Opportunities and Challenges - EBCL - Eu.com
Opportunities and Challenges - EBCL - Eu.com
Opportunities and Challenges - EBCL - Eu.com
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Language Futures: Languages in Higher Education Conference 2012<strong>Eu</strong>ropean Benchmarking Chinese Language– <strong>Opportunities</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Challenges</strong>Lianyi Song, Lik Suen <strong>and</strong> Liang WangSOAS, University of London
<strong>EBCL</strong> project background Increasing dem<strong>and</strong> <strong>and</strong> provision for Chinese languagein <strong>Eu</strong>rope (<strong>and</strong> beyond)- Does the fast expansion in terms of numbers (quantity)ensure the quality of delivery? Need for consistency <strong>and</strong> st<strong>and</strong>ardisation in Chineselanguage learning, teaching <strong>and</strong> assessment Shared interest from colleagues <strong>and</strong> institutionsUniversity of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 20122
CEFR impact <strong>Eu</strong>ropean context –pluralingual in amulticultural <strong>Eu</strong>rope(<strong>Eu</strong>ropean citizens)International A framework for<strong>Eu</strong>ropean languages orfor languages used in<strong>Eu</strong>rope (e.g. Japanese,Chinese)?Day of <strong>Eu</strong>ropean Languages?University of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 20123
From CEFR to <strong>EBCL</strong>Common <strong>Eu</strong>ropean Frameworkof Reference for Languages:Learning, teaching assessment(2001)<strong>Eu</strong>ropean BenchmarkingChinese Language Project(Nov 2010)http://ebcl.eu.<strong>com</strong>/University of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 20124
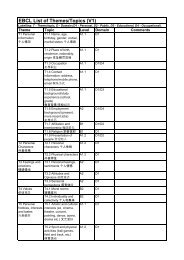
CEFR/<strong>EBCL</strong> feature – 14 domains Personal Public Educational Occupational3 contexts Formal Informal Non-formal 6 key languageproficiency levelsProficientuserIndependentuserBasicuserUniversity of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 20125
CEFR/<strong>EBCL</strong> feature – 2 Action-oriented Can-do statements (‘what’ vs. ‘how’) Global scales+ illustrativedescriptors Assessor+ assesseeUniversity of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 20126
CEFR/<strong>EBCL</strong> feature – 3Communicative activities <strong>and</strong> <strong>com</strong>municationstrategiesReception(Spoken/Written)Production(Spoken/Written)Interaction(Spoken/Written)University of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 20127
CEFR/<strong>EBCL</strong> <strong>com</strong>petence range (adapted from Zhang 2011)CEFC2Can-doStatementsTextsNotions <strong>and</strong> functionsembedded in socio-cultural contextsNotionsC1B2B1A2OperationsEventsObjectsPersonsInstitutionTopicsThemesTopicsNotionsNotionsNotionsNotionsA1 Location Functions Sub-functions FunctionsDomains Personal Public Educational OccupationalUniversity of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 20128
<strong>EBCL</strong> project objectivesTo propose a framework of<strong>com</strong>petence descriptors forChinese in <strong>Eu</strong>ropean contextTo raise awareness of sociocultural<strong>and</strong> linguistic differencesbetween Chinese <strong>and</strong> <strong>Eu</strong>ropeanlanguages<strong>EBCL</strong> ProjectTo create a network in <strong>Eu</strong>rope<strong>and</strong> beyond for teachers <strong>and</strong>institutions concernedTo start a dynamic database ofuniversities (<strong>and</strong> other institutions)in <strong>Eu</strong>rope that offer Chineselanguage coursesUniversity of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 20129
<strong>EBCL</strong> project partnersFreieUniversityBerlinRennes IILaSapienza SOASGE FR IT UKGE FR IT UKProject partnersAssociated schoolsAdvisory BoardUniversity of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 201210
<strong>EBCL</strong> project methodology Intuitive, qualitative approach Prescriptive vs. descriptiveData 1Data 2Data 3…Data nELP/EAQULASCEFR DescriptorsJapanese/ChineseProposed <strong>EBCL</strong>DescriptorsUniversity of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 201211
<strong>EBCL</strong> major resources Bank of CEFR related Descriptors: CEFR descriptors ELP (<strong>Eu</strong>ropean Language Portfolio) self assessment descriptors EAQUALS (<strong>Eu</strong>ropean Association for Quality Language Services)bank of descriptors Japanese Foundation ‘Can do’ statements International Curriculum for Chinese Language Education 国 际 汉 语教 学 通 用 课 程 大 纲 (Beijing, 2010) Profiles of major <strong>Eu</strong>ropean languages Profilo della lingua italiana (Florence, 2010) Profile Deutsch (Berlin, 2005) Niveau A1 pour le français (Paris, 2007) English Profile (Cambridge, 2012)University of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 201212
<strong>EBCL</strong> project timelines10/2010 - 05/2011 20-21/05/2011 - 10/2011 14-15/10/2011Projectlaunch(London)Survey +Casestudies;ProjectwebRomeSeminar:report <strong>and</strong>developmentProposedframework<strong>com</strong>ponents atA1/A2 levels;examplesParis Seminar:openconsultation<strong>and</strong>development- 04/2011 27-29/04/2012 - 07/2012 19-20/07/2012 10/2012RefinedA1/A2 levelsof framework(descriptors+samples)BerlinSeminar:openconsultationProposed B1level offrameworkLondonSeminar:B1-leveldescriptors<strong>and</strong> productBrusselssymposium:promotion <strong>and</strong>furtherdevelopmentUniversity of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 201213
<strong>EBCL</strong> proficiency levelsNote: <strong>EBCL</strong> criterion levels(A1=A1.2, A2=A2.2, B1=B1.2,B2=B2.2; C1=C1.2)University of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 201214
