Monofase Card per Test di Amfetamina (Urina ... - Intermedical.it
Monofase Card per Test di Amfetamina (Urina ... - Intermedical.it
Monofase Card per Test di Amfetamina (Urina ... - Intermedical.it
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
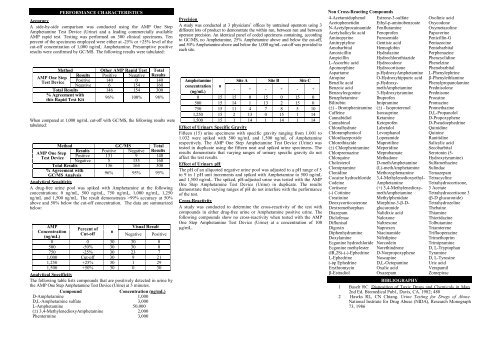
PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS<br />
Accuracy<br />
A side-by-side comparison was conducted using the AMP One Step<br />
Amphetamine <strong>Test</strong> Device (Urine) and a lea<strong>di</strong>ng commercially available<br />
AMP rapid test. <strong>Test</strong>ing was <strong>per</strong>formed on 300 clinical specimens. Ten<br />
<strong>per</strong>cent of the specimens employed were e<strong>it</strong>her at -25% or +25% level of the<br />
cut-off concentration of 1,000 ng/mL Amphetamine. Presumptive pos<strong>it</strong>ive<br />
results were confirmed by GC/MS. The following results were tabulated:<br />
Method<br />
Results<br />
AMP One Step<br />
<strong>Test</strong> Device<br />
Pos<strong>it</strong>ive<br />
Negative<br />
Other AMP Rapid <strong>Test</strong><br />
Pos<strong>it</strong>ive Negative<br />
140 0<br />
6 154<br />
Total<br />
Results<br />
140<br />
160<br />
Total Results 146 154 300<br />
% Agreement w<strong>it</strong>h<br />
this Rapid <strong>Test</strong> K<strong>it</strong><br />
96% 100% 98%<br />
When compared at 1,000 ng/mL cut-off w<strong>it</strong>h GC/MS, the following results were<br />
tabulated:<br />
Method<br />
Results<br />
AMP One Step<br />
<strong>Test</strong> Device<br />
Pos<strong>it</strong>ive<br />
Negative<br />
GC/MS<br />
Pos<strong>it</strong>ive Negative<br />
131 9<br />
5 155<br />
Total<br />
Results<br />
140<br />
160<br />
Total Results 136 164 300<br />
% Agreement w<strong>it</strong>h<br />
GC/MS Analysis<br />
Analytical Sens<strong>it</strong>iv<strong>it</strong>y<br />
96% 95% 95%<br />
A drug-free urine pool was spiked w<strong>it</strong>h Amphetamine at the following<br />
concentrations: 0 ng/mL, 500 ng/mL, 750 ng/mL, 1,000 ng/mL, 1,250<br />
ng/mL and 1,500 ng/mL. The result demonstrates >99% accuracy at 50%<br />
above and 50% below the cut-off concentration. The data are summarized<br />
below:<br />
AMP<br />
Concentration<br />
(ng/mL)<br />
Percent of<br />
Cut-off<br />
n<br />
Visual Result<br />
Negative Pos<strong>it</strong>ive<br />
0 0 30 30 0<br />
500 -50% 30 30 0<br />
750 -25% 30 23 7<br />
1,000 Cut-off 30 9 21<br />
1,250 +25% 30 1 29<br />
1,500 +50% 30 0 30<br />
Analytical Specific<strong>it</strong>y<br />
The following table lists compounds that are pos<strong>it</strong>ively detected in urine by<br />
the AMP One Step Amphetamine <strong>Test</strong> Device (Urine)at 5 minutes.<br />
Compound Concentration (ng/mL)<br />
D-Amphetamine 1,000<br />
D,L-Amphetamine sulfate 3,000<br />
L-Amphetamine 50,000<br />
() 3,4-Methylene<strong>di</strong>oxyAmphetamine 2,000<br />
Phentermine 3,000<br />
Precision<br />
A study was conducted at 3 physicians’ offices by untrained o<strong>per</strong>ators using 3<br />
<strong>di</strong>fferent lots of product to demonstrate the w<strong>it</strong>hin run, between run and between<br />
o<strong>per</strong>ator precision. An identical panel of coded specimens containing, accor<strong>di</strong>ng<br />
to GC/MS, no Amphetamine, 25% Amphetamine above and below the cut-off,<br />
and 50% Amphetamine above and below the 1,000 ng/mL cut-off was provided to<br />
each s<strong>it</strong>e.<br />
Amphetamine<br />
S<strong>it</strong>e A S<strong>it</strong>e B S<strong>it</strong>e C<br />
concentration<br />
(ng/mL)<br />
n<br />
- + - + - +<br />
0 15 15 0 15 0 15 0<br />
500 15 14 1 13 2 15 0<br />
750 15 11 4 7 8 5 10<br />
1,250 15 2 13 0 15 1 14<br />
1,500 15 1 14 1 14 1 14<br />
Effect of <strong>Urina</strong>ry Specific Grav<strong>it</strong>y<br />
Fifteen (15) urine specimens w<strong>it</strong>h specific grav<strong>it</strong>y ranging from 1.001 to<br />
1.032 were spiked w<strong>it</strong>h 500 ng/mL and 1,500 ng/mL of Amphetamine<br />
respectively. The AMP One Step Amphetamine <strong>Test</strong> Device (Urine) was<br />
tested in duplicate using the fifteen neat and spiked urine specimens. The<br />
results demonstrate that varying ranges of urinary specific grav<strong>it</strong>y do not<br />
