Hazardous Waste Disposal with Thermal Oxidation - John Zink ...
Hazardous Waste Disposal with Thermal Oxidation - John Zink ...
Hazardous Waste Disposal with Thermal Oxidation - John Zink ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
WASTE EXAMPLE PRODUCTS OF OXIDATION<br />
Gas<br />
Liquid<br />
Fuel<br />
Air<br />
<strong>Waste</strong><br />
CO 2<br />
H 2<br />
CO<br />
H 2O<br />
N 2<br />
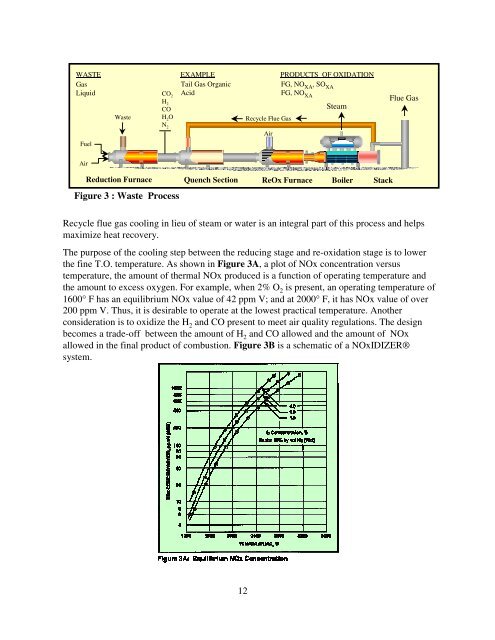
Figure 3 : <strong>Waste</strong> Process<br />
Tail Gas Organic<br />
Acid<br />
Reduction Furnace Quench Section<br />
Recycle flue gas cooling in lieu of steam or water is an integral part of this process and helps<br />
maximize heat recovery.<br />
The purpose of the cooling step between the reducing stage and re-oxidation stage is to lower<br />
the fine T.O. temperature. As shown in Figure 3A, a plot of NOx concentration versus<br />
temperature, the amount of thermal NOx produced is a function of operating temperature and<br />
the amount to excess oxygen. For example, when 2% O 2 is present, an operating temperature of<br />
1600° F has an equilibrium NOx value of 42 ppm V; and at 2000° F, it has NOx value of over<br />
200 ppm V. Thus, it is desirable to operate at the lowest practical temperature. Another<br />
consideration is to oxidize the H 2 and CO present to meet air quality regulations. The design<br />
becomes a trade-off between the amount of H 2 and CO allowed and the amount of NOx<br />
allowed in the final product of combustion. Figure 3B is a schematic of a NOxIDIZER®<br />
system.<br />
12<br />
Recycle Flue Gas<br />
Air<br />
FG, NO XA ,SO XA<br />
FG, NO XA<br />
ReOx Furnace<br />
Steam<br />
Boiler<br />
Stack<br />
Flue Gas