Structure et stratigraphie de la zone de Korabi ... - Archipel - UQAM
Structure et stratigraphie de la zone de Korabi ... - Archipel - UQAM
Structure et stratigraphie de la zone de Korabi ... - Archipel - UQAM
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Zrm02 x 10-4<br />
Rhyolite alC3line<br />
Phonolite Echantillons:<br />
Felsique<br />
0.1<br />
Rhyolite + Dacite<br />
•<br />
Trachyte<br />
. hono1i\e<br />
iep\If\-P<br />
.44.1<br />
.9.2<br />
9.\<br />
.27.1<br />
.73.1<br />
.2.1<br />
PemlO-Triasique<br />
0.01<br />
.22.\<br />
.54.\<br />
Pré-perrniens<br />
.59.\<br />
063.1<br />
Basalte Foidite t4.1<br />
Malique<br />
'-----_'-----..L-l-L-'--.L-LL_----L----'----L-'--J.-LL..Ll.-_--'-----'-'--'--.L.LLl.-NbIY<br />
029.1<br />
.26.t<br />
0.01 Suh-aJC3lin<br />
0.1<br />
AIC3lin UlIra-alC3lin<br />
IO<br />
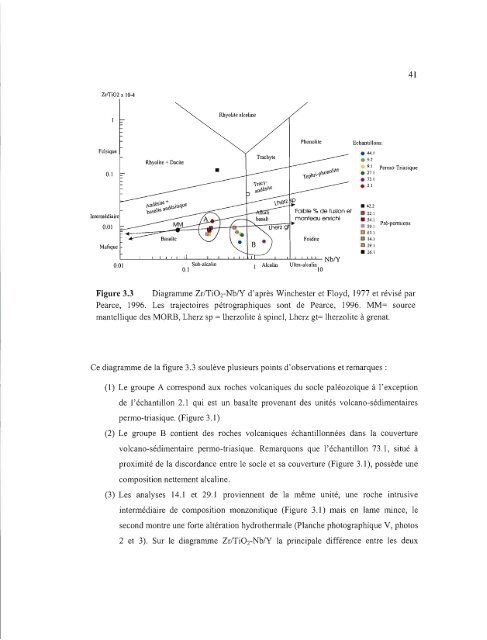
Figure 3.3 Diagramme Zr/TiOrNbIY d'après Winchester <strong>et</strong> Floyd, 1977 <strong>et</strong> révisé par<br />
Pearce, 1996. Les trajectoires pétrographiques sont <strong>de</strong> Pearce, 1996. MM= source<br />
mantellique <strong>de</strong>s MORB, Lherz sp = lherzolite à spinel, Lherz gt= lherzolite à grenat.<br />
Ce diagramme <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> figure 3.3 soulève plusieurs points d'observations <strong>et</strong> remarques:<br />
(1) Le groupe A correspond aux roches volcaniques du socle paléozoïque à l'exception<br />
<strong>de</strong> l'échantillon 2.1 qui est un basalte provenant <strong>de</strong>s unités volcano-sédimentaires<br />
permo-triasique. (Figure 3.1)<br />
(2) Le groupe B contient <strong>de</strong>s roches volcaniques échantillonnées dans <strong>la</strong> couverture<br />
volcano-sédimentaire permo-triasique. Remarquons que l'échantillon 73.1, situé à<br />
proximité <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> discordance entre le socle <strong>et</strong> sa couverture (Figure 3.1), possè<strong>de</strong> une<br />
composition n<strong>et</strong>tement alcaline.<br />
(3) Les analyses 14.1 <strong>et</strong> 29.1 proviennent <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> même unité, une roche intrusive<br />
intermédiaire <strong>de</strong> composition monzonitique (Figure 3.1) mais en <strong>la</strong>me mince, le<br />
second montre une forte altération hydrothermale (P<strong>la</strong>nche photographique V, photos<br />
2 <strong>et</strong> 3). Sur le diagramme Zr/TiOrNbIY <strong>la</strong> principale différence entre les <strong>de</strong>ux<br />
.42.2<br />
41