Rock Physics
Rock Physics
Rock Physics
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
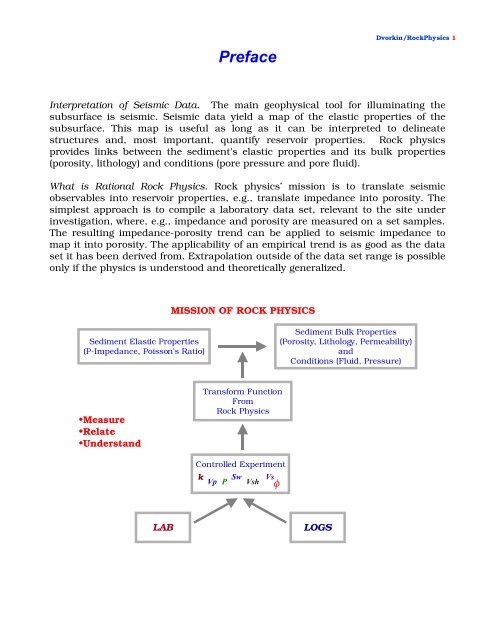
PrefaceDvorkin/<strong>Rock</strong><strong>Physics</strong> 1Interpretation of Seismic Data. The main geophysical tool for illuminating thesubsurface is seismic. Seismic data yield a map of the elastic properties of thesubsurface. This map is useful as long as it can be interpreted to delineatestructures and, most important, quantify reservoir properties. <strong>Rock</strong> physicsprovides links between the sediment's elastic properties and its bulk properties(porosity, lithology) and conditions (pore pressure and pore fluid).What is Rational <strong>Rock</strong> <strong>Physics</strong>. <strong>Rock</strong> physics’ mission is to translate seismicobservables into reservoir properties, e.g., translate impedance into porosity. Thesimplest approach is to compile a laboratory data set, relevant to the site underinvestigation, where, e.g., impedance and porosity are measured on a set samples.The resulting impedance-porosity trend can be applied to seismic impedance tomap it into porosity. The applicability of an empirical trend is as good as the dataset it has been derived from. Extrapolation outside of the data set range is possibleonly if the physics is understood and theoretically generalized.MISSION OF ROCK PHYSICSSediment Elastic Properties(P-Impedance, Poisson’s Ratio)Sediment Bulk Properties(Porosity, Lithology, Permeability)andConditions (Fluid, Pressure)•Measure•Relate•UnderstandTransform FunctionFrom<strong>Rock</strong> <strong>Physics</strong>Controlled Experimentk SwVp P VshVsφLABLOGS