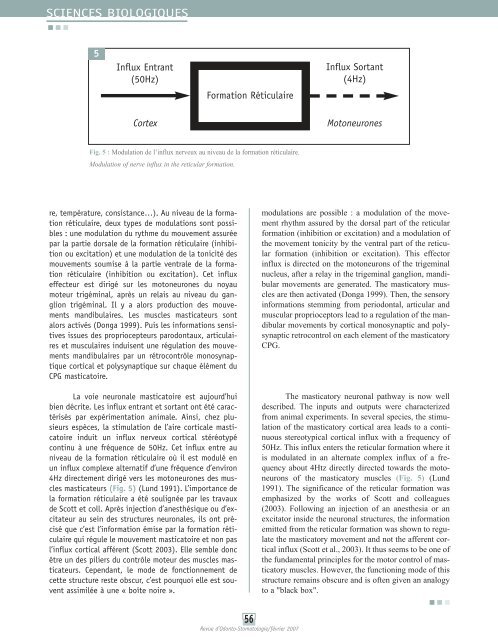
SCIENCES BIOLOGIQUES5Influx Entrant(50Hz)Formation RéticulaireInflux Sortant(4Hz)CortexMotoneuronesFig. 5 : Modulation de l’influx nerveux au niveau de la formation réticulaire.Modulation of nerve influx in the reticular formation.re, température, consistance…). Au niveau de la formationréticulaire, deux types de modulations sont possibles: une modulation du rythme du mouvement assuréepar la partie dorsale de la formation réticulaire (inhibitionou excitation) et une modulation de la tonicité desmouvements soumise à la partie ventrale de la formationréticulaire (inhibition ou excitation). Cet influxeffecteur est dirigé sur les motoneurones du noyaumoteur trigéminal, après un relais au niveau du gangliontrigéminal. Il y a alors production des mouvementsmandibulaires. Les <strong>muscle</strong>s masticateurs sontalors activés (Donga 1999). Puis les informations sensitivesissues des propriocepteurs parodontaux, articulaireset musculaires induisent une régulation des mouvementsmandibulaires par un rétrocontrôle monosynaptiquecortical et polysynaptique sur chaque élément duCPG masticatoire.La voie neuronale masticatoire est aujourd’huibien décrite. Les influx entrant et sortant ont été caractériséspar expérimentation animale. Ainsi, chez plusieursespèces, la stimulation de l’aire corticale masticatoireinduit un influx nerveux cortical stéréotypécontinu à une fréquence de 50Hz. Cet influx entre auniveau de la formation réticulaire où il est modulé enun influx complexe alternatif d’une fréquence d’environ4Hz directement dirigé vers les motoneurones des <strong>muscle</strong>smasticateurs (Fig. 5) (Lund 1991). L’importance dela formation réticulaire a été soulignée par les travauxde Scott et coll. Après injection d’anesthésique ou d’excitateurau sein des structures neuronales, ils ont préciséque c’est l’information émise par la formation réticulairequi régule le mouvement masticatoire et non pasl’influx cortical afférent (Scott 2003). Elle semble doncêtre un des piliers du contrôle moteur des <strong>muscle</strong>s masticateurs.Cependant, le mode de fonctionnement decette structure reste obscur, c’est pourquoi elle est souventassimilée à une « boîte noire ».modulations are possible : a modulation of the movementrhythm assured by the dorsal part of the reticularformation (inhibition or excitation) and a modulation ofthe movement tonicity by the ventral part of the reticularformation (inhibition or excitation). This effectorinflux is directed on the motoneurons of the trigeminalnucleus, after a relay in the trigeminal ganglion, mandibularmovements are generated. The masticatory <strong>muscle</strong>sare then activated (Donga 1999). Then, the sensoryinformations stemming from periodontal, articular andmuscular proprioceptors lead to a regulation of the mandibularmovements by cortical monosynaptic and polysynapticretrocontrol on each element of the masticatoryCPG.The masticatory neuronal pathway is now welldescribed. The inputs and outputs were characterizedfrom animal experiments. In several species, the stimulationof the masticatory cortical area leads to a continuousstereotypical cortical influx with a frequency of50Hz. This influx enters the reticular formation where itis modulated in an alternate complex influx of a frequencyabout 4Htz directly directed towards the motoneuronsof the masticatory <strong>muscle</strong>s (Fig. 5) (Lund1991). The significance of the reticular formation wasemphasized by the works of Scott and colleagues(2003). Following an injection of an anesthesia or anexcitator inside the neuronal structures, the informationemitted from the reticular formation was shown to regulatethe masticatory movement and not the afferent corticalinflux (Scott et al., 2003). It thus seems to be one ofthe fundamental principles for the motor control of masticatory<strong>muscle</strong>s. However, the functioning mode of thisstructure remains obscure and is often given an analogyto a "black box".56Revue d’Odonto-Stomatologie/février 2007
