Building automation â impact on energy efficiency - Siemens ...
Building automation â impact on energy efficiency - Siemens ...
Building automation â impact on energy efficiency - Siemens ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
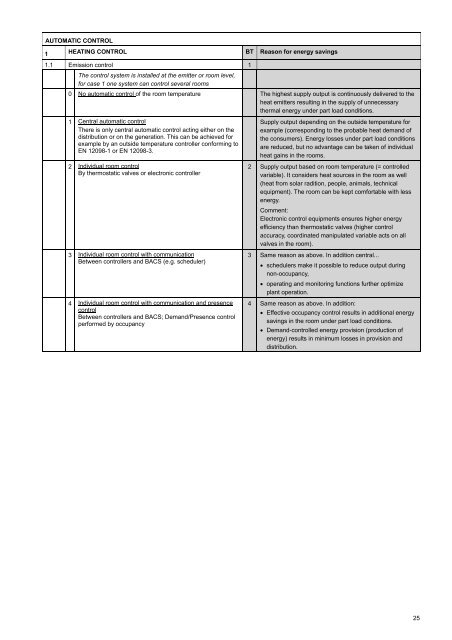
AUTOMATIC CONTROL<br />
1 HEATING CONTROL BT Reas<strong>on</strong> for <strong>energy</strong> savings<br />
1.1 Emissi<strong>on</strong> c<strong>on</strong>trol 1<br />
The c<strong>on</strong>trol system is installed at the emitter or room level,<br />
for case 1 <strong>on</strong>e system can c<strong>on</strong>trol several rooms<br />
0 No automatic c<strong>on</strong>trol of the room temperature The highest supply output is c<strong>on</strong>tinuously delivered to the<br />
heat emitters resulting in the supply of unnecessary<br />
thermal <strong>energy</strong> under part load c<strong>on</strong>diti<strong>on</strong>s.<br />
1 Central automatic c<strong>on</strong>trol<br />
There is <strong>on</strong>ly central automatic c<strong>on</strong>trol acting either <strong>on</strong> the<br />
distributi<strong>on</strong> or <strong>on</strong> the generati<strong>on</strong>. This can be achieved for<br />
example by an outside temperature c<strong>on</strong>troller c<strong>on</strong>forming to<br />
EN 12098-1 or EN 12098-3.<br />
2 Individual room c<strong>on</strong>trol<br />
By thermostatic valves or electr<strong>on</strong>ic c<strong>on</strong>troller<br />
3 Individual room c<strong>on</strong>trol with communicati<strong>on</strong><br />
Between c<strong>on</strong>trollers and BACS (e.g. scheduler)<br />
4 Individual room c<strong>on</strong>trol with communicati<strong>on</strong> and presence<br />
c<strong>on</strong>trol<br />
Between c<strong>on</strong>trollers and BACS; Demand/Presence c<strong>on</strong>trol<br />
performed by occupancy<br />
Supply output depending <strong>on</strong> the outside temperature for<br />
example (corresp<strong>on</strong>ding to the probable heat demand of<br />
the c<strong>on</strong>sumers). Energy losses under part load c<strong>on</strong>diti<strong>on</strong>s<br />
are reduced, but no advantage can be taken of individual<br />
heat gains in the rooms.<br />
2 Supply output based <strong>on</strong> room temperature (= c<strong>on</strong>trolled<br />
variable). It c<strong>on</strong>siders heat sources in the room as well<br />
(heat from solar raditi<strong>on</strong>, people, animals, technical<br />
equipment). The room can be kept comfortable with less<br />
<strong>energy</strong>.<br />
Comment:<br />
Electr<strong>on</strong>ic c<strong>on</strong>trol equipments ensures higher <strong>energy</strong><br />
<strong>efficiency</strong> than thermostatic valves (higher c<strong>on</strong>trol<br />
accuracy, coordinated manipulated variable acts <strong>on</strong> all<br />
valves in the room).<br />
3 Same reas<strong>on</strong> as above. In additi<strong>on</strong> central...<br />
• schedulers make it possible to reduce output during<br />
n<strong>on</strong>-occupancy,<br />
• operating and m<strong>on</strong>itoring functi<strong>on</strong>s further optimize<br />
plant operati<strong>on</strong>.<br />
4 Same reas<strong>on</strong> as above. In additi<strong>on</strong>:<br />
• Effective occupancy c<strong>on</strong>trol results in additi<strong>on</strong>al <strong>energy</strong><br />
savings in the room under part load c<strong>on</strong>diti<strong>on</strong>s.<br />
• Demand-c<strong>on</strong>trolled <strong>energy</strong> provisi<strong>on</strong> (producti<strong>on</strong> of<br />
<strong>energy</strong>) results in minimum losses in provisi<strong>on</strong> and<br />
distributi<strong>on</strong>.<br />
25