures of<br />
variability (range, variance, standard<br />
deviation).<br />
Academic Skills<br />
measures of dispersion to describe data<br />
sets.<br />
Use box-and-whisker plots and<br />
histograms to represent data graphically.<br />
Expected Strategies, Vocabulary &<br />
Assessment<br />
Measures of Dispersion, Range of Data<br />
Values, Standard Deviation, Box-and-<br />
Whisker Plot, Lower and Upper Quartile,<br />
Histogram, Frequency of Data Values,<br />
and Frequency Distribution.<br />
Standard 2: Relations and Functions -<br />
The student will use the relationships<br />
among the solution of an equation,<br />
zero of a function, x-intercepts of a<br />
graph, and factors of a polynomial<br />
expression to solve problems involving<br />
relations and functions.<br />
5. Exponential and Logarithmic<br />
Functions<br />
a. Graph exponential and logarithmic<br />
functions.<br />
Graph exponential growth functions.<br />
Use exponential growth functions to<br />
model real-life situations.<br />
Graph exponential decay functions.<br />
Use exponential decay functions to<br />
model real-life situations.<br />
Use the number e as the base of<br />
exponential functions.<br />
Use the natural base e in real-life<br />
situations.<br />
Evaluate logarithmic functions.<br />
Graph logarithmic functions.<br />
Use properties of logarithms.<br />
Use properties of logarithms to solve<br />
real-life problems.<br />
Exponent Function, Asymptote,<br />
Exponential Growth Function, Growth<br />
Factor, Exponential Decay Function,<br />
Decay Factor, Common and Natural<br />
Logarithm
Nine-<br />
Weeks<br />
4 th Nine<br />
Weeks<br />
Content Area and PASS<br />
<strong>Muskogee</strong> Academic Standards<br />
Academic Skills<br />
Expected Strategies, Vocabulary &<br />
Assessment<br />
Standard 1: Number Systems and<br />
<strong>Algebra</strong>ic Operations - The student<br />
will perform operations with rational,<br />
radical, and polynomial expressions,<br />
as well as expressions involving<br />
complex numbers.<br />
1. Rational Exponents<br />
a. Convert expressions from radical<br />
notations to rational exponents and vice<br />
versa.<br />
b. Add, subtract, multiply, divide, and<br />
simplify radical expressions and<br />
expressions containing rational<br />
exponents.<br />
2. Polynomial and Rational Expressions<br />
a. Divide polynomial expressions by<br />
lower degree polynomials.<br />
b. Add, subtract, multiply, divide, and<br />
simplify rational expressions, including<br />
complex fractions.<br />
3. Complex Numbers<br />
*a. Recognize that to solve certain<br />
problems and equations, number systems<br />
need to be extended from real numbers<br />
to complex numbers.<br />
Note: Asterisks (*) have been used to<br />
identify standards and objectives that<br />
must be assessed by the local school<br />
district. All other skills may be assessed<br />
by the Oklahoma School Testing
Nine-<br />
Weeks<br />
4 th Nine<br />
Weeks<br />
Content Area and PASS<br />
<strong>Muskogee</strong> Academic Standards<br />
Program (OSTP).<br />
b. Add, subtract, multiply, divide, and<br />
simplify expressions involving complex<br />
numbers.<br />
Academic Skills<br />
Expected Strategies, Vocabulary &<br />
Assessment<br />
Standard 2: Relations and Functions -<br />
The student will use the relationships<br />
among the solution of an equation,<br />
zero of a function, x-intercepts of a<br />
graph, and factors of a polynomial<br />
expression to solve problems involving<br />
relations and functions.<br />
1. Functions and Function Notation<br />
a. Recognize the parent graphs of<br />
polynomial, exponential, radical,<br />
quadratic, and logarithmic functions and<br />
predict the effects of transformations on<br />
the parent graphs, using various methods<br />
and tools which may include graphing<br />
calculators.<br />
b. Add, subtract, multiply, and divide<br />
functions using function notation.<br />
c. Combine functions by composition.<br />
d. Use algebraic, interval, and set<br />
notations to specify the domain and<br />
range of functions of various types.<br />
e. Find and graph the inverse of a<br />
function, if it exists.<br />
2. Systems of Equations<br />
a. Model a situation that can be<br />
described by a system of equations or<br />
inequalities and use the model to answer<br />