DiscussionDiscussionLe <strong>muscle</strong> ptérygoïdien latéral semble donc êtreune entité embryologique, histologique et anatomique.Cependant, son rôle stabilisateur de l’articulation temporo-mandibulaire,diarthrose bicondylienne unique del’organisme, lui confère une physiologie particulière. Lacoaptation du disque articulaire sur la tête condyliennedans tous les mouvements mandibulaires nécessite unecontraction des fibres musculaires répondant à desimpératifs biomécaniques précis. Face à cet impératif,de nombreux auteurs reconnaissent un rôle différentdes fibres musculaires du ptérygoïdien latéral(Bertilsson et Strom, 1995).Dernièrement, de récentes publications suggèrentune contraction chronologique des différents faisceauxmusculaires (El Haddioui et coll., 2005 ; Kim etcoll., 2003 ; Murray et coll., 2004 ; Sessle et Gurza,1982). Selon les hypothèses neurobiologiques, il estplausible que la contraction séquentielle des faisceauxdu <strong>muscle</strong> ptérygoïdien latéral soit en fait la résultanted’une activation neuronale sélective entièrement géréeau niveau du CPG masticatoire via la formation réticulaire.Le rôle prépondérant de la formation réticulairedans la gestion des mouvements complexes est actuellementétudié au niveau d’autres diarthroses. Ainsi,cette explication a déjà été proposée au niveau de l’épauleen particulier au niveau du deltoïde et du trapèze.Le deltoïde est un <strong>muscle</strong> triangulaire formé partrois faisceaux localisés sur le dessus de l’épaule. Cestrois faisceaux convergent vers la partie moyenne dubras pour se fixer sur la face externe de l’humérus.Sur le plan fonctionnel, les faisceaux du deltoïdedevraient être considérés comme des <strong>muscle</strong>s distincts.L’action du faisceau antérieur est l’abductionfrontale (antépulsion, élévation frontale) et la rotationinterne du bras. Le faisceau moyen est abducteur latéraldu bras. Le faisceau postérieur est abducteur postérieurdu bras (rétropulsion) (Morris et coll., 2004). Ce<strong>muscle</strong> est innervé par un même nerf : le nerf axillaire.Ces faisceaux peuvent agir en synergie (ex: abduction)ou antagonisme (ex : flexion).La réalisation de mouvements complexes telsque la circumduction est permise par la contractionchronologique des différents faisceaux, rendue possiblepar un schéma de stimulation neuronale précis. Cetteactivation « en vague » serait régulée par la formationThe lateral <strong>pterygoid</strong> <strong>muscle</strong> thus seems to be anembryological, histological and anatomical entity.However, its stabilizing role on the temporo-mandibularjoint, unique bicondylar synovial joint of the body, givesthis <strong>muscle</strong> a particular physiology. The coaptation ofthe articular disc on the condyle head in all mandibularmovements require a contraction of the muscular fibersresponding to precise biomechanical imperatives.Facing these imperatives, several authors recognize adifferent role of muscular fibers of the lateral <strong>pterygoid</strong>(Bertilsson and Strom, 1995).Recent publications suggest a chronologicalcontraction of various <strong>muscle</strong> fibers (El Haddioui et al.,2005 ; Kim et al., 2003 ; Murray et al., 2004 ; Sessle andGurza, 1982). According to the neurobiological hypotheses,it is plausible that the sequential contraction ofthe lateral <strong>pterygoid</strong> <strong>muscle</strong> bundles is in fact the resultantof a selective neuronal activation completely managedin the masticatory CPG via the reticular formation.The dominating role of the reticular formation inthe management of the complex movements is presentlystudied in other synovial joints. This explanation wastherefore already proposed in the shoulder’s joint musculaturein particular in the deltoid and the trapezius.The deltoid is a triangular <strong>muscle</strong> formed by three belliessituated above the shoulder. These three belliesconverge toward the middle part of the arm to insert onthe external surface of the humerus.Functionally, the deltoid bellies should be consideredas three distinct <strong>muscle</strong>s. The action of the anteriorbelly is frontal abduction (anteropulsion and frontalelevation) and internal rotation of the arm. The middlebelly is a lateral abductor of the arm. The posterior bellyis a posterior abductor of the arm (retropulsion) (Morriset al., 2004). This <strong>muscle</strong> is innervated by the samenerve : the axillary nerve. These bundles can act insynergy (ex : abduction) or antagonism (ex : flexion).To perform complex movements such as circumduction,chronological contraction of different bundlesis necessary and possible by a precise neuronal schemaof stimulation. This « wave-like » activation would beregulated by the reticular formation. This particularity is57Revue d’Odonto-Stomatologie/février 2007