Iron sucrose inj
Iron sucrose inj
Iron sucrose inj
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
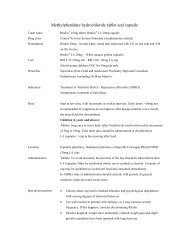
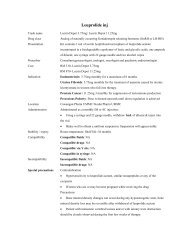
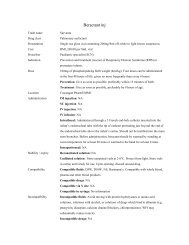
<strong>Iron</strong> <strong>sucrose</strong> <strong>inj</strong>Trade nameDrug classPresentationCostPrescriberIndicationDoseVenofer<strong>Iron</strong> salt5ml ampoule containing 100mg of ironRM 43.00 per ampouleNephrologistParenteral treatment of iron-deficiency anemia in chronic renal failure, includingnondialysis-dependent patients (with or without erythropoietin therapy) and dialysisdependentpatients receiving erythropoietin therapy, in cases where oral iron preparationscannot provide for supplementation such as:Patients who cannot tolerate oral iron therapyPatients who cannot sufficiently absorb orally administered ironDosage has to be individually adapted according to the total iron deficit calculatedwith the following formula:Total iron deficit [mg] = body weight [kg] x (target Hb – actual Hb) [g/l] x 0.24* + depotiron [mg]≤35 kg body weight: target Hb=130 g/l resp. depot iron=15 mg/kg body weight>35 kg body weight: target Hb=150 g/l resp. depot iron=500 mg*Factor 0.24=0.0034 x 0.007 x 1000(<strong>Iron</strong> content of haemoglobin=0.34% / Blood volume=7% of body weight / Factor 1000=conversion from g to mg)Total amount of iron <strong>sucrose</strong> to be administered (in ml) = Total iron deficit [mg]20 mg/mlIf the total necessary dose exceeds the maximum allowed single dose, the administrationhas to be split. If no response of the haematological parameters is observed after 1-2 weeksthe original diagnosis should be reconsidered.Normal posology: 5-10ml (100 to 200mg iron) twice or three times a week depending onthe haemoglobin level.Maximum tolerated single dose:Adults and the elderly:As <strong>inj</strong>ection: 5-10 ml (100 to 200 mg of iron) <strong>inj</strong>ected in as least 10 min.As infusion: if the clinical situation demands the single dose may be increased to 0.25 mliron <strong>sucrose</strong> kg / body weight (=7 mg iron/kg bw) not exceeding 25 ml iron <strong>sucrose</strong> (500mg iron), diluted in 500 ml 0.9% w/v NaCl infused over at least 3.5 h, once a week.Test doseAdults: 1-2.5 ml (20 to 50 mg iron)Children > 14 kg: 1 ml (20 mg iron)
Children < 14 kg: 1.5 mg/kgLocationIn-patient pharmacy: warded patients; Kedai PharmUMMC: outpatient.Administration IM <strong>inj</strong>ection: NASC <strong>inj</strong>ection: NAIV <strong>inj</strong>ection: Slow <strong>inj</strong>ection or directly into the venous limb of the dialyser. Administer ata rate of 1 mL undiluted solution over minute (i.e. 5 min per 5 mL ampoule) not exceeding10mL iron <strong>sucrose</strong> per <strong>inj</strong>ection. After <strong>inj</strong>ection, extend the arm of the patient.IV infusion: Each mL (20 mg) of iron <strong>sucrose</strong> has to be diluted exclusively in maximumof 20 mL 0.9% w/v NaCl, immediately prior infusion and infused at a rate of : 100mL (100mg) in at least 15 min ; 200 mL (200mg) in at least 30 min ; 300 mL in at least 1.5 h ; 400mL in at least 2.5 h ; 500mL in at least 3.5h. For stability reasons, dilution of lowerconcentrations are not permissible. If clinical circumstances demand, iron <strong>sucrose</strong> may bediluted in less than specified amount of 0.9% w/v NaCl solution, producing a higherconcentration. The rate of infusion must be adapted according to the amount of iron givenper minute (200mg iron should be infused in at least 30 minutes ; 500 mg iron should beinfused in at least 3.5h).Intrathecal: NAIntraperitoneal: NAStability / expiry Reconstituted solution: Stable at controlled room temperature for 12 hours if storedbetween 4-25°C in the day light.Undiluted solution: Store a controlled room temperature of 4 to 25°CCompatibility Compatible fluids: NSCompatible drugs: NACompatible via Y site: NACompatible in syringe: NAIncompatibility Incompatible fluids: NAIncompatible drugs: Oral iron preparationSpecial precautions • Should only be administered where the indication is confirmed by appropriateinvestigations (e.g. serum ferritin, haemoglobin, haematocrit, erythrocyte count or redcell indices – MCV, MCH, MCHC).• Parenterally administered iron preparations can cause allergic or anaphylactoidreactions, including serious or life-threatening reactions. Patients with bronchialasthma, with low iron binding capacity and/or folic acid deficiency are particularly atrisk of an allergic or anaphylactic reaction.• Before administration of the 1 st therapeutic dose of iron <strong>sucrose</strong> in a new patient, a testdose should be given by the chosen method of administration with facilities forcardiopulmonary resuscitation being made available. If no adverse reactions occur
within 15 min after administration, the remaining portion of the initial dose can begiven• Hypotension has been reported frequently in hemodialysis dependent patients.• Used during pregnancy only if clearly needed. Caution during lactation.• Safety and efficacy in children have not been established.• Should not be administered concomitantly with oral iron preparations since theabsorption of iron is reduced. Oral iron therapy should at least be started 5 days afterthe last <strong>inj</strong>ection.• Overdosage can cause acute iron overloading which may manifest as haemosiderosis.Symptoms: hypotension, headache, vomiting, nausea, dizziness, joint aches,parasthesia, abdominal and muscle pain, oedema and cardiovascular collapse. Treatedwith supportive measures (IV fluids, hydrocortisone, and/or antihistamines) and, ifrequired, an oral chelating agent.Special notes • Stock from Inpatient pharmacy is for inpatients only.• Outpatients are required to purchase from Kedai PharmUMMCPatient information • Side effects: hypotension (caution when driving or climbing stairs); black tarry stools(normal), nausea, vomiting (taking with meals with reduce this), constipation(adequate fluids and exercise may help, may need a stool softener); or diarrhea(buttermilk, boiled milk or yogurt may help).• Report severe unresolved GI irritation (cramping, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea,constipation); headache, lethargy, fatigue, dizziness or other CNS changes; rapidrespiration; leg cramps’ chest pain or palpitations; swelling of extremities orunexplained weight gain; vision changes; choking sensation; loss of consciousness; orconvulsion.Prepared/checked by Yeap Li Ling / PDS / HKD / PLDate compiled/edition 20 July 2009, 1 st edition