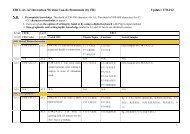
<strong>EBCL</strong> project progress – 1 Revised A1/A2/B1.1 level descriptors <strong>and</strong> samples Reception (6 categories) Production (5 categories) Interaction (9 categories) Strategies (7 categories) Reception (5 categories) Production (3 categories) Interaction (3 categories)SpokenWrittenUniversity of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 201215
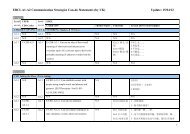
<strong>EBCL</strong> project progress – 2Generic <strong>and</strong> illustrative descriptors (A1-A2)Socio-linguistic <strong>com</strong>ponents(themes <strong>and</strong> topics)Pragmatic <strong>com</strong>ponents(language functions)Linguistic <strong>com</strong>ponents(vocabulary/character,grammar, grapheme, etc.)Intercultural <strong>com</strong>ponents(knowledge, attitude,skills, awareness)University of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 201216
<strong>EBCL</strong> project challenge – 2 Lack of corpora for real-life use of language Spoken form vs written formUniversity of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 201218
<strong>EBCL</strong> project challenge – 3 The gap between <strong>EBCL</strong> <strong>and</strong> CEFR Graphemic element Number of vocabulary (lexical items) The integration of the intercultural dimension Being (doing + knowing)University of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 201219
<strong>EBCL</strong> project challenge – 4 International collaboration Intercultural mediation <strong>and</strong> management Time, fundingUniversity of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 201220
<strong>EBCL</strong> implicationsSt<strong>and</strong>ardisation <strong>and</strong> sustainabilityComparability of learning out<strong>com</strong>es (with otherCEFR-based <strong>Eu</strong>ropean languages)Syllabus <strong>and</strong> course designMaterial/textbook developmentAssessmentPolicy makingEmployabilityLanguage certificateUniversity of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 2012 21
<strong>EBCL</strong> project next steps Disseminate <strong>and</strong> pilot the out<strong>com</strong>es (A1.1-B1.2) atuniversities, schools, <strong>and</strong> enterprises for modification<strong>and</strong> improvement Move up to C1 level descriptors to provide a <strong>com</strong>pleteset of descriptors in line with CEFR Flesh out the framework with adequate samples atdifferent levels for <strong>com</strong>piling the Chinese ProfileUniversity of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 201222
<strong>EBCL</strong> Survey – UK HE <strong>EBCL</strong> Internet Survey May 2011 Among 190 universities in the UK, 92 university runvarious Chinese courses. 6 universities in Irel<strong>and</strong> have various Chinese courses The number has been growingLLAS University of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 201223
<strong>EBCL</strong> Survey – UK HE Types of courses Degree courses (single) Degree courses (<strong>com</strong>bined) Credit courses (open access) Diploma courses Evening courses Confucius institute coursesLLAS University of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 201224
<strong>EBCL</strong> survey – UK HE Contact hours Majority 1.5-2 hours per week, teaching 14-30 weeks peryear Diploma courses 3-4 hours per week, 20-22 weeks peryear Degree courses 6 hours per week, 20-22 weeks per yearLLAS University of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 201225
UK HE-CEFR level (?) A sample from a university 4 hours per week, 22 weeks, total 88 hours 4 language skills With background of learning other <strong>Eu</strong>ropeanlanguages Fast track course Achieve A2LLAS University of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 201226
Schools CEFR UK It normally takes 3 years school education to sit GCSEChinese exam, which is A2 (C grade +). It is roughlyequivalent to 350 hours. SLO ( National expertisecentrum leerplanontwikkeling of Netherl<strong>and</strong>s ) Suggested 480 contact sessions over 3 years to achieveA2.LLAS University of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 201227
Taiwan, Test Of Chinese as a Foreign Language (Reading) A1: Level 1, 180 hours (1-2 years) 500 words A2: Level 2, 480-720 hours (1-2 years), 800 words B1: Level 3, 720-960 hours (2-3 years), 1500 words B2: Level 4, 960-1920 hours (3-4 years), 5000 words C1: Level 5, More than 1920 hours, 8000 wordsLLAS University of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 201228
Possible solutions Set separate target for different skills. Listening <strong>and</strong> Speaking skills can be developed at asimilar speed to other modern languages. Reading skill will be developed rather slowly but needto be included in the teaching plan. Chinese charactersneed to be taught although in small number Writing skill can be developed <strong>and</strong> assessed via using<strong>com</strong>puter , not ideal for character learning but canrelease lots of time for the development of other skills.LLAS University of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 201229
What’s <strong>com</strong>ing up… Brussels Symposium, Oct 2012 (Date/Venue TBC) Updated information about the project, please visithttp://ebcl.eu.<strong>com</strong>/Contact:Lik Suen, lx@soas.ac.ukLiang Wang, l.wang@soas.ac.ukLianyi Song, ls2@soas.ac.uk (Coordinator)Acknowledgement:We are grateful to Dr George Zhang, who led the project between 11/2010 <strong>and</strong>11/2011, for his contribution to the development of this project work.LLAS University of Edinburgh, 5-6 July 201230