El holograma y su utilización como un medio de ense˜nanza de la f ...
El holograma y su utilización como un medio de ense˜nanza de la f ...
El holograma y su utilización como un medio de ense˜nanza de la f ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
1401-6 Toledo et al.<br />
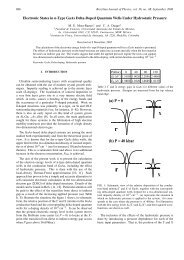
Tab<strong>la</strong> 1 - Diferencias f<strong>un</strong>damentales entre <strong>la</strong> fotografía y <strong>la</strong><br />
holografía.<br />
Fotografía<br />
1. Resolución <strong>de</strong>l material<br />
baja.<br />
2. Se utiliza para iluminar<br />
el objeto cualquier fuente <strong>de</strong><br />
luz normal.<br />
3. Se usa <strong>un</strong>a lente para formar<br />
<strong>la</strong> imagen en el <strong>medio</strong> <strong>de</strong><br />
registro.<br />
4. Almacena <strong>la</strong> información<br />
re<strong>la</strong>cionada con <strong>la</strong> intensidad.<br />
5. Los p<strong>un</strong>tos individuales<br />
bril<strong>la</strong>ntes y oscuros son <strong>la</strong><br />
imagen.<br />
6. Se obtiene <strong>un</strong> negativo y<br />
<strong>la</strong> foto se hace a partir <strong>de</strong>l<br />
negativo.<br />
7. La foto re<strong>su</strong>ltante es <strong>un</strong>a<br />
imagen p<strong>la</strong>na o bidimensional<br />
<strong>de</strong>l objeto sin para<strong>la</strong>je.<br />
Holografía<br />
1. Resolución <strong>de</strong>l material<br />
alta.<br />
2. Se utiliza para iluminar<br />
el objeto <strong>un</strong> láser.<br />
3. No usa <strong>un</strong>a lente y no se<br />
forma <strong>la</strong> imagen en el <strong>medio</strong><br />
<strong>de</strong> registro. Lo que se forma<br />
en el mismo es <strong>un</strong> patrón <strong>de</strong><br />
interferencia.<br />
4. Almacena <strong>la</strong> información<br />
re<strong>la</strong>cionada con <strong>la</strong> intensidad<br />
y con <strong>la</strong> fase.<br />
5. Las áreas bril<strong>la</strong>ntes y oscuras<br />
son franjas <strong>de</strong> interferencia<br />
microscópicas que no<br />
son <strong>la</strong> imagen <strong>de</strong>l objeto.<br />
6. Se obtiene directamente<br />
el <strong>holograma</strong><br />
7. La imagen re<strong>su</strong>ltante<br />
en el <strong>holograma</strong> es tridimensional<br />
con para<strong>la</strong>je total.<br />
• Permite vi<strong>su</strong>alizar efectos no apreciables a simple<br />
vista (estados tensionales y <strong>de</strong>formacionales <strong>de</strong> los<br />
cuerpos <strong>de</strong>l or<strong>de</strong>n <strong>de</strong> 10 –6 m). Esto se logra mediante<br />
<strong>la</strong> holografía <strong>de</strong> doble exposición y constituye<br />
<strong>un</strong>a técnica <strong>de</strong> ensayo óptico no <strong>de</strong>structivo.<br />
• Permite obtener imágenes tridimensionales <strong>de</strong> objetos<br />
con perspectiva invertida.<br />
• Permite mostrar en el au<strong>la</strong> <strong>la</strong> imagen tridimensional<br />
<strong>de</strong> objetos imposibles <strong>de</strong> mostrar directamente<br />
por <strong>su</strong>s características, medidas excepcionales<br />
<strong>de</strong> seguridad y conservación, etc.<br />
• Permite obtener imágenes con ampliación o reducción<br />
<strong>de</strong>l tamaño real <strong>de</strong>l objeto (<strong>holograma</strong>s<br />
<strong>de</strong> imagen enfocada). Especialmente importante<br />
para que el estudiante o el público en general<br />
pueda apreciar <strong>de</strong>talles muy pequeños, no perceptibles<br />
a simple vista.<br />
• Se pue<strong>de</strong> lograr el cambio <strong>de</strong> color <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> imagen<br />
<strong>de</strong>l objeto al cambiar <strong>la</strong> posición <strong>de</strong> observación<br />
(<strong>holograma</strong>s <strong>de</strong> arcoiris).<br />
Existen alg<strong>un</strong>as limitantes en <strong>la</strong> utilización <strong>de</strong> <strong>holograma</strong>s<br />
<strong>como</strong> <strong>medio</strong>s <strong>de</strong> enseñanza y <strong>de</strong> educación social<br />
entre <strong>la</strong>s cuales po<strong>de</strong>mos <strong>de</strong>stacar <strong>la</strong>s siguientes:<br />
• Existen alg<strong>un</strong>os objetos que por <strong>su</strong>s características<br />
no son holografiables.<br />
• Existe limitación en <strong>la</strong> realización <strong>de</strong> <strong>holograma</strong>s<br />
