Chapter 2 Introduction to Neural network
Chapter 2 Introduction to Neural network
Chapter 2 Introduction to Neural network
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
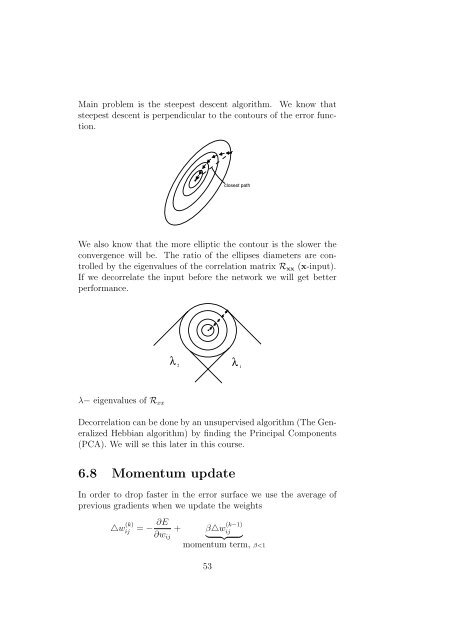
Main problem is the steepest descent algorithm. We know that<br />
steepest descent is perpendicular <strong>to</strong> the con<strong>to</strong>urs of the error function.<br />
closest path<br />
We also know that the more elliptic the con<strong>to</strong>ur is the slower the<br />
convergence will be. The ratio of the ellipses diameters are controlled<br />
by the eigenvalues of the correlation matrix R xx (x-input).<br />
If we decorrelate the input before the <strong>network</strong> we will get better<br />
performance.<br />
λ<br />
2 λ<br />
1<br />
λ− eigenvalues of R xx<br />
Decorrelation can be done by an unsupervised algorithm (The Generalized<br />
Hebbian algorithm) by finding the Principal Components<br />
(PCA). We will se this later in this course.<br />
6.8 Momentum update<br />
In order <strong>to</strong> drop faster in the error surface we use the average of<br />
previous gradients when we update the weights<br />
△w (k)<br />
ij<br />
= − ∂E + β△w (k−1)<br />
ij<br />
∂w ij } {{ }<br />
momentum term, β