Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
20<br />
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services in rice environments<br />
The term biodiversity is being used to describe the richness and variety of<br />
life on earth. It includes diversity at the genetic level, such as that between<br />
individuals in a population, diversity of species and the diversity at the habitat<br />
and ecosystem levels. The general assumption is that the biodiversity of<br />
monocultures, such as rice, is decreased and therefore unstable and prone to<br />
pest attacks and need to be protected . This thinking, not necessarily true<br />
(Way and Heong 1994), has persisted for decades and is still dominant among<br />
agricultural scientists and policy makers, has been the key driver of pesticide<br />
use in many agricultural systems.<br />
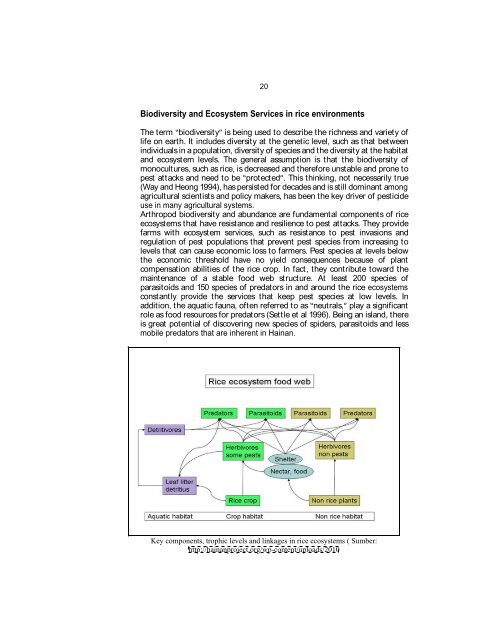
Arthropod biodiversity and abundance are fundamental components of rice<br />
ecosystems that have resistance and resilience to pest attacks. They provide<br />
farms with ecosystem services, such as resistance to pest invasions and<br />
regulation of pest populations that prevent pest species from increasing to<br />
levels that can cause economic loss to farmers. Pest species at levels below<br />
the economic threshold have no yield consequences because of plant<br />
compensation abilities of the rice crop. In fact, they contribute toward the<br />
maintenance of a stable food web structure. At least 200 species of<br />
parasitoids and 150 species of predators in and around the rice ecosystems<br />
constantly provide the services that keep pest species at low levels. In<br />
addition, the aquatic fauna, often referred to as neutrals, play a significant<br />
role as food resources for predators (Settle et al 1996). Being an island, there<br />
is great potential of discovering new species of spiders, parasitoids and less<br />
mobile predators that are inherent in Hainan.<br />
Key components, trophic levels and linkages in rice ecosystems ( Sumber:<br />
http://hainanproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2010