Conducting Rubric Student Self-Assessment - band4me
Conducting Rubric Student Self-Assessment - band4me
Conducting Rubric Student Self-Assessment - band4me
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
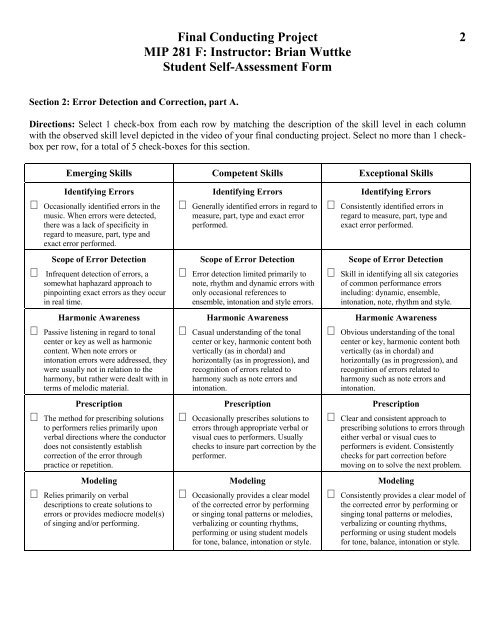
Final <strong>Conducting</strong> Project 2<br />
MIP 281 F: Instructor: Brian Wuttke<br />
<strong>Student</strong> <strong>Self</strong>-<strong>Assessment</strong> Form<br />
Section 2: Error Detection and Correction, part A.<br />
Directions: Select 1 check-box from each row by matching the description of the skill level in each column<br />
with the observed skill level depicted in the video of your final conducting project. Select no more than 1 checkbox<br />
per row, for a total of 5 check-boxes for this section.<br />
Emerging Skills Competent Skills Exceptional Skills<br />
Identifying Errors<br />
Occasionally identified errors in the<br />
music. When errors were detected,<br />
there was a lack of specificity in<br />
regard to measure, part, type and<br />
exact error performed.<br />
Scope of Error Detection<br />
Infrequent detection of errors, a<br />
somewhat haphazard approach to<br />
pinpointing exact errors as they occur<br />
in real time.<br />
Harmonic Awareness<br />
Passive listening in regard to tonal<br />
center or key as well as harmonic<br />
content. When note errors or<br />
intonation errors were addressed, they<br />
were usually not in relation to the<br />
harmony, but rather were dealt with in<br />
terms of melodic material.<br />
Prescription<br />
The method for prescribing solutions<br />
to performers relies primarily upon<br />
verbal directions where the conductor<br />
does not consistently establish<br />
correction of the error through<br />
practice or repetition.<br />
Modeling<br />
Relies primarily on verbal<br />
descriptions to create solutions to<br />
errors or provides mediocre model(s)<br />
of singing and/or performing.<br />
Identifying Errors<br />
Generally identified errors in regard to<br />
measure, part, type and exact error<br />
performed.<br />
Scope of Error Detection<br />
Error detection limited primarily to<br />
note, rhythm and dynamic errors with<br />
only occasional references to<br />
ensemble, intonation and style errors.<br />
Harmonic Awareness<br />
Casual understanding of the tonal<br />
center or key, harmonic content both<br />
vertically (as in chordal) and<br />
horizontally (as in progression), and<br />
recognition of errors related to<br />
harmony such as note errors and<br />
intonation.<br />
Prescription<br />
Occasionally prescribes solutions to<br />
errors through appropriate verbal or<br />
visual cues to performers. Usually<br />
checks to insure part correction by the<br />
performer.<br />
Modeling<br />
Occasionally provides a clear model<br />
of the corrected error by performing<br />
or singing tonal patterns or melodies,<br />
verbalizing or counting rhythms,<br />
performing or using student models<br />
for tone, balance, intonation or style.<br />
Identifying Errors<br />
Consistently identified errors in<br />
regard to measure, part, type and<br />
exact error performed.<br />
Scope of Error Detection<br />
Skill in identifying all six categories<br />
of common performance errors<br />
including: dynamic, ensemble,<br />
intonation, note, rhythm and style.<br />
Harmonic Awareness<br />
Obvious understanding of the tonal<br />
center or key, harmonic content both<br />
vertically (as in chordal) and<br />
horizontally (as in progression), and<br />
recognition of errors related to<br />
harmony such as note errors and<br />
intonation.<br />
Prescription<br />
Clear and consistent approach to<br />
prescribing solutions to errors through<br />
either verbal or visual cues to<br />
performers is evident. Consistently<br />
checks for part correction before<br />
moving on to solve the next problem.<br />
Modeling<br />
Consistently provides a clear model of<br />
the corrected error by performing or<br />
singing tonal patterns or melodies,<br />
verbalizing or counting rhythms,<br />
performing or using student models<br />
for tone, balance, intonation or style.