Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
the brain. The individuals who volunteered were<br />
young healthy men and women ranging from 22 to 36<br />
years old with no record of obesity, hypertension,<br />
alcohol misuse, anxiety, and other mental disorders.<br />
They all went under MRI brain scans and took the<br />
NEO-Five-Factors-Inventory personality assessment.<br />
This assessment is made up of 60 questions, each<br />
question is a description of behavior which is<br />
answered on a five point Likert scale. The results show<br />
that individuals who scored high on neuroticism are<br />
characterized by higher cortical thickness with this<br />
trait having a negative correlation to cortical surface<br />
area and volume. Those who scored higher on<br />
extraversion are linked to higher cortical thickness,<br />
lower surface area and volume in the temporal gyrus<br />
and higher cortical folding. Higher openness scores<br />
are characterized by lower cortical thickness and have<br />
a positive correlation to cortical surface area, volume,<br />
and folding. Those with larger agreeableness scores<br />
have negative associations with cortical thickness,<br />
surface area, and volume. Rather, this trait shows<br />
increased folding in the area of the temporal lobe.<br />
Lastly, individuals whose scores are high in<br />
conscientiousness are connected to higher cortical<br />
thickness, lower surface area, volume, and folding in<br />
specific areas of the brain.<br />
As most of the findings in this study have been in the<br />
cortex, it is helpful to understand that humans have<br />
the most highly evolved cortex, more specifically the<br />
prefrontal cortex. This area of the brain distinguishes<br />
us from apes and other animals by our high level of<br />
social cognitive skills. These skills develop over our<br />
lifetime; for example, as we mature neuroticism<br />
decreases and conscientiousness increases as we are<br />
able to handle our emotions and reactions better. This<br />
is why there is a contrast between thicknesses for<br />
these two traits. However, those that suffer from<br />
mental illnesses will have brain different brain<br />
development and can show pronounced areas of the<br />
cortical regions that connect certain traits to their<br />
mental illness. There are limitations to this new<br />
research but it leads to open doors for mental illness<br />
research and detailed autopsies.<br />
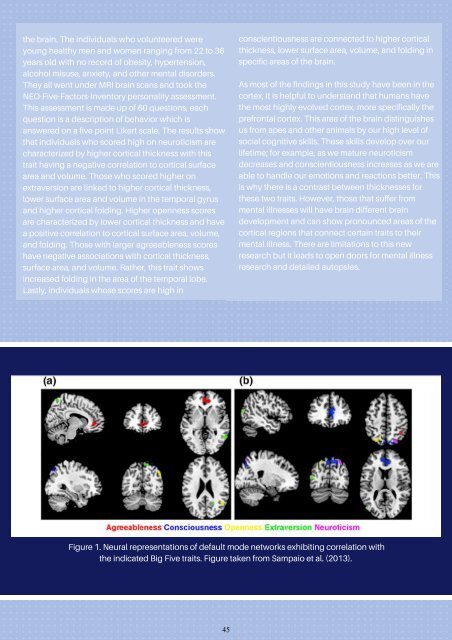
Figure 1. Neural representations of default mode networks exhibiting correlation with<br />
the indicated Big Five traits. Figure taken from Sampaio et al. (2013).