affect the test results.<br />
Effect of <strong>Urina</strong>ry pH<br />
The pH of an aliquoted negative urine pool was adjusted to a pH range of 5<br />
to 9 in 1 pH un<strong>it</strong> increments and spiked w<strong>it</strong>h Amphetamine to 500 ng/mL<br />
and 1,500 ng/mL. The spiked, pH-adjusted urine was tested w<strong>it</strong>h the AMP<br />
One Step Amphetamine <strong>Test</strong> Device (Urine) in duplicate. The results<br />
demonstrate that varying ranges of pH do not interfere w<strong>it</strong>h the <strong>per</strong>formance<br />
of the test.<br />
Cross-Reactiv<strong>it</strong>y<br />
A study was conducted to determine the cross-reactiv<strong>it</strong>y of the test w<strong>it</strong>h<br />
compounds in e<strong>it</strong>her drug-free urine or Amphetamine pos<strong>it</strong>ive urine. The<br />
following compounds show no cross-reactiv<strong>it</strong>y when tested w<strong>it</strong>h the AMP<br />
One Step Amphetamine <strong>Test</strong> Device (Urine) at a concentration of 100<br />
g/mL.<br />
Non Cross-Reacting Compounds<br />
4-Acetamidophenol Estrone-3-sulfate Oxolinic acid<br />
Acetopheneti<strong>di</strong>n Ethyl-p-aminobenzoate Oxycodone<br />
N-Acetylprocainamide Fenfluramine Oxymetazoline<br />
Acetylsalicylic acid Fenoprofen Papaverine<br />
Aminopyrine Furosemide Penicillin-G<br />
Am<strong>it</strong>ryptyline Gentisic acid Pentazocine<br />
Amobarb<strong>it</strong>al Hemoglobin Pentobarb<strong>it</strong>al<br />
Amoxicillin Hydralazine Perphenazine<br />
Ampicillin Hydrochlorothiazide Phencycli<strong>di</strong>ne<br />
L-Ascorbic acid Hydrocodone Phenelzine<br />
Apomorphine Hydrocortisone Phenobarb<strong>it</strong>al<br />
Aspartame p-HydroxyAmphetamine L-Phenylephrine<br />
Atropine O-Hydroxyhippuric acid -Phenylethlamine<br />
Benzilic acid p-Hydroxy-<br />
Phenylpropanolamine<br />
Benzoic acid<br />
methAmphetamine Prednisolone<br />
Benzoylecgonine 3-Hydroxytyramine Prednisone<br />
Benzphetamine Ibuprofen Procaine<br />
Bilirubin Imipramine Promazine<br />
() - Brompheniramine () - Isoproterenol Promethazine<br />
Caffeine Isoxsuprine D,L-Propanolol<br />
Cannabi<strong>di</strong>ol Ketamine D-Propoxyphene<br />
Cannabinol Ketoprofen D-Pseudoephedrine<br />
Chloralhydrate Labetalol Quini<strong>di</strong>ne<br />
Chloramphenicol Levorphanol Quinine<br />
Chlor<strong>di</strong>azepoxide Lo<strong>per</strong>amide Ran<strong>it</strong>i<strong>di</strong>ne<br />
Chlorothiazide Maprotiline Salicylic acid<br />
() Chlorpheniramine Me<strong>per</strong>i<strong>di</strong>ne Secobarb<strong>it</strong>al<br />
Chlorpromazine Meprobamate<br />
Serotonin (5-<br />
Chlorquine Methadone<br />
Hydroxytyramine)<br />
Cholesterol D-methAmphetamine Sulfamethazine<br />
Clomipramine (L)-methAmphetamine Sulindac<br />
Cloni<strong>di</strong>ne Methoxyphenamine Temazepam<br />
Cocaine hydrochloride 3,4-Methylene<strong>di</strong>oxyethyl- Tetracycline<br />
Codeine<br />
Amphetamine<br />
Tetrahydrocortisone,<br />
Cortisone<br />
(+) 3,4-Methylene<strong>di</strong>oxy- 3 Acetate<br />
(-) Cotinine<br />
methAmphetamine Tetrahydrocortisone 3<br />
Creatinine Methylphenidate (-D glucuronide)<br />
Deoxycorticosterone Morphine-3--D- Tetrahydrozoline<br />
Dextromethorphan glucuronide Thebaine<br />
Diazepam Nali<strong>di</strong>xic acid Thiamine<br />
Diclofenac Naloxone Thioridazine<br />
Diflunisal Naltrexone Tolbutamine<br />
Digoxin Naproxen Triamterene<br />
Diphenhydramine Niacinamide Trifluo<strong>per</strong>azine<br />
Doxylamine Nife<strong>di</strong>pine Trimethoprim<br />
Ecgonine hydrochloride Norcodein Trimipramine<br />
Ecgonine methylester Norethindrone D, L-Tryptophan<br />
(IR,2S)-(-)-Ephedrine D-Norpropoxyphene Tyramine<br />
L-Ephedrine Noscapine D, L-Tyrosine<br />
(-)ψ Ephedrine D,L-Octopamine Uric acid<br />
Erythromycin Oxalic acid Verapamil<br />
-Estra<strong>di</strong>ol Oxazepam Zomepirac<br />
BIBLIOGRAPHY<br />
1 Baselt RC. Dispos<strong>it</strong>ion of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man.<br />
2nd Ed. Biome<strong>di</strong>cal Publ., Davis, CA. 1982; 488<br />
2 Hawks RL, CN Chiang. Urine <strong>Test</strong>ing for Drugs of Abuse.<br />
National Inst<strong>it</strong>ute for Drug Abuse (NIDA), Research Monograph<br />
73, 1986