Estructura de computadores
Estructura de computadores
Estructura de computadores
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
CC-BY-SA • PID_00177071 23 Juego <strong>de</strong> instrucciones<br />
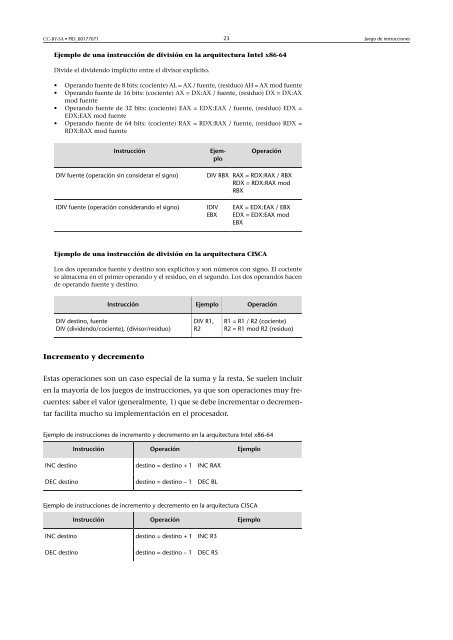
Ejemplo <strong>de</strong> una instrucción <strong>de</strong> división en la arquitectura Intel x86-64<br />
Divi<strong>de</strong> el divi<strong>de</strong>ndo implícito entre el divisor explícito.<br />
• Operando fuente <strong>de</strong> 8 bits: (cociente) AL = AX / fuente, (residuo) AH = AX mod fuente<br />
• Operando fuente <strong>de</strong> 16 bits: (cociente) AX = DX:AX / fuente, (residuo) DX = DX:AX<br />
mod fuente<br />
• Operando fuente <strong>de</strong> 32 bits: (cociente) EAX = EDX:EAX / fuente, (residuo) EDX =<br />
EDX:EAX mod fuente<br />
• Operando fuente <strong>de</strong> 64 bits: (cociente) RAX = RDX:RAX / fuente, (residuo) RDX =<br />
RDX:RAX mod fuente<br />
Instrucción Ejemplo<br />
Operación<br />
DIV fuente (operación sin consi<strong>de</strong>rar el signo) DIV RBX RAX = RDX:RAX / RBX<br />
RDX = RDX:RAX mod<br />
RBX<br />
IDIV fuente (operación consi<strong>de</strong>rando el signo) IDIV<br />
EBX<br />
EAX = EDX:EAX / EBX<br />
EDX = EDX:EAX mod<br />
EBX<br />
Ejemplo <strong>de</strong> una instrucción <strong>de</strong> división en la arquitectura CISCA<br />
Los dos operandos fuente y <strong>de</strong>stino son explícitos y son números con signo. El cociente<br />
se almacena en el primer operando y el residuo, en el segundo. Los dos operandos hacen<br />
<strong>de</strong> operando fuente y <strong>de</strong>stino.<br />
Instrucción Ejemplo Operación<br />
DIV <strong>de</strong>stino, fuente<br />
DIV (divi<strong>de</strong>ndo/cociente), (divisor/residuo)<br />
Incremento y <strong>de</strong>cremento<br />
DIV R1,<br />
R2<br />
R1 = R1 / R2 (cociente)<br />
R2 = R1 mod R2 (residuo)<br />
Estas operaciones son un caso especial <strong>de</strong> la suma y la resta. Se suelen incluir<br />
en la mayoría <strong>de</strong> los juegos <strong>de</strong> instrucciones, ya que son operaciones muy fre-<br />
cuentes: saber el valor (generalmente, 1) que se <strong>de</strong>be incrementar o <strong>de</strong>cremen-<br />
tar facilita mucho su implementación en el procesador.<br />
Ejemplo <strong>de</strong> instrucciones <strong>de</strong> incremento y <strong>de</strong>cremento en la arquitectura Intel x86-64<br />
Instrucción Operación Ejemplo<br />
INC <strong>de</strong>stino <strong>de</strong>stino = <strong>de</strong>stino + 1 INC RAX<br />
DEC <strong>de</strong>stino <strong>de</strong>stino = <strong>de</strong>stino – 1 DEC BL<br />
Ejemplo <strong>de</strong> instrucciones <strong>de</strong> incremento y <strong>de</strong>cremento en la arquitectura CISCA<br />
Instrucción Operación Ejemplo<br />
INC <strong>de</strong>stino <strong>de</strong>stino = <strong>de</strong>stino + 1 INC R3<br />
DEC <strong>de</strong>stino <strong>de</strong>stino = <strong>de</strong>stino – 1 DEC R5