Oxygen sensor monitoring a deterioration of a three-way ... - UMEL
Oxygen sensor monitoring a deterioration of a three-way ... - UMEL
Oxygen sensor monitoring a deterioration of a three-way ... - UMEL
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
8 K. Moriya, T. Sako / Sensors and Actuators B 3646 (2000) 1–10<br />
Table 6<br />
Relationship between the performance <strong>of</strong> the system and the <strong>sensor</strong> degradation<br />
Sensor type Engine Time (h) (Abnormal: (); normal: (*))<br />
Sensor condition<br />
System performance<br />
a2 OZA-25F MAN-MSG12V12E 10650 * <br />
a3 OZA-25F MAN-MSG12V12E 16590 * *<br />
a4 OZA-25F CAT-3408CTA 2784 * *<br />
a5 OZA-25F WA-L5108GSI 2228 * *<br />
b2 OZA-21F KOM-SA6N170 3483 * *<br />
b3 OZA-21F CAT-3408CTA 3081 <br />
b4 OZA-21F CAT-3408CTA 3000 <br />
b5 OZA-21F KOM-SA6N170 12899 <br />
c2 OZA-31F WA-L5108GSI 5 * <br />
c3 OZA-31F KOM-SA6N170 2237 * <br />
c4 OZA-31F CAT-3408CTA 545 <br />
c5 OZA-31F MAN-MSG12V12E 860 <br />
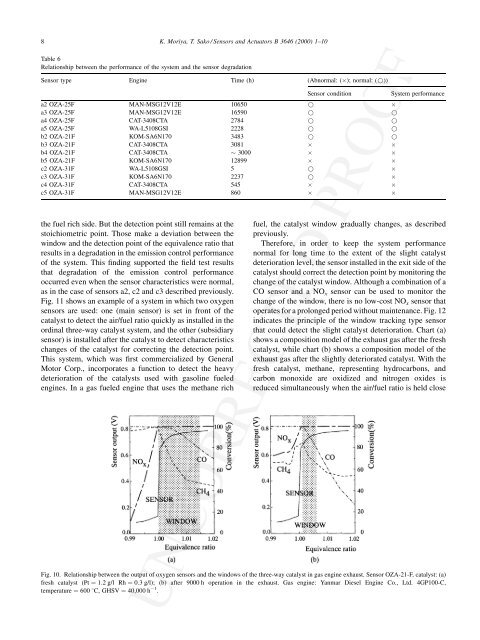
the fuel rich side. But the detection point still remains at the<br />
stoichiometric point. Those make a deviation between the<br />
window and the detection point <strong>of</strong> the equivalence ratio that<br />
results in a degradation in the emission control performance<br />
<strong>of</strong> the system. This finding supported the field test results<br />
that degradation <strong>of</strong> the emission control performance<br />
occurred even when the <strong>sensor</strong> characteristics were normal,<br />
as in the case <strong>of</strong> <strong>sensor</strong>s a2, c2 and c3 described previously.<br />
Fig. 11 shows an example <strong>of</strong> a system in which two oxygen<br />
<strong>sensor</strong>s are used: one (main <strong>sensor</strong>) is set in front <strong>of</strong> the<br />
catalyst to detect the air/fuel ratio quickly as installed in the<br />
ordinal <strong>three</strong>-<strong>way</strong> catalyst system, and the other (subsidiary<br />
<strong>sensor</strong>) is installed after the catalyst to detect characteristics<br />
changes <strong>of</strong> the catalyst for correcting the detection point.<br />
This system, which was first commercialized by General<br />
Motor Corp., incorporates a function to detect the heavy<br />
<strong>deterioration</strong> <strong>of</strong> the catalysts used with gasoline fueled<br />
engines. In a gas fueled engine that uses the methane rich<br />
fuel, the catalyst window gradually changes, as described<br />
previously.<br />
Therefore, in order to keep the system performance<br />
normal for long time to the extent <strong>of</strong> the slight catalyst<br />
<strong>deterioration</strong> level, the <strong>sensor</strong> installed in the exit side <strong>of</strong> the<br />
catalyst should correct the detection point by <strong>monitoring</strong> the<br />
change <strong>of</strong> the catalyst window. Although a combination <strong>of</strong> a<br />
CO <strong>sensor</strong> and a NO x <strong>sensor</strong> can be used to monitor the<br />
change <strong>of</strong> the window, there is no low-cost NO x <strong>sensor</strong> that<br />
operates for a prolonged period without maintenance. Fig. 12<br />
indicates the principle <strong>of</strong> the window tracking type <strong>sensor</strong><br />
that could detect the slight catalyst <strong>deterioration</strong>. Chart (a)<br />
shows a composition model <strong>of</strong> the exhaust gas after the fresh<br />
catalyst, while chart (b) shows a composition model <strong>of</strong> the<br />
exhaust gas after the slightly deteriorated catalyst. With the<br />
fresh catalyst, methane, representing hydrocarbons, and<br />
carbon monoxide are oxidized and nitrogen oxides is<br />
reduced simultaneously when the air/fuel ratio is held close<br />
Fig. 10. Relationship between the output <strong>of</strong> oxygen <strong>sensor</strong>s and the windows <strong>of</strong> the <strong>three</strong>-<strong>way</strong> catalyst in gas engine exhaust. Sensor OZA-21-F, catalyst: (a)<br />
fresh catalyst (Pt ¼ 1:2 g/l Rh ¼ 0:3 g/l); (b) after 9000 h operation in the exhaust. Gas engine: Yanmar Diesel Engine Co., Ltd. 4GP100-C,<br />
temperature ¼ 600 8C, GHSV ¼ 40;000 h 1 .<br />
UNCORRECTED PROOF