Water & Wastewater Asia January/February 2022
Water & Wastewater Asia is an expert source of industry information, cementing its position as an indispensable tool for trade professionals in the water and wastewater industry. As the most reliable publication in the region, industry experts turn this premium journal for credible journalism and exclusive insight provided by fellow industry professionals. Water & Wastewater Asia incorporates the official newsletter of the Singapore Water Association (SWA).
Water & Wastewater Asia is an expert source of industry information, cementing its position as an indispensable tool for trade professionals in the water and wastewater industry. As the most reliable publication in the region, industry experts turn this premium journal for credible journalism and exclusive insight provided by fellow industry professionals. Water & Wastewater Asia incorporates the official newsletter of the Singapore Water Association (SWA).
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
ENVIRONMENTAL REPORT<br />
Contact was up to 10 minutes.<br />
Ozone was effective against all the<br />
micropollutants analysed, including<br />
Atenolol, Atenololsaure, Benzotriazol,<br />
Carbamazepine, Clarithomycin,<br />
Diclophenac, Gebapentin,<br />
Hydrochlorothiazid, Levetriazepam,<br />
Mefenamisnaure, Methyl-benzotriazo,<br />
Sulfamethoxazol, Trimetoprim,<br />
Valsartan, and Venlafaxin. Doubling<br />
the contact time made minimal<br />
difference in effectiveness.<br />
MULTI-BARRIER TREATMENT<br />
APPROACH TO CEC<br />
As seen in the examples above, we<br />
know ozone alone can effectively<br />
oxidise target pollutants. When ozone<br />
is combined with a biologically active<br />
filter (BAF), the result is a multi-barrier<br />
advanced bioactive filter process that<br />
provides several additional process<br />
benefits.<br />
Instead of the complete oxidation of<br />
the targeted organic compounds with<br />
ozone alone, the De Nora Tetra ABF<br />
bioactive filter uses a lower dose of<br />
ozone to partially oxidise and break<br />
the long chain recalcitrant carbon<br />
into smaller biodegradable organic<br />
compounds. The smaller chain organic<br />
compounds are then removed in the<br />
downstream BAF. This process allows<br />
for lower ozone doses, and lower<br />
capacity ozone equipment versus<br />
conventional ozone only treatment.<br />
This, in turn, may reduce capital costs<br />
and energy consumption. In addition,<br />
the ABF process does not require<br />
upstream reverse osmosis (RO) or UF<br />
membranes commonly used with other<br />
types of direct and indirect water reuse<br />
schemes.<br />
The synergy created by combining<br />
ozone and BAF treatment has proven<br />
effective in removing common DBPs<br />
and provides a biologically stable<br />
effluent by oxidising assimilable<br />
organic carbon (AOC) generated by<br />
ozonation alone. This may reduce the<br />
risk of downstream biofilm growth in<br />
the filter.<br />
ABF USED FOR TOC REMOVAL<br />
AND DBP REDUCTION<br />
In the summer of 2019, a 9 MGD<br />
water treatment plant in Pennsylvania<br />
commissioned a De Nora pilot to<br />
evaluate the use of ozone and BAF<br />
to treat settled surface water. They<br />
were hoping to improve their TOC<br />
removal and achieve significant DBP<br />
reduction without adversely impacting<br />
current water quality performance.<br />
The existing plant has six filters at<br />
576sf/filter designed for 16 MGD.<br />
Media is 4-inch anthracite on top<br />
of 1-inch sand. A containerised<br />
ABF pilot was deployed featuring a<br />
20-foot-long, high-cube container with<br />
ozone generation equipment having<br />
a capacity of 20g/h, and two 8-inch<br />
diameter BAF with capacity to handle<br />
a total flow of 6gpm. The system is<br />
operated automatically, with remote<br />
control and monitoring capability<br />
through cellular communication.<br />
Specific objectives for the pilot were<br />
to achieve close to a 50% reduction in<br />
raw water TOC that could be reliably<br />
and consistently achieved with the full<br />
combined treatment train throughout<br />
the year. In 2017, raw water TOC<br />
reached 10mg/litre. With respect to<br />
DBP reduction, the pilot goal was to<br />
achieve a 25% reduction of the mean<br />
TTHM value and a 25% reduction of<br />
the mean HAA5 value. Additionally,<br />
all other regulated parameters would<br />
show no significant increase as<br />
compared to the plant values of the<br />
pilot testing period.<br />
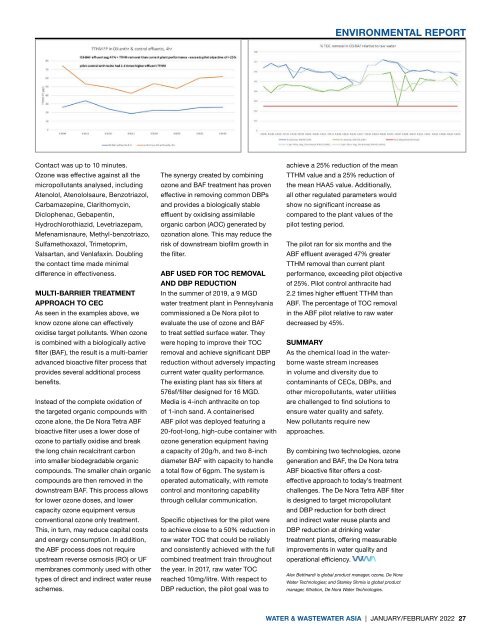
The pilot ran for six months and the<br />
ABF effluent averaged 47% greater<br />
TTHM removal than current plant<br />
performance, exceeding pilot objective<br />
of 25%. Pilot control anthracite had<br />
2.2 times higher effluent TTHM than<br />
ABF. The percentage of TOC removal<br />
in the ABF pilot relative to raw water<br />
decreased by 45%.<br />
SUMMARY<br />
As the chemical load in the waterborne<br />
waste stream increases<br />
in volume and diversity due to<br />
contaminants of CECs, DBPs, and<br />
other micropollutants, water utilities<br />
are challenged to find solutions to<br />
ensure water quality and safety.<br />
New pollutants require new<br />
approaches.<br />
By combining two technologies, ozone<br />
generation and BAF, the De Nora tetra<br />
ABF bioactive filter offers a costeffective<br />
approach to today’s treatment<br />
challenges. The De Nora Tetra ABF filter<br />
is designed to target micropollutant<br />
and DBP reduction for both direct<br />
and indirect water reuse plants and<br />
DBP reduction at drinking water<br />
treatment plants, offering measurable<br />
improvements in water quality and<br />
operational efficiency.<br />
Alex Bettinardi is global product manager, ozone, De Nora<br />
<strong>Water</strong> Technologies; and Stanley Shmia is global product<br />
manager, filtration, De Nora <strong>Water</strong> Technologies.<br />
WATER & WASTEWATER ASIA | JANUARY/FEBRUARY <strong>2022</strong> 27