Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
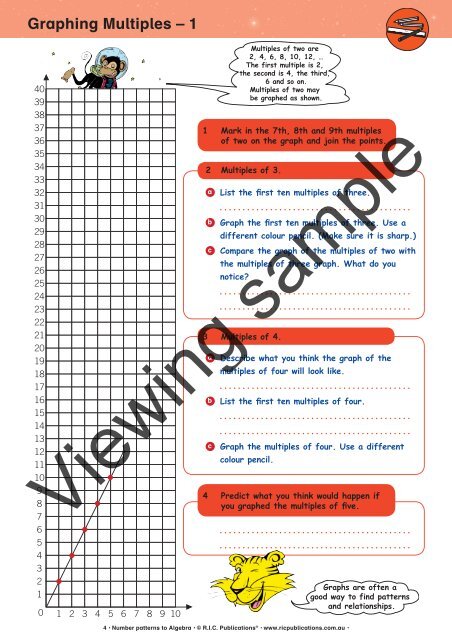
Graphing Multiples – 1<br />
Ruler<br />
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30<br />
Multiples of two are<br />
2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, …<br />
The first multiple is 2,<br />
the second is 4, the third,<br />
6 and so on.<br />
Multiples of two may<br />
be graphed as shown.<br />
1 Mark in the 7th, 8th and 9th multiples<br />
of two on the graph and join the points.<br />
2 Multiples of 3.<br />
a List the first ten multiples of three.<br />
b Graph the first ten multiples of three. Use a<br />
different colour pencil. (Make sure it is sharp.)<br />
c Compare the graph of the multiples of two with<br />
the multiples of three graph. What do you<br />
notice?<br />
3 Multiples of 4.<br />
a Describe what you think the graph of the<br />
multiples of four will look like.<br />
b List the first ten multiples of four.<br />
c Graph the multiples of four. Use a different<br />
colour pencil.<br />
Viewing sample<br />
4 Predict what you think would happen if<br />
you graphed the multiples of five.<br />
Graphs are often a<br />
good way <strong>to</strong> find patterns<br />
and relationships.<br />
4 • <strong>Number</strong> patterns <strong>to</strong> <strong>Algebra</strong> • © R.I.C. Publications ® • www.ricpublications.com.au •