Reconstruction using surface dedicated tensorial fields - ENSEA
Reconstruction using surface dedicated tensorial fields - ENSEA
Reconstruction using surface dedicated tensorial fields - ENSEA
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
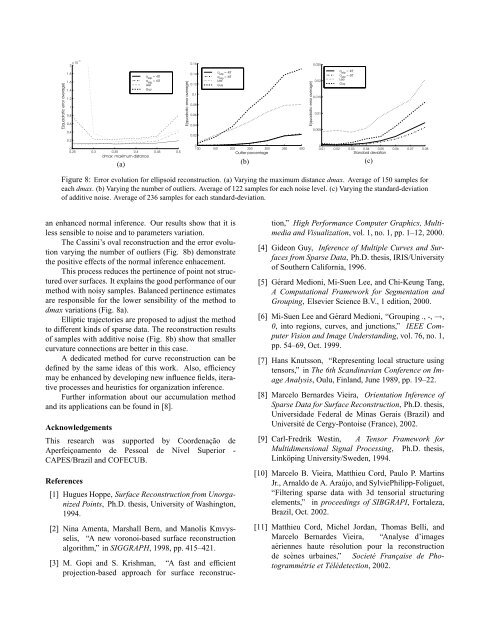
E(quadratic error average)E(quadratic error average)E(quadratic error average)0.160.0252 x 10 -3 a elip= 45°1.81.61.41.2a elip= 60°LeeGuy0.140.120.1a elip= 45°a elip= 60°LeeGuy0.020.015a elip= 45°a elip= 60°LeeGuy10.80.080.060.010.60.40.200.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5dmax: maximum distance(a)0.040.020100 150 200 250 300 350 400Outlier porcentage(b)0.00500.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08Standard deviation(c)Figure 8: Error evolution for ellipsoid reconstruction. (a) Varying the maximum distance dmax. Average of 150 samples foreach dmax. (b) Varying the number of outliers. Average of 122 samples for each noise level. (c) Varying the standard-deviationof additive noise. Average of 236 samples for each standard-deviation.an enhanced normal inference. Our results show that it isless sensible to noise and to parameters variation.The Cassini’s oval reconstruction and the error evolutionvarying the number of outliers (Fig. 8b) demonstratethe positive effects of the normal inference enhacement.This process reduces the pertinence of point not structuredover <strong>surface</strong>s. It explains the good performance of ourmethod with noisy samples. Balanced pertinence estimatesare responsible for the lower sensibility of the method todmax variations (Fig. 8a).Elliptic trajectories are proposed to adjust the methodto different kinds of sparse data. The reconstruction resultsof samples with additive noise (Fig. 8b) show that smallercurvature connections are better in this case.A <strong>dedicated</strong> method for curve reconstruction can bedefined by the same ideas of this work. Also, efficiencymay be enhanced by developing new influence <strong>fields</strong>, iterativeprocesses and heuristics for organization inference.Further information about our accumulation methodand its applications can be found in [8].AcknowledgementsThis research was supported by Coordenação deAperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior -CAPES/Brazil and COFECUB.References[1] Hugues Hoppe, Surface <strong>Reconstruction</strong> from UnorganizedPoints, Ph.D. thesis, University of Washington,1994.[2] Nina Amenta, Marshall Bern, and Manolis Kmvysselis,“A new voronoi-based <strong>surface</strong> reconstructionalgorithm,” in SIGGRAPH, 1998, pp. 415–421.[3] M. Gopi and S. Krishman, “A fast and efficientprojection-based approach for <strong>surface</strong> reconstruction,”High Performance Computer Graphics, Multimediaand Visualization, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 1–12, 2000.[4] Gideon Guy, Inference of Multiple Curves and Surfacesfrom Sparse Data, Ph.D. thesis, IRIS/Universityof Southern California, 1996.[5] Gérard Medioni, Mi-Suen Lee, and Chi-Keung Tang,A Computational Framework for Segmentation andGrouping, Elsevier Science B.V., 1 edition, 2000.[6] Mi-Suen Lee and Gérard Medioni, “Grouping ., -, →,0, into regions, curves, and junctions,” IEEE ComputerVision and Image Understanding, vol. 76, no. 1,pp. 54–69, Oct. 1999.[7] Hans Knutsson, “Representing local structure <strong>using</strong>tensors,” in The 6th Scandinavian Conference on ImageAnalysis, Oulu, Finland, June 1989, pp. 19–22.[8] Marcelo Bernardes Vieira, Orientation Inference ofSparse Data for Surface <strong>Reconstruction</strong>, Ph.D. thesis,Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais (Brazil) andUniversité de Cergy-Pontoise (France), 2002.[9] Carl-Fredrik Westin, A Tensor Framework forMultidimensional Signal Processing, Ph.D. thesis,Linköping University/Sweden, 1994.[10] Marcelo B. Vieira, Matthieu Cord, Paulo P. MartinsJr., Arnaldo de A. Araújo, and SylviePhilipp-Foliguet,“Filtering sparse data with 3d <strong>tensorial</strong> structuringelements,” in proceedings of SIBGRAPI, Fortaleza,Brazil, Oct. 2002.[11] Matthieu Cord, Michel Jordan, Thomas Belli, andMarcelo Bernardes Vieira, “Analyse d’imagesaériennes haute résolution pour la reconstructionde scènes urbaines,” Societé Française de Photogrammétrieet Télédetection, 2002.