2017 HCHB_digital
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
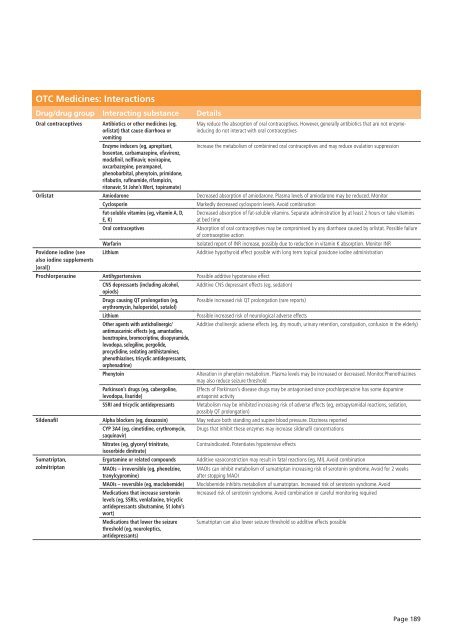
OTC Medicines: Interactions<br />
Drug/drug group Interacting substance Details<br />
Oral contraceptives<br />
Antibiotics or other medicines (eg,<br />
orlistat) that cause diarrhoea or<br />
vomiting<br />
Enzyme inducers (eg, aprepitant,<br />
bosentan, carbamazepine, efavirenz,<br />
modafinil, nelfinavir, nevirapine,<br />
oxcarbazepine, perampanel,<br />
phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone,<br />
rifabutin, rufinamide, rifampicin,<br />
ritonavir, St John’s Wort, topiramate)<br />
May reduce the absorption of oral contraceptives. However, generally antibiotics that are not enzymeinducing<br />
do not interact with oral contraceptives<br />
Increase the metabolism of combinined oral contraceptives and may reduce ovulation suppression<br />
Orlistat Amiodarone Decreased absorption of amiodarone. Plasma levels of amiodarone may be reduced. Monitor<br />
Cyclosporin<br />
Markedly decreased cyclosporin levels. Avoid combination<br />
Povidone iodine (see<br />
also iodine supplements<br />
[oral])<br />
Fat-soluble vitamins (eg, vitamin A, D,<br />
E, K)<br />
Oral contraceptives<br />
Warfarin<br />
Lithium<br />
Decreased absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. Separate administration by at least 2 hours or take vitamins<br />
at bed time<br />
Absorption of oral contraceptives may be compromised by any diarrhoea caused by orlistat. Possible failure<br />
of contraceptive action<br />
Isolated report of INR increase, possibly due to reduction in vitamin K absorption. Monitor INR<br />
Additive hypothyroid effect possible with long term topical povidone iodine administration<br />
Prochlorperazine Antihypertensives Possible additive hypotensive effect<br />
CNS depressants (including alcohol, Additive CNS depressant effects (eg, sedation)<br />
opiods)<br />
Drugs causing QT prolongation (eg, Possible increased risk QT prolongation (rare reports)<br />
erythromycin, haloperidol, sotalol)<br />
Lithium<br />
Possible increased risk of neurological adverse effects<br />
Other agents with anticholinergic/ Additive cholinergic adverse effects (eg, dry mouth, urinary retention, constipation, confusion in the elderly)<br />
antimuscarinic effects (eg, amantadine,<br />
benztropine, bromocriptine, disopyramide,<br />
levodopa, selegiline, pergolide,<br />
procyclidine, sedating antihistamines,<br />
phenothiazines, tricyclic antidepressants,<br />
orphenadrine)<br />
Phenytoin<br />
Alteration in phenytoin metabolism. Plasma levels may be increased or decreased. Monitor.Phenothiazines<br />
may also reduce seizure threshold<br />
Parkinson’s drugs (eg, cabergoline,<br />
levodopa, lisuride)<br />
SSRI and tricyclic antidepressants<br />
Effects of Parkinson’s disease drugs may be antagonised since prochlorperazine has some dopamine<br />
antagonist activity<br />
Metabolism may be inhibited increasing risk of adverse effects (eg, extrapyramidal reactions, sedation,<br />
possibly QT prolongation)<br />
Sildenafil Alpha blockers (eg, doxazosin) May reduce both standing and supine blood pressure. Dizziness reported<br />
CYP 3A4 (eg, cimetidine, erythromycin, Drugs that inhibit these enzymes may increase sildenafil concentrations<br />
saquinavir)<br />
Nitrates (eg, glyceryl trinitrate,<br />
Contraindicated. Potentiates hypotensive effects<br />
isosorbide dinitrate)<br />
Sumatriptan,<br />
zolmitriptan<br />
Ergotamine or related compounds Additive vasoconstriction may result in fatal reactions (eg, MI). Avoid combination<br />
MAOIs – irreversible (eg, phenelzine,<br />
tranylcypromine)<br />
MAOIs – reversible (eg, moclobemide)<br />
Medications that increase serotonin<br />
levels (eg, SSRIs, venlafaxine, tricyclic<br />
antidepressants sibutramine, St John’s<br />
wort)<br />
Medications that lower the seizure<br />
threshold (eg, neuroleptics,<br />
antidepressants)<br />
MAOIs can inhibit metabolism of sumatriptan increasing risk of serotonin syndrome. Avoid for 2 weeks<br />
after stopping MAOI<br />
Moclobemide inhibits metabolism of sumatriptan. Increased risk of serotonin syndrome. Avoid<br />
Increased risk of serotonin syndrome. Avoid combination or careful monitoring required<br />
Sumatriptan can also lower seizure threshold so additive effects possible<br />
Page 189