3B SCIENTIFIC PHYSICS ELEKTROCHEMIE U11110 ...
3B SCIENTIFIC PHYSICS ELEKTROCHEMIE U11110 ...
3B SCIENTIFIC PHYSICS ELEKTROCHEMIE U11110 ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Experiment 5 - Measuring voltage Teacher's instructions<br />
Measuring the standard potential of various metals<br />
Chemicals Hazard<br />
symbols<br />
Copper (II)-sulfate-(5 H2O)<br />
Zinc sulfate-(7H2O)<br />
Silver nitrate<br />
Iron (II)-sulfate-(7 H2O)<br />
Hydrochloric acid 1 mol/l<br />
R phrases S phrases Equipment<br />
22-36/38-50/53 22-60-61<br />
Meter<br />
Electrodes:<br />
1 Cu, 1 Zn, 1 Ag, 1 Fe,<br />
1 platinum gauze<br />
36/38-50/53 22-25-60-61 2 Experiment cables<br />
34-50/53 26-45-60-61 1 Mains power supply<br />
22-36/38 24/25 2 Pipettes<br />
36/37/38 26 1 3V adapter<br />
Distilled water --- ---<br />
Warning: Please take care: Salts of heavy metals are poisonous! Hydrochloric acid is corrosive!<br />
Experiment procedure:<br />
1. The prepared 1.0 molar electrolyte solutions should be given to the students. Students require no more than 10 ml of<br />
the relevant solution each.<br />
2. Assemble the battery block as described.<br />
3. Add the 1 molar hydrochloric acid to one chamber of the battery block using the pipette and insert the platinum<br />
gauze electrode into this cell.<br />
4. Add a 1 molar CuSO4 solution to a second chamber (opposite the platinum gauze electrode) and insert a copper<br />
electrode.<br />
5. To form a normalized hydrogen electrode, a 3V adapter is connected to the power supply. Connect the negative<br />
pole of the 3V adapter to the platinum gauze electrode and the positive pole to the copper electrode using<br />
experiment cables. Connect the power supply to the 230 V mains and electrolyze the platinum gauze for about 30<br />
seconds. Hydrogen forms at the platinum gauze and completely surrounds the gauze.<br />
6. The 3V adapter is then replaced by the meter and the voltage can then be read off.<br />
7. Proceed as in steps 4 to 6 with each of the other metals using the corresponding electrolyte for each metal (AgNO3 /<br />
Ag , ZnSO4 / Zn and FeSO4 / Fe).<br />
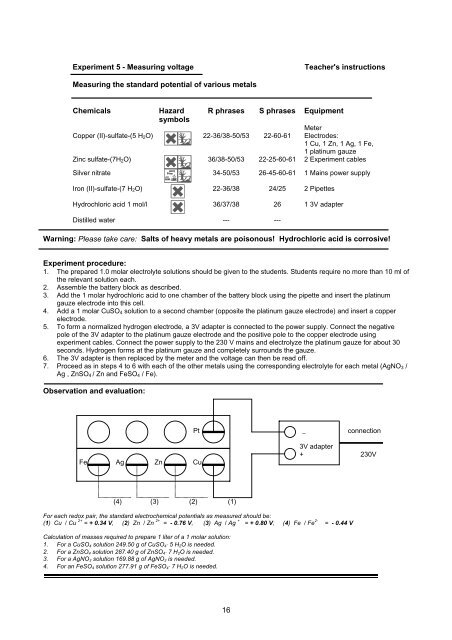
Observation and evaluation:<br />
Fe Ag Zn Cu<br />
(4) (3) (2) (1)<br />
Pt _ connection<br />
16<br />
3V adapter<br />
+ 230V<br />
For each redox pair, the standard electrochemical potentials as measured should be:<br />
(1) Cu / Cu 2+ = + 0.34 V, (2) Zn / Zn 2+ = - 0.76 V, (3) Ag / Ag + = + 0.80 V, (4) Fe / Fe 2- = - 0.44 V<br />
Calculation of masses required to prepare 1 liter of a 1 molar solution:<br />
1. For a CuSO4 solution 249.50 g of CuSO4⋅ 5 H2O is needed.<br />
2. For a ZnSO4 solution 287.40 g of ZnSO4⋅ 7 H2O is needed.<br />
3. For a AgNO3 solution 169.88 g of AgNO3 is needed.<br />
4. For an FeSO4 solution 277.91 g of FeSO4⋅ 7 H2O is needed.