- Page 1 and 2: MECANICA DE MATERIALES PRACTICAS Y
- Page 3 and 4: PROLOGO La Mecánica de Materiales,
- Page 5 and 6: MECANICA DE MATERIALES (CI80) PRACT
- Page 7 and 8: 6. ¿Qué esfuerzos se producirán
- Page 9 and 10: 3. Determinamos los esfuerzos:
- Page 11 and 12: T 10.10 0,0040 .0,75 14,5.10 .1,30
- Page 13 and 14: 2. Se tiene un peso de 3T sostenido
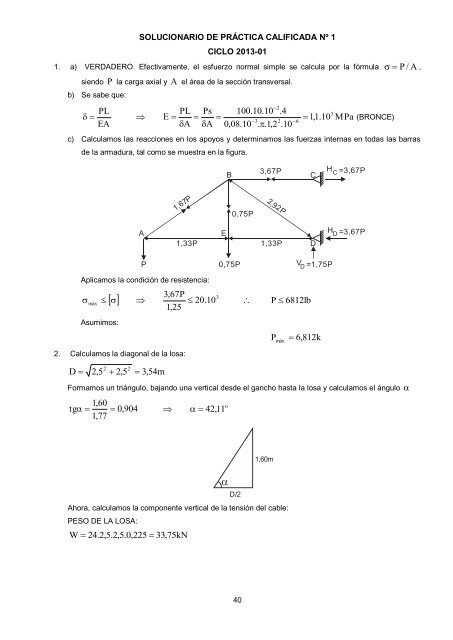
- Page 15 and 16: SOLUCIONARIO DE PRÁCTICA CALIFICAD
- Page 17 and 18: o o F Y 0 239,062 F2sen30 (F2 3
- Page 19 and 20: 19 De donde: c c al al c c al al c
- Page 21 and 22: A B D E 2 C 3. Determine el alargam
- Page 23 and 24: SOLUCIONARIO DE PRÁCTICA CALIFICAD
- Page 25 and 26: c 40.10 10.10 3 4 40MPa El diag
- Page 27 and 28: Reemplazamos (b) en (a): En consecu
- Page 29 and 30: 2 b x L x SECCIÓN TRANSVERSAL b t
- Page 31 and 32: SOLUCIONARIO DE PRÁCTICA CALIFICAD
- Page 33 and 34: P B B P=40kN C 4m 2m D Luego, la ba
- Page 35 and 36: C O B R E A B 1,1m RB A L U M I N
- Page 37 and 38: MECANICA DE MATERIALES (CI80) PRACT
- Page 39: L 1 2 A B a a 6. En el sistema estr
- Page 43 and 44: Luego: E f f E Reemplazamos (f)
- Page 45 and 46: MECANICA DE MATERIALES (CI80) EXAME
- Page 47 and 48: SOLUCIONARIO DE EXAMEN PARCIAL CICL
- Page 49 and 50: X 20 10 3 3 2 I3 XY Y YZ 10 0 10
- Page 51 and 52: Reducción T0 Tf del par T 0 (100
- Page 53 and 54: MECANICA DE MATERIALES (CI80) EXAME
- Page 55 and 56: 1. Como: SOLUCIONARIO DE EXAMEN PAR
- Page 57 and 58: TBL T(3L / 4) GI GI p p 2T(L / 4)
- Page 59 and 60: MECANICA DE MATERIALES (CI80) EXAME
- Page 61 and 62: 1. Como: Luego: Dividimos (b) entre
- Page 63 and 64: Restamos (f) menos (e): Además: De
- Page 65 and 66: 65 d a d b d x x L Además: 4 t d I
- Page 67 and 68: P a a a 4. Refiriéndose a la barra
- Page 69 and 70: 1. Por dato del problema: SOLUCIONA
- Page 71 and 72: Efectuando operaciones obtenemos: 3
- Page 73 and 74: MECANICA DE MATERIALES (CI80) EXAME
- Page 75 and 76: 1. Se sabe que: SOLUCIONARIO DE EXA
- Page 77 and 78: c) Determinamos el esfuerzo tangenc
- Page 79 and 80: MECANICA DE MATERIALES (CI80) PRACT
- Page 81 and 82: SOLUCIONARIO DE PRÁCTICA CALIFICAD
- Page 83 and 84: I z 0,16.0,3 12 3 0,05.0,26 2 12
- Page 85 and 86: CONCRETO: M c máx máx máx c y
- Page 87 and 88: 4. Elegir el perfil I más adecuado
- Page 89 and 90: y máx d I Z 4 d 4. 64 d 4 2
- Page 91 and 92:
Aplicamos la condición de resisten
- Page 93 and 94:
MECANICA DE MATERIALES (CI80) PRACT
- Page 95 and 96:
SOLUCIONARIO DE PRÁCTICA CALIFICAD
- Page 97 and 98:
M x 1,5m 0,5P 22,41 P 44,82kN
- Page 99 and 100:
6. Esquematizamos para la zona de c
