Importance of Protein sorting Cell organization depend on sorting ...
Importance of Protein sorting Cell organization depend on sorting ...
Importance of Protein sorting Cell organization depend on sorting ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
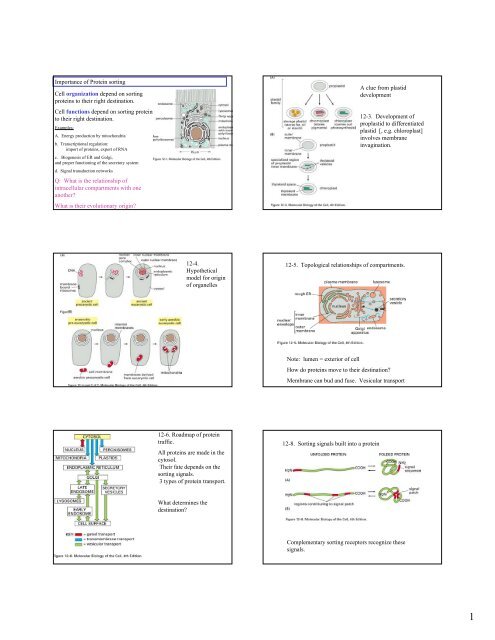
<str<strong>on</strong>g>Importance</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>Protein</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>sorting</str<strong>on</strong>g><str<strong>on</strong>g>Cell</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>organizati<strong>on</strong></str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>depend</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>sorting</str<strong>on</strong>g>proteins to their right destinati<strong>on</strong>.<str<strong>on</strong>g>Cell</str<strong>on</strong>g> functi<strong>on</strong>s <str<strong>on</strong>g>depend</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>sorting</str<strong>on</strong>g> proteinsto their right destinati<strong>on</strong>.Examples:A. Energy producti<strong>on</strong> by mitoch<strong>on</strong>driab. Transcripti<strong>on</strong>al regulati<strong>on</strong>:import <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> proteins, export <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> RNAc. Biogenesis <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> ER and Golgi,and proper functi<strong>on</strong>ing <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the secretory systemd. Signal transducti<strong>on</strong> networksQ: What is the relati<strong>on</strong>ship <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g>intracellular compartments with <strong>on</strong>eanother?What is their evoluti<strong>on</strong>ary origin?A clue from plastiddevelopment12-3. Development <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g>proplastid to differentiatedplastid [, e.g. chloroplast]involves membraneinvaginati<strong>on</strong>.12-4.Hypotheticalmodel for origin<str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> organelles12-5. Topological relati<strong>on</strong>ships <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> compartments.Note: lumen = exterior <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> cellHow do proteins move to their destinati<strong>on</strong>?Membrane can bud and fuse. Vesicular transport12-6. Roadmap <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> proteintraffic.All proteins are made in thecytosol.Their fate <str<strong>on</strong>g>depend</str<strong>on</strong>g>s <strong>on</strong> the<str<strong>on</strong>g>sorting</str<strong>on</strong>g> signals.3 types <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> protein transport.12-8. Sorting signals built into a proteinWhat determines thedestinati<strong>on</strong>?Complementary <str<strong>on</strong>g>sorting</str<strong>on</strong>g> receptors recognize thesesignals.1
17-1. Sorting <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> nuclear encoded proteinsAtCNX: 1 MRQRQLFSVF LLLLAFVSFQ KLCYCDDQTV LYESFDEPFDER Calnexin, type ICytosolsolubleperipheralCytosolicRibosomes<str<strong>on</strong>g>Protein</str<strong>on</strong>g>Synthesis- cytosolOrganellar:Nuc: solubleMitoch: sol +membChloroplast: sol +membraneER-bound Ribosomes->secreted protein or membrane proteinsSoluble:ER lumenGolgi lumenVac lumenExtracellularNuc Env lumenMembrane:ERGolgiNucPMVacMOCB 639, Lodish 2000, ch. 17-1, 17-2; Alberts-ch 12Synthesis and <str<strong>on</strong>g>sorting</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> nuclear-encoded proteins to organellesMajor questi<strong>on</strong>s1. How do proteins recognize their target destinati<strong>on</strong>?2. What is the identity <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the molecules that recognize targeting informati<strong>on</strong>?3. How do large molecules pass through membranes? What is the driving force?4. What c<strong>on</strong>trols protein <str<strong>on</strong>g>sorting</str<strong>on</strong>g>?5. What approaches are used to study these questi<strong>on</strong>s?What lines <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> evidence support the model?Mitoch<strong>on</strong>dria: