You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Conceptos básicos de la iluminación · Basic lighting concepts<br />
LUMINANCIA<br />
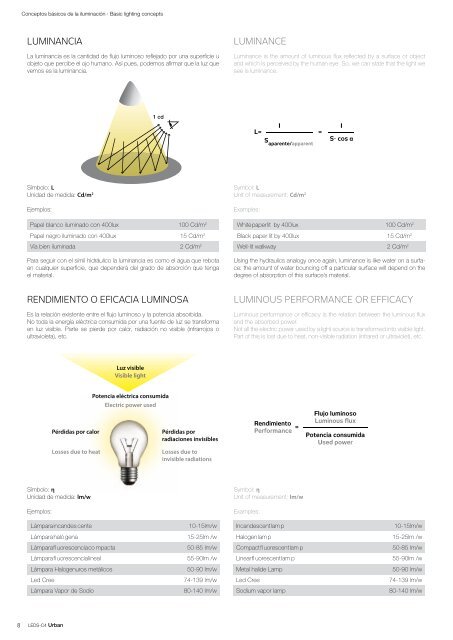
La luminancia es la cantidad de flujo luminoso reflejado por una superficie u<br />
objeto que percibe el ojo humano. Así pues, podemos afirmar que la luz que<br />
vemos es la luminancia.<br />
LUMINANCE<br />
Luminance is the amount of luminous flux reflected by a surface or object<br />
and which is perceived by the human eye. So, we can state that the light we<br />
see is luminance.<br />
1 cd<br />
I<br />
L= =<br />
S aparente/apparent<br />
I<br />
S· cos<br />
Símbolo: L<br />
<strong>Uni</strong>dad de medida: Cd/m 2<br />
Ejemplos:<br />
Symbol: L<br />
<strong>Uni</strong>t of measurement: Cd/m 2<br />
Examples:<br />
Papel blanco iluminado con 400lux 100 Cd/m 2<br />
Papel negro iluminado con 400lux 15 Cd/m 2<br />
Vía bien iluminada 2 Cd/m 2<br />
Para seguir con el símil hidráulico la luminancia es como el agua que rebota<br />
en cualquier superficie, que dependerá del grado de absorción que tenga<br />
el material.<br />
White paper lit by 400lux 100 Cd/m 2<br />
Black paper lit by 400lux 15 Cd/m 2<br />
Well-lit walkway 2 Cd/m 2<br />
Using the hydraulics analogy once again, luminance is like water on a surface:<br />
the amount of water bouncing off a particular surface will depend on the<br />
degree of absorption of this surface’s material.<br />
RENDIMIENTO O EFICACIA LUMINOSA<br />
Es la relación existente entre el flujo luminoso y la potencia absorbida.<br />
No toda la energía eléctrica consumida por una fuente de luz se transforma<br />
en luz visible. Parte se pierde por calor, radiación no visible (infrarrojos o<br />
ultravioleta), etc.<br />
LUMINOUS PERFORMANCE OR EFFICACY<br />
Luminous performance or efficacy is the relation between the luminous flux<br />
and the absorbed power.<br />
Not all the electric power used by a light source is transformed into visible light.<br />
Part of this is lost due to heat, non-visible radiation (infrared or ultraviolet), etc.<br />
Luz visible<br />
Visible light<br />
Pérdidas por calor<br />
Losses due to heat<br />
Potencia eléctrica consumida<br />
Electric power used<br />
Pérdidas por<br />
radiaciones invisibles<br />
Losses due to<br />
invisible radiations<br />
Rendimiento<br />
Performance =<br />
Flujo luminoso<br />
Luminous flux<br />
Potencia consumida<br />
Used power<br />
Símbolo: η<br />
<strong>Uni</strong>dad de medida: lm/w<br />
Ejemplos:<br />
Symbol: η<br />
<strong>Uni</strong>t of measurement: lm/w<br />
Examples:<br />
Lámpara incandes cente<br />
10-15lm/w<br />
Incandescent lam p<br />
10-15lm/w<br />
Lámpara haló gena 15-25 lm /w<br />
Halogen lam p 15-25 lm /w<br />
Lámpara fl uorescencia co mpacta<br />
50-85 lm/w<br />
Compact fl uorescent lam p<br />
50-85 lm/w<br />
Lámpara fl uorescencia lineal 55-90 lm /w<br />
Linear fl uorescent lam p 55-90 lm /w<br />
Lámpara Halogenuros metálicos<br />
50-90 lm/w<br />
Metal halide Lamp<br />
50-90 lm/w<br />
Led Cree<br />
74-139 lm/w<br />
Led Cree<br />
74-139 lm/w<br />
Lámpara Vapor de Sodio<br />
80-140 lm/w<br />
Sodium vapor lamp<br />
80-140 lm/w<br />
8<br />
LEDS-C4 Urban