- Page 101 and 102:
Se pide: a) Elegir el perfil I más
- Page 103 and 104:
1. Por dato del problema: sup in
- Page 105 and 106:
B V máx I Z S b B Z 3 42.10 .159
- Page 107 and 108:
VS (V)(0,375b B 3 Z B' 1,519 0,
- Page 109 and 110:
Posteriormente, aplicamos las condi
- Page 111 and 112:
C 1,1m A q 1,6m I B 1,1m D SECCION
- Page 113 and 114:
A 0,8q VIGA CD: Graficamos el diagr
- Page 115 and 116:
Asumimos: P máx 11,27kN De esta m
- Page 117 and 118:
De los resultados obtenidos, elegim
- Page 119 and 120:
4. METODO DE LA VIGA CONJUGADA. La
- Page 121 and 122:
Orientamos el momento en A en senti
- Page 123 and 124:
4. a) BARRA ESCALONADA PL 2E 2 PL 2
- Page 125 and 126:
MECANICA DE MATERIALES (CI80) PRACT
- Page 127 and 128:
SOLUCIONARIO DE PRÁCTICA CALIFICAD
- Page 129 and 130:
PRINCIPIO DE CONTINUIDAD: c) Si x
- Page 131 and 132:
Ahora, lo transformamos en viga con
- Page 133 and 134:
4. METODO DE LA VIGA CONJUGADA. Par
- Page 135 and 136:
CONDICIONES: a) Si x 0 0 b) Si
- Page 137 and 138:
3 L a x EIy P C1x C L 6 CO
- Page 139 and 140:
Para determinar la ecuación de la
- Page 141 and 142:
4. METODO DE LA VIGA CONJUGADA. Par
- Page 143 and 144:
De esta manera, la ecuación quedar
- Page 145 and 146:
VA x EIy' 2 VA x EIy 6 CONDICIONE
- Page 147 and 148:
5. Liberamos el apoyo en C, lo reem
- Page 149 and 150:
4. METODO DE LA VIGA CONJUGADA. Par
- Page 151 and 152:
Px EIy' 2 Px EIy 6 2 3 3P(x a)
- Page 153 and 154:
ECUACION DE LA CURVA DE DEFLEXION:
- Page 155 and 156:
Con los diagramas obtenidos, aplica
- Page 157 and 158:
MECANICA DE MATERIALES (CI80) EXAME
- Page 159 and 160:
SOLUCIONARIO DE EXAMEN FINAL CICLO
- Page 161 and 162:
Luego: 1 2. EI PL 3EI L 1 EI 1
- Page 163 and 164:
Luego: 227,276P 5509,158 0 EA P
- Page 165 and 166:
4. TEOREMA DE CASTIGLIANO. Una viga
- Page 167 and 168:
Determinamos la deflexión vertical
- Page 169 and 170:
DESPLAZAMIENTO HORIZONTAL EN “D
- Page 171 and 172:
TRAMO BC ( 0 x 3) M I M V V x 10
- Page 173 and 174:
4. TEOREMA DE CASTIGLIANO. Para la
- Page 175 and 176:
Ahora, aplicamos una carga vertical
- Page 177 and 178:
TRAMO AB ( 0 x 3a) M I M I Q P1
- Page 179 and 180:
c) 25,625 d) + 15,625 14,375 112,5
- Page 181 and 182:
4. TEOREMA DE CASTIGLIANO. Para la
- Page 183 and 184:
0,1111 El signo negativo, indica qu
- Page 185 and 186:
TRAMO AB ( 0 x L) M I M kM N
- Page 187 and 188:
EA 2EA EA MECANICA DE MATERIALES (C
- Page 189 and 190:
SOLUCIONARIO DE EXAMEN FINAL CICLO
- Page 191 and 192:
PENDIENTE EN “A”: A 1 EI 1
- Page 193 and 194:
TRAMO II-II ( 1 x 2) M II M H II
- Page 195:
INDICE PROLOGO…………………