questions about the situation.<br />
b. Solve systems of linear equations and
Nine-<br />
Weeks<br />
Content Area and PASS<br />
<strong>Muskogee</strong> Academic Standards<br />
inequalities using various methods and<br />
tools which may include substitution,<br />
elimination, matrices, graphing, and<br />
graphing calculators.<br />
*c. Use either one quadratic equation<br />
and one linear equation or two quadratic<br />
equations to solve problems.<br />
3. Quadratic Equations and Functions<br />
a. Solve quadratic equations by<br />
graphing, factoring, completing the<br />
square and quadratic formula.<br />
b. Graph a quadratic function and<br />
identify the x- and y-intercepts and<br />
maximum or minimum value, using<br />
various methods and tools which may<br />
include a graphing calculator.<br />
c. Model a situation that can be<br />
described by a quadratic function and<br />
use the model to answer questions about<br />
the situation.<br />
4. Identify, graph, and write the<br />
equations of the conic sections (circle,<br />
ellipse, parabola, and hyperbola).<br />
5. Exponential and Logarithmic<br />
Functions<br />
a. Graph exponential and logarithmic<br />
functions.<br />
b. Apply the inverse relationship<br />
between exponential and logarithmic<br />
functions to convert from one form to<br />
another.<br />
c. Model a situation that can be<br />
described by an exponential or<br />
logarithmic function and use the model<br />
Academic Skills<br />
Expected Strategies, Vocabulary &<br />
Assessment
Nine-<br />
Weeks<br />
Content Area and PASS<br />
<strong>Muskogee</strong> Academic Standards<br />
to answer questions about the situation.<br />
6. Polynomial Equations and Functions<br />
a. Solve polynomial equations using<br />
various methods and tools which may<br />
include factoring and synthetic division.<br />
b. Sketch the graph of a polynomial<br />
function.<br />
c. Given the graph of a polynomial<br />
function, identify the x- and y-intercepts,<br />
relative maximums and relative<br />
minimums, using various methods and<br />
tools which may include a graphing<br />
calculator.<br />
d. Model a situation that can be<br />
described by a polynomial function and<br />
use the model to answer questions about<br />
the situation.<br />
7. Rational Equations and Functions<br />
a. Solve rational equations.<br />
b. Sketch the graph of a rational<br />
function. c. Given the graph of a rational<br />
function, identify the x- and y-intercepts,<br />
vertical asymptotes, using various<br />
methods and tools which may include a<br />
graphing calculator.<br />
d. Model a situation that can be<br />
described by a rational function and use<br />
the model to answer questions about the<br />
situation.<br />
Academic Skills<br />
Expected Strategies, Vocabulary &<br />
Assessment<br />
Standard 3: Data Analysis and<br />
Statistics - The student will use data<br />
analysis and statistics to formulate<br />
and justify predictions from a set of
Nine-<br />
Weeks<br />
Content Area and PASS<br />
<strong>Muskogee</strong> Academic Standards<br />
data.<br />
1. Analysis of Collected Data Involving<br />
Two Variables<br />
a. Interpret data on a scatter plot using a<br />
linear, exponential, or quadratic<br />
model/equation.<br />
b. Identify whether the model/equation is<br />
a curve of best fit for the data, using<br />
various methods and tools which may<br />
include a graphing calculator.<br />
* 2. Measures of Central Tendency and<br />
Variability<br />
a. Analyze and synthesize data from a<br />
sample using appropriate measures of<br />
central tendency (mean, median, mode,<br />
weighted average).<br />
b. Analyze and synthesize data from a<br />
sample using appropriate measures of<br />
variability (range, variance, standard<br />
deviation).<br />
c. Use the characteristics of the Gaussian<br />
normal distribution (bell-shaped curve)<br />
to solve problems.<br />
d. Identify how given outliers affect<br />
representations of data.<br />
3. Identify and use arithmetic and<br />
geometric sequences and series to solve<br />
problems.<br />
Academic Skills<br />
Expected Strategies, Vocabulary &<br />
Assessment
Nine-<br />
Weeks<br />
Content Area and PASS<br />
<strong>Muskogee</strong> Academic Standards<br />
Academic Skills<br />
Expected Strategies, Vocabulary &<br />
Assessment