- Page 1 and 2: Workshop on Polari
- Page 3 and 4: Surface Analysis of Damaged Superla
- Page 5 and 6: High Brightness and High Polarizati
- Page 7 and 8: FIGURE 1. Schematic drawing of the
- Page 9 and 10: To be independent from possible ins
- Page 11 and 12: vacuum gauge (AxTRAN X-11,ULVAC). B
- Page 13 and 14: In order to research QE degradation
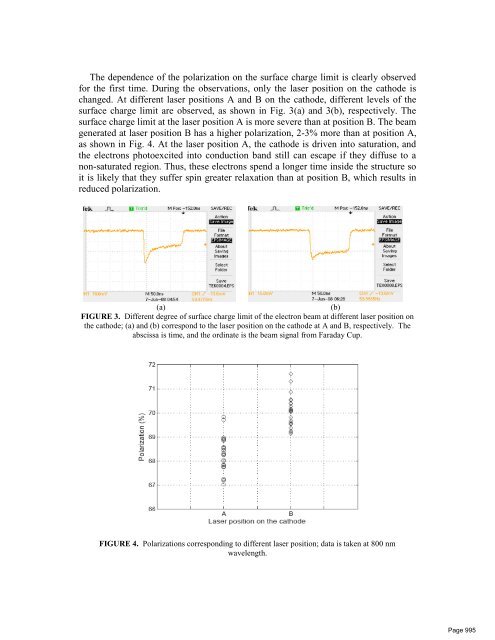
- Page 15 and 16: Polarized Photocathode R&D for Futu
- Page 17: charge limitation can be measured.
- Page 21 and 22: The most difficult task is to achie
- Page 23 and 24: The run with a small laser spot cen
- Page 25 and 26: Hydrogen Cleaning of Superlattice P
- Page 27 and 28: HABS Prep Load UHV Vessel Ion Pump
- Page 29 and 30: FIGURE 4. Comparison of results ach
- Page 31 and 32: Heidelberg photoelectron target and
- Page 33 and 34: However, it is emphasized here that
- Page 35 and 36: Atomic Hydrogen Treatment Atomic hy
- Page 37 and 38: Rydberg binding energy. In many cas
- Page 39 and 40: the ring dispersion and from fluctu
- Page 41 and 42: The valence band splitting ∆Ehh-l
- Page 43 and 44: will be achieved by taking the last
- Page 45 and 46: A Study of the Activated GaAs Surfa
- Page 47 and 48: diffraction (LEED) and auger electr
- Page 49 and 50: FIGURE 4. LEED pattern of the GaAs
- Page 51 and 52: HIGH POLARIZATION PHOTOEMITTER IMMU
- Page 53 and 54: QE (%) 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 650 Cs
- Page 55 and 56: Superlattice Photocathode Damage An
- Page 57 and 58: and reactivated between February 11
- Page 59 and 60: Discussion of SIMS data and Compari
- Page 61 and 62: MBE Growth of Graded Structures for
- Page 63 and 64: conduction miniband is higher that
- Page 65 and 66: GRADED ALUMINUM GALLIUM ARSENIDE SU
- Page 67 and 68: Three wafers were grown with differ
- Page 69 and 70:
FIGURE 10. Polarization and QE as a
- Page 71 and 72:
PHOTOCATHODE WITH NEA SURFACE USING
- Page 73 and 74:
FIGURE 2. Dependence of DOS on exci
- Page 75 and 76:
High Brightness and high polarizati
- Page 77 and 78:
Laser Substrate GaP 355 μm Zoom Bu
- Page 79 and 80:
process of NEA-PC with SL layers, o
- Page 81 and 82:
FIGURE 1. (a) Band-graded photocath
- Page 83 and 84:
Left (a): Homogeneous (HM) layer Ri
- Page 85 and 86:
K2CsSb Cathode Development John Sme
- Page 87 and 88:
for the potassium deposition. 40nm
- Page 89 and 90:
ias of 500V, with 60µA of emitted
- Page 91 and 92:
analyzing chamber are used for samp
- Page 93 and 94:
spectrum of the film was observed a
- Page 95 and 96:
Demo Free Electron Laser (FEL) [1]
- Page 97 and 98:
hours, or if the emitter returns at
- Page 99 and 100:
neon or argon would have helped pro
- Page 101 and 102:
for emittance compensation solenoid
- Page 103 and 104:
If one can make electrodes that do
- Page 105 and 106:
The last important parameter is cat
- Page 107 and 108:
Status of the ALICE Energy Recovery
- Page 109 and 110:
TABLE 1. Booster & main linac gradi
- Page 111 and 112:
• The beam was fully-characterise
- Page 113 and 114:
photocathode. This limitation means
- Page 115 and 116:
whilst focusing the heat onto the p
- Page 117 and 118:
Development of an electron gun for
- Page 119 and 120:
FIGURE 2. Preparation, loading, and
- Page 121 and 122:
may help to avoid electric field co
- Page 123 and 124:
from its neighbors. The core-to-win
- Page 125 and 126:
series connection and the output cu
- Page 127 and 128:
Low Emittance Electron Gun for XFEL
- Page 129 and 130:
FIGURE 3. Copper cathode and corres
- Page 131 and 132:
current in the secondary which oppo
- Page 133 and 134:
Equation (2) shows that the effect
- Page 135 and 136:
Generally, the equation for the rad
- Page 137 and 138:
High-Fidelity RF Gun Simulations wi
- Page 139 and 140:
Causal Moving Window The methods us
- Page 141 and 142:
(a) y / mm y / mm Transverse Distri
- Page 143 and 144:
studies like long term studies of p
- Page 145 and 146:
ehavior of the curves is independen
- Page 147 and 148:
In Fig. 4 the curve shows an ASTRA
- Page 149 and 150:
TABLE 1. RF cavity parameters calcu
- Page 151 and 152:
PASSBAND AND ON-AXIS FIELD DISTRIBU
- Page 153 and 154:
If the frequency shift on crest is
- Page 155 and 156:
In order to increase the quality fa
- Page 157 and 158:
THE EXPERIMENT The experimental set
- Page 159 and 160:
FIRST COOL-DOWN In the first cool-d
- Page 161 and 162:
Non Evaporable Getter (NEG) Pumps:
- Page 163 and 164:
Examples of Applications NEG pumps
- Page 165 and 166:
isotherms in a controlled and repro
- Page 167 and 168:
chemical gettering that results whe
- Page 169 and 170:
inside the photogun remains very go
- Page 171 and 172:
High Brightness and High Polarizati
- Page 173 and 174:
focusing lens is mounted on a trans
- Page 175 and 176:
of electron polarization obtained b
- Page 177 and 178:
FIGURE 7. Reduced brightness depend
- Page 179 and 180:
FIGURE 1. Mott polarimeter with two
- Page 181 and 182:
� ��� �� � ���
- Page 183 and 184:
Compton Polarimetry at ELSA Wolfgan
- Page 185 and 186:
In order to be detected, the Compto
- Page 187 and 188:
monitored after the interaction by
- Page 189 and 190:
where n + and n - are the counting
- Page 191 and 192:
Our test cavity (Figure 3.) consist
- Page 193 and 194:
Polarimetry at the Superconducting
- Page 195 and 196:
30-130 MEV MØLLER POLARIMETER A 30
- Page 197 and 198:
Benchmark studies among own and com
- Page 199 and 200:
d2z = ds2 d2x = ds2 eQ eQ 4πε0 m0
- Page 201 and 202:
ments of his tracing cord developin
- Page 203 and 204:
all requires a slot in the side for
- Page 205 and 206:
simulations in GPT show that these
- Page 207 and 208:
Polarized Positrons at Jefferson La
- Page 209 and 210:
GEANT4 [11]. Using Stokes parameter
- Page 211 and 212:
Ultimately, the shower of particles
- Page 213 and 214:
It was gratifying to hear about the
- Page 215 and 216:
gun/photocathode, and likely repres
- Page 217 and 218:
induced emittance growth, especiall
- Page 219 and 220:
PESP Workshop Prog
- Page 221 and 222:
PESP Posters Posters (17 total) •
- Page 223 and 224:
Clendenin, James SLAC National Acce
- Page 225 and 226:
McCarter, James Jefferson Lab 12000
- Page 227 and 228:
Surles-Law, Ken Jefferson Lab 12050