Organic Chemistry Structures of Organic Compounds
Organic Chemistry Structures of Organic Compounds
Organic Chemistry Structures of Organic Compounds
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
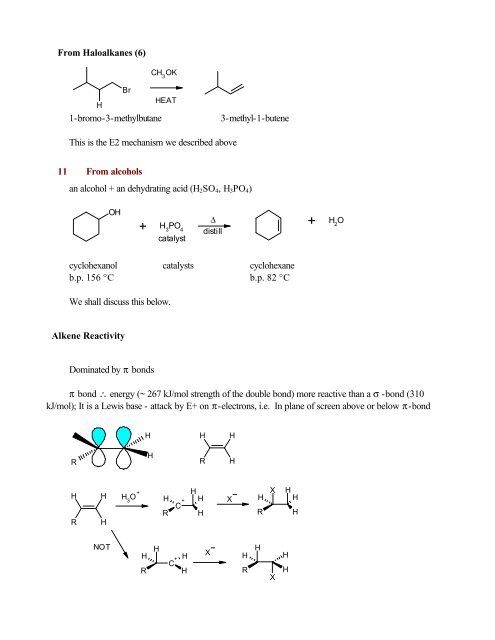
From Haloalkanes (6)CH 3OKBrHEATH1-bromo-3-methylbutane3-methyl-1-buteneThis is the E2 mechanism we described above11 From alcoholsan alcohol + an dehydrating acid (H 2 SO 4 , H 3 PO 4 )OH+ H 3 PO 4catalyst∆ + H 2Odistillcyclohexanol catalysts cyclohexaneb.p. 156 °C b.p. 82 °CWe shall discuss this below.Alkene ReactivityDominated by π bondsπ bond ∴ energy (~ 267 kJ/mol strength <strong>of</strong> the double bond) more reactive than a σ -bond (310kJ/mol); It is a Lewis base - attack by E+ on π-electrons, i.e. In plane <strong>of</strong> screen above or below π-bondHHHRHRHHHHHHXHXHHRHH 3O + C +R HRHNOTHHHXHHHRC + HRXH