2017 HCHB_digital
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
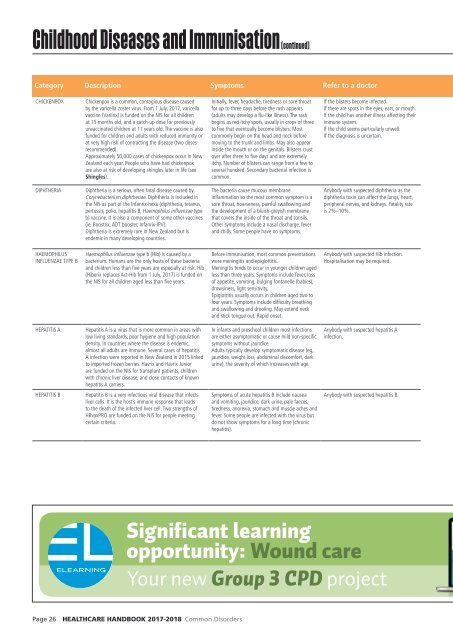
Childhood Diseases and Immunisation (continued)<br />
Category Description Symptoms Refer to a doctor<br />
CHICKENPOX<br />
Chickenpox is a common, contagious disease caused<br />
by the varicella zoster virus. From 1 July, <strong>2017</strong>, varicella<br />
vaccine (Varilrix) is funded on the NIS for all children<br />
at 15 months old, and a catch-up dose for previously<br />
unvaccinated children at 11 years old. The vaccine is also<br />
funded for children and adults with reduced immunity or<br />
at very high risk of contracting the disease (two doses<br />
recommended).<br />
Approximately 50,000 cases of chickenpox occur in New<br />
Zealand each year. People who have had chickenpox<br />
are also at risk of developing shingles later in life (see<br />
Shingles).<br />
Initially, fever, headache, tiredness or sore throat<br />
for up to three days before the rash appears<br />
(adults may develop a flu-like illness). The rash<br />
begins as red itchy spots, usually in crops of three<br />
to five that eventually become blisters. Most<br />
commonly begin on the head and neck before<br />
moving to the trunk and limbs. May also appear<br />
inside the mouth or on the genitals. Blisters crust<br />
over after three to five days and are extremely<br />
itchy. Number of blisters can range from a few to<br />
several hundred. Secondary bacterial infection is<br />
common.<br />
If the blisters become infected.<br />
If there are spots in the eyes, ears, or mouth.<br />
If the child has another illness affecting their<br />
immune system.<br />
If the child seems particularly unwell.<br />
If the diagnosis is uncertain.<br />
DIPHTHERIA<br />
Diphtheria is a serious, often fatal disease caused by<br />
Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Diphtheria is included in<br />
the NIS as part of the Infanrix-hexa (diphtheria, tetanus,<br />
pertussis, polio, hepatitis B, Haemophilus influenzae type<br />
b) vaccine. It is also a component of some other vaccines<br />
(ie, Boostrix, ADT booster, Infanrix-IPV).<br />
Diphtheria is extremely rare in New Zealand but is<br />
endemic in many developing countries.<br />
The bacteria cause mucous membrane<br />
inflammation so the most common symptom is a<br />
sore throat, hoarseness, painful swallowing and<br />
the development of a bluish-greyish membrane<br />
that covers the inside of the throat and tonsils.<br />
Other symptoms include a nasal discharge, fever<br />
and chills. Some people have no symptoms.<br />
Anybody with suspected diphtheria as the<br />
diphtheria toxin can affect the lungs, heart,<br />
peripheral nerves, and kidneys. Fatality rate<br />
is 2%–10%.<br />
HAEMOPHILUS<br />
INFLUENZAE TYPE B<br />
Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) is caused by a<br />
bacterium. Humans are the only hosts of these bacteria<br />
and children less than five years are especially at risk. Hib<br />
(Hiberix replaces Act-Hib from 1 July, <strong>2017</strong>) is funded on<br />
the NIS for all children aged less than five years.<br />
Before immunisation, most common presentations<br />
were meningitis and epiglottitis.<br />
Meningitis tends to occur in younger children aged<br />
less than three years. Symptoms include fever, loss<br />
of appetite, vomiting, bulging fontanelle (babies),<br />
drowsiness, light sensitivity.<br />
Epiglottitis usually occurs in children aged two to<br />
four years. Symptoms include difficulty breathing<br />
and swallowing and drooling. May extend neck<br />
and stick tongue out. Rapid onset.<br />
Anybody with suspected Hib infection.<br />
Hospitalisation may be required.<br />
HEPATITIS A<br />
Hepatitis A is a virus that is more common in areas with<br />
low living standards, poor hygiene and high population<br />
density. In countries where the disease is endemic,<br />
almost all adults are immune. Several cases of hepatitis<br />
A infection were reported in New Zealand in 2015 linked<br />
to imported frozen berries. Havrix and Havrix Junior<br />
are funded on the NIS for transplant patients, children<br />
with chronic liver disease, and close contacts of known<br />
hepatitis A carriers.<br />
In infants and preschool children most infections<br />
are either asymptomatic or cause mild non-specific<br />
symptoms without jaundice.<br />
Adults typically develop symptomatic disease (eg,<br />
jaundice, weight loss, abdominal discomfort, dark<br />
urine), the severity of which increases with age.<br />
Anybody with suspected hepatitis A<br />
infection.<br />
HEPATITIS B<br />
Hepatitis B is a very infectious viral disease that infects<br />
liver cells. It is the host’s immune response that leads<br />
to the death of the infected liver cell. Two strengths of<br />
HBvaxPRO are funded on the NIS for people meeting<br />
certain criteria.<br />
Symptoms of acute hepatitis B include nausea<br />
and vomiting, jaundice, dark urine, pale faeces,<br />
tiredness, anorexia, stomach and muscle aches and<br />
fever. Some people are infected with the virus but<br />
do not show symptoms for a long time (chronic<br />
hepatitis).<br />
Anybody with suspected hepatitis B.<br />
Significant learning<br />
opportunity: Wound care<br />
Your new Group 3 CPD project<br />
Page 26 HEALTHCARE HANDBOOK <strong>2017</strong>-2018 Common Disorders