12 The History of Life
12 The History of Life
12 The History of Life
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
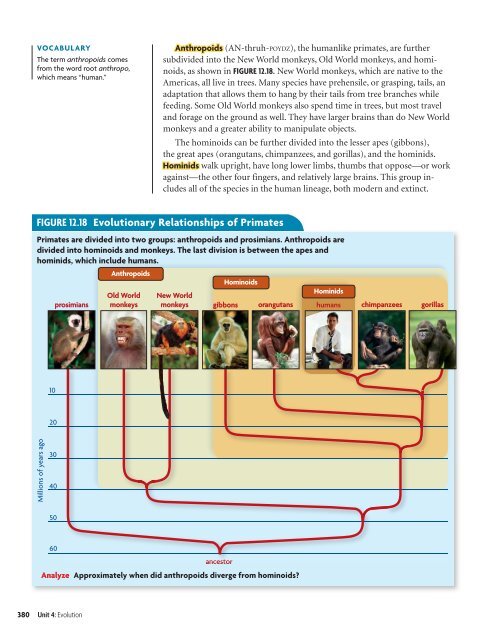
VOCABULARY<strong>The</strong> term anthropoids comesfrom the word root anthropo,which means “human.”Anthropoids (AN-thruh-POYDZ), the humanlike primates, are furthersubdivided into the New World monkeys, Old World monkeys, and hominoids,as shown in FIGURE <strong>12</strong>.18. New World monkeys, which are native to theAmericas, all live in trees. Many species have prehensile, or grasping, tails, anadaptation that allows them to hang by their tails from tree branches whilefeeding. Some Old World monkeys also spend time in trees, but most traveland forage on the ground as well. <strong>The</strong>y have larger brains than do New Worldmonkeys and a greater ability to manipulate objects.<strong>The</strong> hominoids can be further divided into the lesser apes (gibbons),the great apes (orangutans, chimpanzees, and gorillas), and the hominids.Hominids walk upright, have long lower limbs, thumbs that oppose—or workagainst—the other four fingers, and relatively large brains. This group includesall <strong>of</strong> the species in the human lineage, both modern and extinct.FIGURE <strong>12</strong>.18 Evolutionary Relationships <strong>of</strong> PrimatesPrimates are divided into two groups: anthropoids and prosimians. Anthropoids aredivided into hominoids and monkeys. <strong>The</strong> last division is between the apes andhominids, which include humans.prosimiansAnthropoidsOld WorldmonkeysHominoidsNew WorldHominidsmonkeys gibbons orangutans humans chimpanzees gorillas1020Millions <strong>of</strong> years ago30405060ancestorAnalyze Approximately when did anthropoids diverge from hominoids?380 Unit 4: Evolution