SPACE EXPLORATION - Science World Resources
SPACE EXPLORATION - Science World Resources
SPACE EXPLORATION - Science World Resources
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
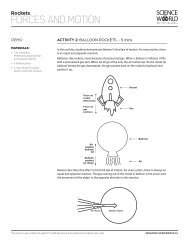
Space <strong>Science</strong><strong>SPACE</strong> <strong>EXPLORATION</strong>MAKE & TAKEMATERIALS:Per class (an assortment of thefollowing supplies)• elastic bands• masking tape• paper clip• string/yarn• aluminum foil• straws• cotton balls• paper plates, bowls, cups• toilet paper tubes• balloons• any other items you thinkmight be relevantACTIVITY 7: LUNATIC LANDERS - 45 mins–1.5 hrsIn this twist on the classic egg drop activity, students are assigned the task of designinga manned spacecraft to land on another planet. Their challenge is to build a spacecraftthat will house an astronaut (a raw egg) that can land successfully near a given targetfrom a set height.Over the years, many different types of spacecraft have landed on other planets, theMoon, and then back to Earth. In order for these missions to be successful the spacecraftmust not only be intact upon landing, but also the humans and/or the delicate scienceand computer equipment in the spacecraft must be undamaged. Imagine a Mars roverdescending towards the planet at speeds over 19,000km/hour—you’d need to have somespecial equipment to ensure a successful landing. Through various landings, specializedequipment such as parachutes, air bags and rockets have been developed. What will youdevelop to land your craft?Per group• 1 price list• paper, pencil and erasers• 1 raw egg• 1 pair scissorsThis resource modified from H.R. MacMillan Space Centre's Engaging <strong>Science</strong> “Exploring Space” unit.http://www.spacecentre.caRESOURCES.SCIENCEWORLD.CA
Space <strong>Science</strong><strong>SPACE</strong> <strong>EXPLORATION</strong>WHAT TO DOPreparation1. Prepare copies of the materials price list (students will be working within a budget tobuild their spacecraft) and arrange the materials at the front of the class.2. Choose a launch area (e.g. top of ladder or second storey window) and mark a targetlanding spot.Activity1. In small groups, develop a diagram of a spacecraft that is able to land on a planet.The lander must:a. hit a target area on the planet (plan for accuracy),b. protect your astronaut (egg) during landing,c. allow the astronaut to exit the lander to conduct moon walks andd. be within budget.Get familiar with the launch area and target landing spot to create the best design forthat terrain.2. Share your designs with other groups and discuss the advantages and disadvantages ofeach design.3. Based on the feedback of the other groups, make modifications to improve your design.4. “Buy” the materials, build your spacecraft and place your “astronaut” inside.5. Test the landers by dropping them from the designated height onto the target area. Checkeach to see if the astronaut arrived safely.6. Discuss why some designs worked and some did not, based on the results of the landings.KEY QUESTIONS» What are some features you think would help to land your spacecraft safely?» What are the advantages and disadvantages of these elements?» Why did you choose particular elements of your spacecraft design?» What are some of the disadvantages of the elements you chose?What were the advantages?» If you were to redesign your lander, what would you change and why?This resource modified from H.R. MacMillan Space Centre's Engaging <strong>Science</strong> “Exploring Space” unit.http://www.spacecentre.caRESOURCES.SCIENCEWORLD.CA
Space <strong>Science</strong><strong>SPACE</strong> <strong>EXPLORATION</strong>EXTENSIONS» Watch video footage of different planetary landing craft. Compare the aspects of thedesigns that played a role in their successful landings.Watch the rover mission landing from 2004:http://origin.mars5.jpl.nasa.gov/gallery/video/animation.htmlWatch the Curiosity landing in 2012 at:http://www.nasa.gov/multimedia/videogallery/index.html?media_id=150865751» Discuss the use of “splashdown” as an alternative method for landing spacecraft safely.Splashdown is the method of landing a spacecraft by parachute in a body of water. Theproperties of water cushion the spacecraft enough that there is no need for a retrorocket toslow the final descent.» Research the similarities and differences between Earth, the Moon and Mars and discusshow spacecraft might change their designs for landing at each location.Consider the atmosphere, gravity and surface type at each location. For example, the Moonhas no atmosphere and Mars has little atmosphere. (Parachutes are only effective wherethere is an atmosphere.) Mars has only a third of Earth’s gravity, so objects will fall sloweron Mars than on Earth. On which planet is there the option for a water landing?NOTESThis resource modified from H.R. MacMillan Space Centre's Engaging <strong>Science</strong> “Exploring Space” unit.http://www.spacecentre.caRESOURCES.SCIENCEWORLD.CA
ITEM AMOUNT PRICEElastic Band 3 $25Masking Tape 1m $25Paper Clip 5 $25String 50cm $25Tin Foil 50cm $25Straws 2 $50Cotton balls 10 $50Plate 1 $50Bowl 1 $75Cup 2 $100Toilet Paper Tube 1 $100Balloon 1 $100YOUR BUDGET IS $This resource modified from H.R. MacMillan Space Centre's Engaging <strong>Science</strong> “Exploring Space” unit.http://www.spacecentre.caRESOURCES.SCIENCEWORLD.CA