Scottish Further Education Funding Council: A ... - Audit Scotland
Scottish Further Education Funding Council: A ... - Audit Scotland
Scottish Further Education Funding Council: A ... - Audit Scotland
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
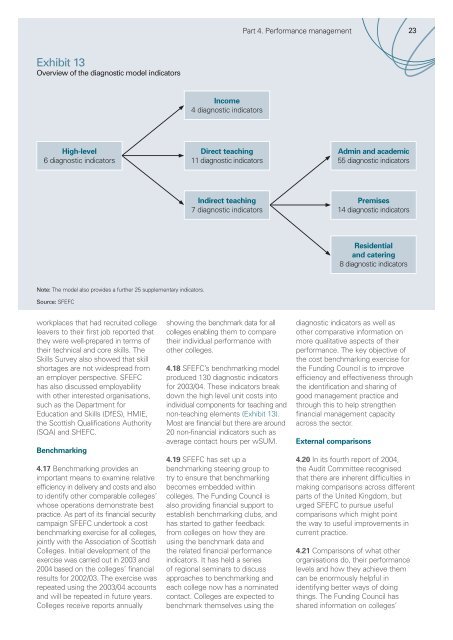
Part 4. Performance management 23Exhibit 13Overview of the diagnostic model indicatorsIncome4 diagnostic indicatorsHigh-level6 diagnostic indicatorsDirect teaching11 diagnostic indicatorsAdmin and academic55 diagnostic indicatorsIndirect teaching7 diagnostic indicatorsPremises14 diagnostic indicatorsResidentialand catering8 diagnostic indicatorsNote: The model also provides a further 25 supplementary indicators.Source: SFEFCworkplaces that had recruited collegeleavers to their first job reported thatthey were well-prepared in terms oftheir technical and core skills. TheSkills Survey also showed that skillshortages are not widespread froman employer perspective. SFEFChas also discussed employabilitywith other interested organisations,such as the Department for<strong>Education</strong> and Skills (DfES), HMIE,the <strong>Scottish</strong> Qualifications Authority(SQA) and SHEFC.Benchmarking4.17 Benchmarking provides animportant means to examine relativeefficiency in delivery and costs and alsoto identify other comparable colleges’whose operations demonstrate bestpractice. As part of its financial securitycampaign SFEFC undertook a costbenchmarking exercise for all colleges,jointly with the Association of <strong>Scottish</strong>Colleges. Initial development of theexercise was carried out in 2003 and2004 based on the colleges’ financialresults for 2002/03. The exercise wasrepeated using the 2003/04 accountsand will be repeated in future years.Colleges receive reports annuallyshowing the benchmark data for allcolleges enabling them to comparetheir individual performance withother colleges.4.18 SFEFC’s benchmarking modelproduced 130 diagnostic indicatorsfor 2003/04. These indicators breakdown the high level unit costs intoindividual components for teaching andnon-teaching elements (Exhibit 13).Most are financial but there are around20 non-financial indicators such asaverage contact hours per wSUM.4.19 SFEFC has set up abenchmarking steering group totry to ensure that benchmarkingbecomes embedded withincolleges. The <strong>Funding</strong> <strong>Council</strong> isalso providing financial support toestablish benchmarking clubs, andhas started to gather feedbackfrom colleges on how they areusing the benchmark data andthe related financial performanceindicators. It has held a seriesof regional seminars to discussapproaches to benchmarking andeach college now has a nominatedcontact. Colleges are expected tobenchmark themselves using thediagnostic indicators as well asother comparative information onmore qualitative aspects of theirperformance. The key objective ofthe cost benchmarking exercise forthe <strong>Funding</strong> <strong>Council</strong> is to improveefficiency and effectiveness throughthe identification and sharing ofgood management practice andthrough this to help strengthenfinancial management capacityacross the sector.External comparisons4.20 In its fourth report of 2004,the <strong>Audit</strong> Committee recognisedthat there are inherent difficulties inmaking comparisons across differentparts of the United Kingdom, buturged SFEFC to pursue usefulcomparisons which might pointthe way to useful improvements incurrent practice.4.21 Comparisons of what otherorganisations do, their performancelevels and how they achieve themcan be enormously helpful inidentifying better ways of doingthings. The <strong>Funding</strong> <strong>Council</strong> hasshared information on colleges’