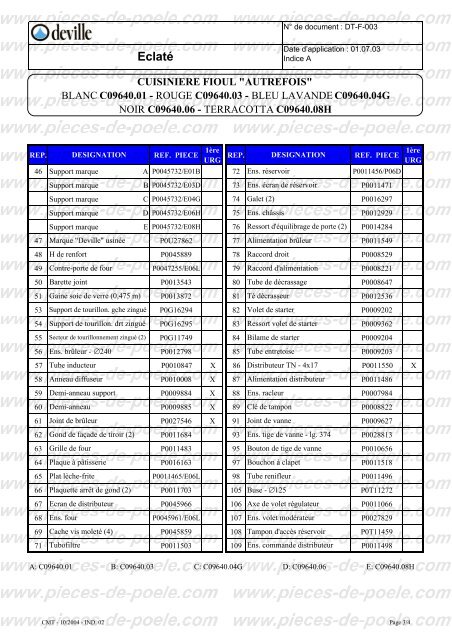
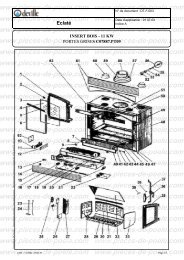
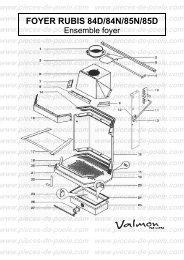
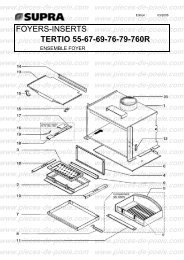
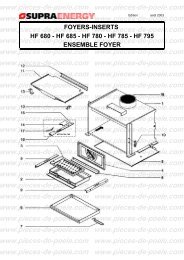
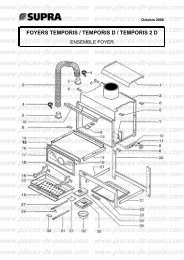
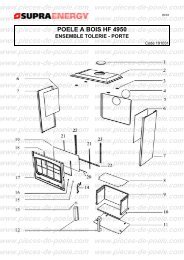
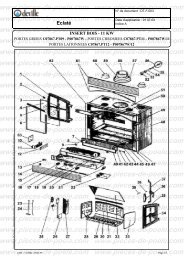
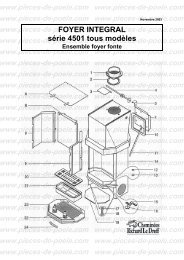
télécharger la vue éclatée
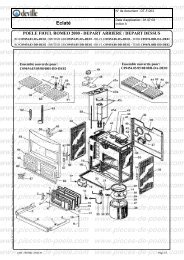
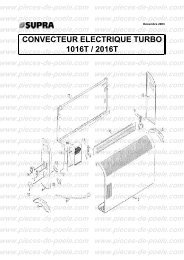
télécharger la vue éclatée
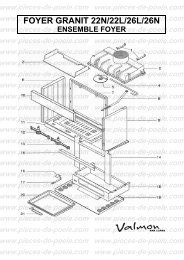
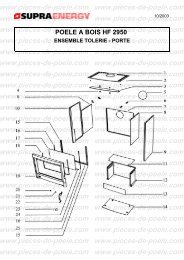
télécharger la vue éclatée
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
the HIV/hepatitis C coinfection clinic at the Miriam Hospitalin Providence, Rhode Is<strong>la</strong>nd.MethadoneMethadone is a synthetic opiate that has been used formore than 30 years to treat opioid dependence. Methadoneis a full opioid agonist, which means that it bindsto and activates opioid receptors. Low-dose methadone(30–60 mg/day) stops withdrawal symptoms. Higherdoses (80–120 mg/day) also reduce drug cravings anddiscourage opiate use by preventing people from feelingthe effects of opiates.Methadone is taken orally, once daily. Methadoneoverdose is possible, particu<strong>la</strong>rly when it is combinedwith antidepressants, alcohol, or cocaine.Methadone has significant drug–drug interactionswith some antiretroviral agents (see insert, Table 1). Itinteracts with several psychiatric medications, includingamitriptyline (E<strong>la</strong>vil), fluvoxamine (Luvox), desipramine(Norpramin), risperidone (Risperdal), quetiapine (Seroquel),carbamazepine (Tegretol), diazepam (Valium), andmidazo<strong>la</strong>m (Versed). 14 Methadone is avai<strong>la</strong>ble throughopioid treatment programs regu<strong>la</strong>ted by the SubstanceAbuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAM-HSA) Center for Substance Abuse Treatment.BuprenorphineBuprenorphine is a semisynthetic opioid that preventswithdrawal symptoms. Because it is a partial opioid agonist,buprenorphine does not stimu<strong>la</strong>te the same degreeof activity at the brain’s opioid receptors as full opioidagonists do (e.g., heroin, morphine, oxycontin, fentanyl,and methadone). As a result, people using buprenorphinemay still experience euphoria and become physicallydependent, but to a lesser extent than occurs withfull agonists. Buprenorphine reduces drug cravings andprevents people from feeling the effects of opiates byfirst knocking them off the brain’s opioid receptors andthen tightly binding to and blocking the receptors.In 2002, the FDA approved two forms of buprenorphineto treat opioid dependence: Subutex (a white,oval-shaped tablet that contains only buprenorphine)and Suboxone (an orange, hexagonal pill containing fourparts buprenorphine to one part naloxone). Naloxone isan opioid antagonist; it binds to and blocks opioid receptors.Suboxone was created to discourage buprenorphinediversion, because buprenorphine can produce a“high” when people not dependent on opiods inject it.Naloxone causes withdrawal symptoms when injectedbut not when taken orally.Buprenorphine reaches its full effect (known as the“ceiling effect”) at 16 to 32 mg. Overdose is less likely withbuprenorphine than with full opioid agonists, but it canoccur when buprenorphine is used with <strong>la</strong>rge amountsof alcohol or benzodiazepines (i.e., medications such asdiazepam, which are used to treat insomnia, anxiety, orseizures). Physicians need to evaluate coadministrationof buprenorphine and benzodiazepines.Buprenorphine has fewer drug–drug interactionswith antiretroviral agents than does methadone (seeTable 1). Interactions between buprenorphine and psychiatricmedications have not been studied in humans,except for citalopram (Celexa) and sertraline (Zoloft);neither drug has clinically significant interactions withbuprenorphine. 14Doctors can obtain a waiver allowing them to prescribebuprenorphine. The Drug Addiction Treatment Actof 2000 (DATA 2000) waiver allows primary care physiciansto treat 30 patients (see “Online Resources,” p. 7). After ayear, approved prescribers can apply for an exemption totreat up to 100 patients. SAMHSA estimates that 19,000physicians are certified to prescribe buprenorphine in theUnited States. DATA 2000 waivers allow SUD treatment tobecome integrated into HIV primary care.MAT AND HIV PRIMARY CAREMAT with buprenorphine is an important option for patientswho want to stop opioid use without making dailyvisits to a metha done clinic or going to a drug treatmentprogram. Some people may not be comfortable disclosingtheir HIV status during drug treatment, or they mayrequire medical or mental health care that is not alwaysBUPRENORPHINE INITIATIVEThe Ryan White Special Projects of National Significance(SPNS) Program has funded the BuprenorphineInitiative to assess feasibility and effectiveness ofintegrating buprenorphine treatment for opioidabuse into HIV primary care settings at 10 demonstrationsites. HRSA will be releasing a monographof findings from the Buprenorphine Initiative inSummer 2011. To learn more about the project,visit: http://hab.hrsa.gov/special/bup_index.htm.3