VERTEC White Paper.indd - Jands
VERTEC White Paper.indd - Jands
VERTEC White Paper.indd - Jands
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
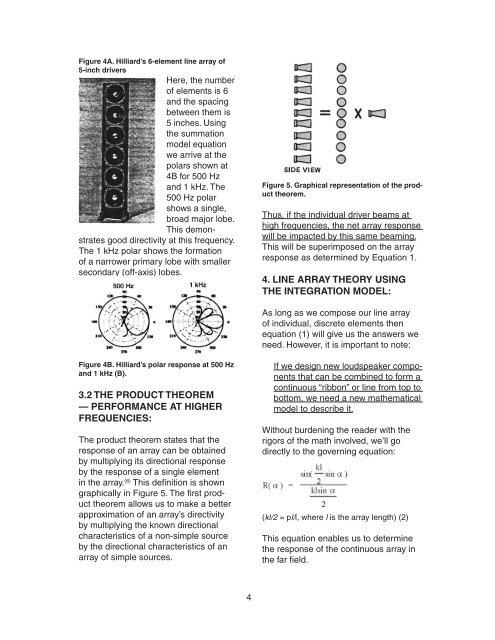
Figure 4A. Hilliard’s 6-element line array of5-inch driversHere, the numberof elements is 6and the spacingbetween them is5 inches. Usingthe summationmodel equationwe arrive at thepolars shown at4B for 500 Hzand 1 kHz. The500 Hz polarshows a single,broad major lobe.This demonstratesgood directivity at this frequency.The 1 kHz polar shows the formationof a narrower primary lobe with smallersecondary (off-axis) lobes.Figure 5. Graphical representation of the producttheorem.Thus, if the individual driver beams athigh frequencies, the net array responsewill be impacted by this same beaming.This will be superimposed on the arrayresponse as determined by Equation 1.4. LINE ARRAY THEORY USINGTHE INTEGRATION MODEL:As long as we compose our line arrayof individual, discrete elements thenequation (1) will give us the answers weneed. However, it is important to note:Figure 4B. Hilliard’s polar response at 500 Hzand 1 kHz (B).3.2 THE PRODUCT THEOREM— PERFORMANCE AT HIGHERFREQUENCIES:The product theorem states that theresponse of an array can be obtainedby multiplying its directional responseby the response of a single elementin the array. (6) This definition is showngraphically in Figure 5. The first producttheorem allows us to make a betterapproximation of an array’s directivityby multiplying the known directionalcharacteristics of a non-simple sourceby the directional characteristics of anarray of simple sources.If we design new loudspeaker componentsthat can be combined to form acontinuous “ribbon” or line from top tobottom, we need a new mathematicalmodel to describe it.Without burdening the reader with therigors of the math involved, we’ll godirectly to the governing equation:(kl/2 = pl/l, where l is the array length) (2)This equation enables us to determinethe response of the continuous array inthe far field.4