1ª Parte – Questões Objetivas 2 1 - Curso Objetivo
1ª Parte – Questões Objetivas 2 1 - Curso Objetivo
1ª Parte – Questões Objetivas 2 1 - Curso Objetivo
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
U<br />
Como R = <strong>–</strong><strong>–</strong><strong>–</strong> , concluímos que R é constante<br />
i<br />
e o resistor é ôhmico.<br />
{<br />
U = 0,5V<br />
2) t = 10s<br />
i = 1,0A<br />
OBJETIVO<br />
U 0,5<br />
R = <strong>–</strong><strong>–</strong><strong>–</strong> = <strong>–</strong><strong>–</strong><strong>–</strong> (Ω) ⇒<br />
i 1,0<br />
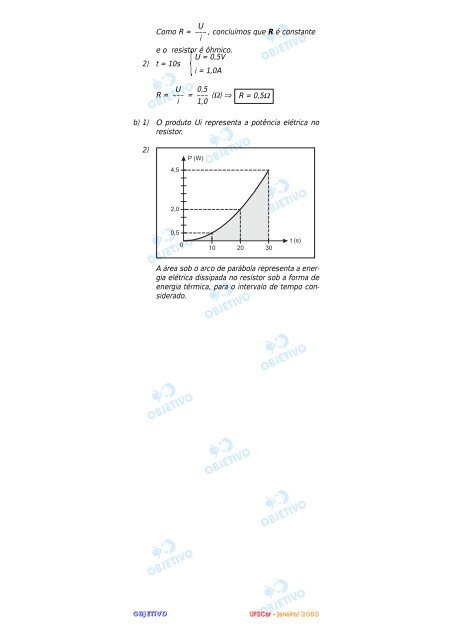
b) 1) O produto Ui representa a potência elétrica no<br />
resistor.<br />
2)<br />
R = 0,5Ω<br />
A área sob o arco de parábola representa a energia<br />
elétrica dissipada no resistor sob a forma de<br />
energia térmica, para o intervalo de tempo considerado.<br />
UFSCar - Janeiro/2005