model <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> transmembrane transporta. Review <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> mitoch<strong>on</strong>dria structure, functi<strong>on</strong>Most proteins coded by nuclear genes, synth in cyt, and imported.b. Method to study importc. Cyt Chaper<strong>on</strong>es deliver proteins to mitod. Mito receptors transfer protein to channele. Import <str<strong>on</strong>g>depend</str<strong>on</strong>g>s <strong>on</strong> pmf and mito chaper<strong>on</strong>es to keep proteins unfoldedf. Expt evidence for the model.Import into chloroplast16-7, 16-9. Mitoch<strong>on</strong>dri<strong>on</strong>2
17.3. Study protein import into mitoch<strong>on</strong>dria in a cell-free systemBiochemical approach = in vitroA. Label protein withisotope: In vitro synthesismRNA +35S-Metb. import assayFollow isotope-labeledprotein over time.Check protein is inside byprotease resistance.C. Test requirement forcytosolic factors or energyd. Test requirement formitoch<strong>on</strong>dria proteinswith mutant lacking amitoch. protein.Other approaches to study mechanism <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> translocati<strong>on</strong>see panel 12-1Transfecti<strong>on</strong> ApproachFind the <str<strong>on</strong>g>sorting</str<strong>on</strong>g> signal for mitoch<strong>on</strong>dria.Fuse targeting signal with cytosolic proteins.Genetic approache.g. yeast mutants defective in <strong>on</strong>e protein <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the uptake machinerycannot uptake mitoch<strong>on</strong>dria-destined proteinsSignal peptide is anamphipathic alpha helixwith no sequencehomology to othermito. Signals.Surface receptor andtranslocati<strong>on</strong> pore form acomplexRecogniti<strong>on</strong>, inserti<strong>on</strong>,translocati<strong>on</strong> and processingEnergy is needed at 3 different steps:ATP and H+ gradient3
Repeated Hsp binding and ATP hydrolysis pullin proteinFig. 17-9. Chloroplast developmentand structureLight energy is used to oxidize water. Electr<strong>on</strong>s are transferred toreduce NADPH and prot<strong>on</strong> gradient is used to form ATP.CO 2 + RuBP -- rubisco--> 2 PGAPGA --NADPH, ATP --> G3P2G3P --> glucoseCF1FoTaiz + Zeiger (1998) Fig. 7-22Targeting proteins to the chloroplast:a. matrix Rubisco has single matrix signal sequenceb. thylakoid protein has 2.17-8. <str<strong>on</strong>g>Protein</str<strong>on</strong>g>s move into the thylakoid by <strong>on</strong>e <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> four pathways.A. Sec ATP, ∆pH [PC, OEC33]b. SRP, GTP, ∆pH [LHCP]c. ∆pH [OE22, RR-p]d. Sp<strong>on</strong>taneous [CFo-II]Keegstra K, Cline K. 1999.<str<strong>on</strong>g>Protein</str<strong>on</strong>g> import and routing systems <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> chloroplasts. Plant <str<strong>on</strong>g>Cell</str<strong>on</strong>g>. 11(4):557-70.4
Summary and a problemProblem: Do mito andchloroplast-destined proteins havedistinct matrix targetingsequences? Design anexperiment to test yourhypothesis.Evidence for matrix targeting signal Fig. 17-2Yeast ADH3p: 1 mlrtstlftr rvqpslfsrn ilrlqstaai pktqkgvify3-5 n<strong>on</strong>-c<strong>on</strong>secutive Arg(R) or Lys (K),with Ser (S) and Thr (T),no Asp (D) or Glu (E)<str<strong>on</strong>g>Protein</str<strong>on</strong>g> Import into mitoch<strong>on</strong>drial matrixEvidence:1. Import <str<strong>on</strong>g>depend</str<strong>on</strong>g>s <strong>on</strong> cytosolic factors2. ATP is needed to keep protein unfolded3. Mitoch<strong>on</strong>drial receptors are needed4. Import <str<strong>on</strong>g>depend</str<strong>on</strong>g>s <strong>on</strong> pmf and matrix chaper<strong>on</strong>espmf: provides a driving force17-4. <str<strong>on</strong>g>Protein</str<strong>on</strong>g> Import intomitoch<strong>on</strong>drial matrixEvidence:1. Need for cytosolic factors2. cyt ATP is needed to keepprotein unfolded3. Mitoch<strong>on</strong>drial receptors areneeded and being identified4. Import <str<strong>on</strong>g>depend</str<strong>on</strong>g>s <strong>on</strong> pmf andmatrix chaper<strong>on</strong>es5