Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection - Patient Guide 2022
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
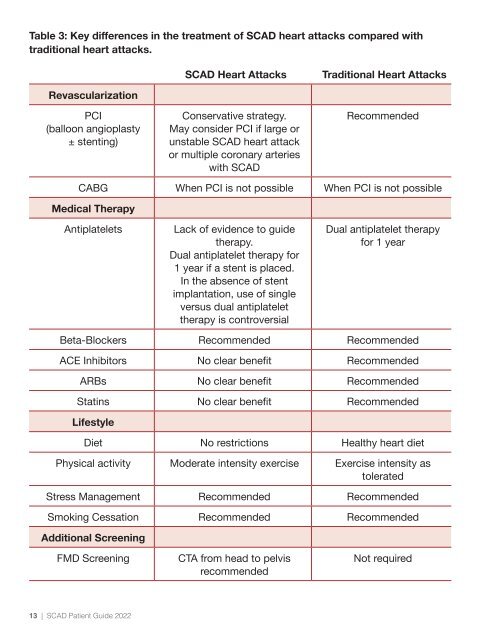
Table 3: Key differences in the treatment of SCAD heart attacks compared with<br />
traditional heart attacks.<br />
SCAD Heart Attacks<br />
Traditional Heart Attacks<br />
Revascularization<br />
PCI<br />
(balloon angioplasty<br />
± stenting)<br />
Conservative strategy.<br />
May consider PCI if large or<br />
unstable SCAD heart attack<br />
or multiple coronary arteries<br />
with SCAD<br />
Recommended<br />
CABG When PCI is not possible When PCI is not possible<br />
Medical Therapy<br />
Antiplatelets<br />
Lack of evidence to guide<br />
therapy.<br />
Dual antiplatelet therapy for<br />
1 year if a stent is placed.<br />
In the absence of stent<br />
implantation, use of single<br />
versus dual antiplatelet<br />
therapy is controversial<br />
Dual antiplatelet therapy<br />
for 1 year<br />
Beta-Blockers Recommended Recommended<br />
ACE Inhibitors No clear benefit Recommended<br />
ARBs No clear benefit Recommended<br />
Statins No clear benefit Recommended<br />
Lifestyle<br />
Diet No restrictions Healthy heart diet<br />
Physical activity Moderate intensity exercise Exercise intensity as<br />
tolerated<br />
Stress Management Recommended Recommended<br />
Smoking Cessation Recommended Recommended<br />
Additional Screening<br />
FMD Screening<br />
CTA from head to pelvis<br />
recommended<br />
Not required<br />
13 | SCAD <strong>Patient</strong> <strong>Guide</strong> <strong>2022</strong>