Etude par Sonde Atomique Tomographique de la formation de nano ...
Etude par Sonde Atomique Tomographique de la formation de nano ...
Etude par Sonde Atomique Tomographique de la formation de nano ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
tel-00751814, version 1 - 14 Nov 2012<br />
Chapter 2. Materials, experimental and simu<strong>la</strong>tion techniques<br />
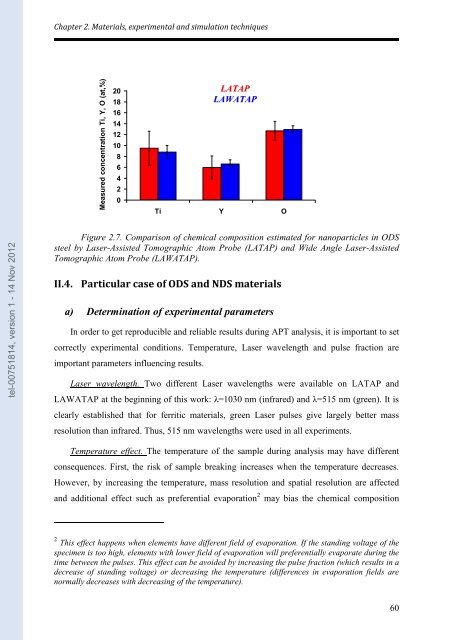
Measured concentration Ti, Y, O (at,%)<br />
20<br />
18<br />
16<br />
14<br />
12<br />
10<br />
8<br />
6<br />
4<br />
2<br />
0<br />
Figure 2.7. Com<strong>par</strong>ison of chemical composition estimated for <strong>nano</strong><strong>par</strong>ticles in ODS<br />
steel by Laser-Assisted Tomographic Atom Probe (LATAP) and Wi<strong>de</strong> Angle Laser-Assisted<br />
Tomographic Atom Probe (LAWATAP).<br />
II.4. Particu<strong>la</strong>r case of ODS and NDS materials<br />
a) Determination of experimental <strong>par</strong>ameters<br />
In or<strong>de</strong>r to get reproducible and reliable results during APT analysis, it is important to set<br />
correctly experimental conditions. Temperature, Laser wavelength and pulse fraction are<br />
important <strong>par</strong>ameters influencing results.<br />
LATAP<br />
LAWATAP<br />
core TAP<br />
core LAWATAP<br />
Ti Y O<br />
Laser wavelength. Two different Laser wavelengths were avai<strong>la</strong>ble on LATAP and<br />
LAWATAP at the beginning of this work: λ=1030 nm (infrared) and λ=515 nm (green). It is<br />
clearly established that for ferritic materials, green Laser pulses give <strong>la</strong>rgely better mass<br />
resolution than infrared. Thus, 515 nm wavelengths were used in all experiments.<br />
Temperature effect. The temperature of the sample during analysis may have different<br />
consequences. First, the risk of sample breaking increases when the temperature <strong>de</strong>creases.<br />
However, by increasing the temperature, mass resolution and spatial resolution are affected<br />
and additional effect such as preferential evaporation 2 may bias the chemical composition<br />
2 This effect happens when elements have different field of evaporation. If the standing voltage of the<br />
specimen is too high, elements with lower field of evaporation will preferentially evaporate during the<br />
time between the pulses. This effect can be avoi<strong>de</strong>d by increasing the pulse fraction (which results in a<br />
<strong>de</strong>crease of standing voltage) or <strong>de</strong>creasing the temperature (differences in evaporation fields are<br />
normally <strong>de</strong>creases with <strong>de</strong>creasing of the temperature).<br />
60