Journal 1pages FINAL 34- - National Board Of Examination
Journal 1pages FINAL 34- - National Board Of Examination
Journal 1pages FINAL 34- - National Board Of Examination
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
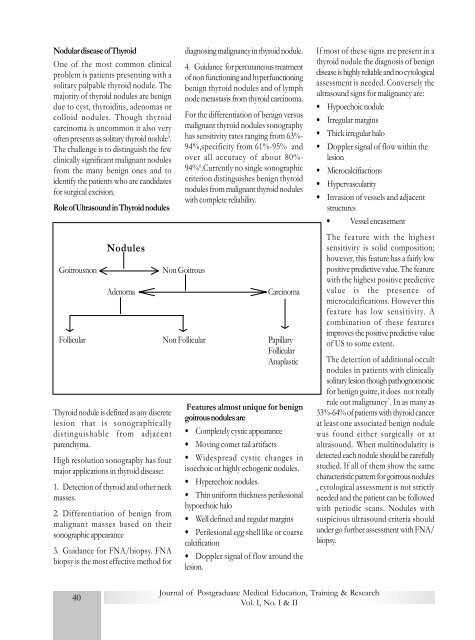
Nodular disease of ThyroidOne of the most common clinicalproblem is patients presenting with asolitary palpable thyroid nodule. Themajority of thyroid nodules are benigndue to cyst, thyroiditis, adenomas orcolloid nodules. Though thyroidcarcinoma is uncommon it also veryoften presents as solitary thyroid nodule 5 .The challenge is to distinguish the fewclinically significant malignant nodulesfrom the many benign ones and toidentify the patients who are candidatesfor surgical excision.Role of Ultrasound in Thyroid nodulesGoitrousnonNodulesAdenomaThyroid nodule is defined as any discretelesion that is sonographicallydistinguishable from adjacentparenchyma.High resolution sonography has fourmajor applications in thyroid disease:1. Detection of thyroid and other neckmasses.2. Differentiation of benign frommalignant masses based on theirsonographic appearance3. Guidance for FNA/biopsy. FNAbiopsy is the most effective method fordiagnosing malignancy in thyroid nodule.4. Guidance for percutaneous treatmentof non functioning and hyperfunctioningbenign thyroid nodules and of lymphnode metastasis from thyroid carcinoma.For the differentiation of benign versusmalignant thyroid nodules sonographyhas sensitivity rates ranging from 63%-94%,specificity from 61%-95% andover all accuracy of about 80%-94% 6 .Currently no single sonographiccriterion distinguishes benign thyroidnodules from malignant thyroid noduleswith complete reliability.Non GoitrousCarcinomaFollicular Non Follicular PapillaryFollicularAnaplasticFeatures almost unique for benigngoitrous nodules are• Completely cystic appearance• Moving comet tail artifacts• Widespread cystic changes inisoechoic or highly echogenic nodules.• Hyperechoic nodules.• Thin uniform thickness perilesionalhypoechoic halo• Well defined and regular margins• Perilesional egg shell like or coarsecalcification• Doppler signal of flow around thelesion.If most of these signs are present in athyroid nodule the diagnosis of benigndisease is highly reliable and no cytologicalassessment is needed. Conversely theultrasound signs for malignancy are:• Hypoechoic nodule• Irregular margins• Thick irregular halo• Doppler signal of flow within thelesion• Microcalcifiactions• Hypervascularity• Invasion of vessels and adjacentstructures• Vessel encasementThe feature with the highestsensitivity is solid composition;however, this feature has a fairly lowpositive predictive value. The featurewith the highest positive predictivevalue is the presence ofmicrocalcifications. However thisfeature has low sensitivity. Acombination of these featuresimproves the positive predictive valueof US to some extent.The detection of additional occultnodules in patients with clinicallysolitary lesion though pathognomonicfor benign goitre, it does not totallyrule out malignancy 7 . In as many as33%-64% of patients with thyroid cancerat least one associated benign nodulewas found either surgically or atultrasound. When multinodularity isdetected each nodule should be carefullystudied. If all of them show the samecharacteristic pattern for goitrous nodules, cytological assessment is not strictlyneeded and the patient can be followedwith periodic scans. Nodules withsuspicious ultrasound criteria shouldunder go further assessment with FNA/biopsy.40<strong>Journal</strong> of Postgraduate Medical Education, Training & ResearchVol. I, No. I & II