<strong>de</strong> objetos con mucha prof<strong>un</strong>didad.<br />
• Para po<strong>de</strong>r ver los <strong>holograma</strong>s se necesita <strong>un</strong>a<br />
fuente <strong>de</strong> luz b<strong>la</strong>nca p<strong>un</strong>tual o con fi<strong>la</strong>mento estrecho.<br />
• Los <strong>holograma</strong>s poseen <strong>un</strong> ángulo <strong>de</strong> visión re<strong>la</strong>tivamente<br />
restringido por lo que no se pue<strong>de</strong>n ver<br />
<strong>de</strong>s<strong>de</strong> cualquier posición <strong>de</strong>l observador.<br />
• Es <strong>un</strong> <strong>medio</strong> re<strong>la</strong>tivamente costoso y para <strong>su</strong> construcción<br />
<strong>de</strong>ben crearse <strong>la</strong>s condiciones materiales<br />
necesarias.<br />
• Para <strong>su</strong> e<strong>la</strong>boración <strong>de</strong>be existir <strong>un</strong>a experiencia<br />
<strong>de</strong> investigación en los profesores y técnicos <strong>de</strong>l<br />
Departamento Docente.<br />
4. Utilización <strong>de</strong>l <strong>holograma</strong> <strong>como</strong> <strong>medio</strong><br />
<strong>de</strong> enseñanza <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> física en ingeniería<br />
Al realizar <strong>un</strong> análisis <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> literatura con<strong>su</strong>ltada en<br />
re<strong>la</strong>ción con este tema, y <strong>de</strong> alg<strong>un</strong>as <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong>s tesis <strong>de</strong> doctorado<br />
<strong>de</strong>fendidas recientemente sobre <strong>la</strong> enseñanza <strong>de</strong><br />
<strong>la</strong> física en ingeniería [35-39] po<strong>de</strong>mos p<strong>la</strong>ntear que no<br />
se ha encontrado en <strong>la</strong> literatura con<strong>su</strong>ltada <strong>la</strong> f<strong>un</strong>damentación<br />
<strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> Exposición Didáctica <strong>como</strong> <strong>un</strong> tipo <strong>de</strong><br />
c<strong>la</strong>se <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> Educación Superior. En particu<strong>la</strong>r no existen<br />
referencias a <strong>la</strong> construcción y utilización <strong>de</strong> <strong>un</strong>a<br />
Exposición Didáctica <strong>de</strong> holografía para <strong>la</strong> enseñanza<br />
<strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> disciplina física en carreras <strong>de</strong> ingeniería.<br />
Alg<strong>un</strong>os <strong>de</strong> los f<strong>un</strong>damentos p<strong>la</strong>nteados por Alvarez<br />
[40] que sirvieron <strong>de</strong> base a <strong>la</strong> c<strong>la</strong>sificación <strong>de</strong> los tipos<br />
<strong>de</strong> c<strong>la</strong>se <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> educación <strong>su</strong>perior utilizada han sido:<br />
La forma organizativa <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> actividad docente<br />
es <strong>la</strong> estructuración y el or<strong>de</strong>namiento<br />
interno <strong>de</strong> los componentes personales <strong>de</strong> dicho<br />
proceso: profesor y estudiante, y <strong>de</strong> los<br />
elementos <strong>de</strong>l contenido <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong>s disciplinas:<br />
conocimientos y habilida<strong>de</strong>s, con vistas a<br />
lograr <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> manera más eficiente los objetivos<br />
propuestos.<br />
La tipología (c<strong>la</strong>sificación) <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> forma<br />
<strong>de</strong> enseñanza <strong>de</strong>be hacerse atendiendo a<br />
<strong>un</strong> rasgo f<strong>un</strong>damental que <strong>la</strong>s caracteriza.<br />
Nosotros nos inclinamos por c<strong>la</strong>sificar <strong>la</strong>s<br />
formas <strong>de</strong> enseñanza <strong>de</strong> acuerdo con el componente<br />
<strong>de</strong>l proceso docente en que se <strong>de</strong>sarrol<strong>la</strong>,<br />
con el objetivo que cumple (grado<br />
<strong>de</strong> dominio <strong>de</strong>l contenido y tipo <strong>de</strong> habilidad<br />
a formar).<br />
Así <strong>la</strong>s c<strong>la</strong>ses se pue<strong>de</strong>n c<strong>la</strong>sificar en <strong>la</strong> siguiente<br />
tipología: